 84
84
Micromelanconis kaihuiae C.M. Tian & N. Jiang, sp. nov.2021
MycoBank No: 838928
Holotype: China, Hunan Province, Changsha City, Changsha Coun ty, Kaihui Town, chestnut plantation, 40°24'32.16"N, 117°28'56.24"E, 262 m asl, on stems and branches of Castanea mollissima, Tian Chengming and Ning Jiang, 10 November 2020 (BJFC-S1831, holotype; ex-type culture, CFCC 54572 = KH5-3). Ibid. (BJFC-S1832, KH5-4).
Morphological description
Sexual morph: Undetermined
Asexual morph: Conidiomata acervu lar, 350–800 μm diam., conspicuous, immersed in host bark to erumpent, covered by brown to blackish exuding conidial masses at maturity. Central column beneath the disc more or less conical. Conidiophores unbranched, aseptate, cylindrical, pale brown, smooth-walled. Conidiogenous cells annellidic, occasionally with distinct annellations and collarettes, 12.4–47.1 × 1.2–3.8 μm. Conidia hyaline when immature, becoming pale brown, ellipsoid, multiguttulate, aseptate, 7.6–10.3 × 3.1–4.1 μm, L/W = 2–3.2, with hyaline sheath, 1 μm.
Culture characteristics: Colony on PDA at 25 °C irregular, grey olivaceous, margin becoming diffuse, aerial hyphae short, dense, surface becoming imbricate, growth lim ited and ceasing after two weeks. Conidiomata formed after three weeks, randomly dis tributed, black. Conidiophores unbranched, septate, cylindrical, pale brown, smooth walled. Conidiogenous cells annellidic, 9.1–18.5 × 2.5–5.3 μm. Conidia pale brown, long dumbbell-shaped, narrow at the middle and wide at both ends, multiguttulate, aseptate, 10.4–13.5 × 4–5 μm, L/W = 2.3–3.3, with hyaline sheath, 1.5 μm.
Habitat:
Distribution: China
GenBank Accession: ITS MW414473; LSU MW414373; tef1a MW419880; rpb2 MW419878
ITS MW414474; LSU MW414374; tef1a MW419881; rpb2 MW419879
Notes: Micromelanconis kaihuiae on Castanea mollissima (Fagaceae, Fagales) is phylogenetically close to Neopseudomelanconis castaneae on Castanea mollissima and Pseudomelanconis caryae on Carya cathayensis (Juglandaceae, Juglandales) (Fig. 1). All these three species are discovered on tree branches in China, and share similar mor phological characters in having pale brown conidia with conspicuous hyaline sheath. Micromelanconis kaihuiae and Neopseudomelanconis castaneae even share the same host. However, they can be easily distinguished based on conidia shape, color and overall size of conidia (M. kaihuiae, pale brown, ellipsoid and aseptate conidia, 7.6–10.3 × 3.1–4.1 μm; pale brown, long dumbbell-shaped and aseptate conidia, 10.4–13.5 × 4–5 μm vs. N. castaneae, brown, ellipsoid to oblong and septate conidia, 18–21.5 × 4.8–7 μm vs. P. caryae, pale brown, ellipsoid to oblong and aseptate conidia, 12.5–16 × 4–5 μm) (Fan et al. 2018a; Jiang et al. 2018a). Furthermore, M. kaihuiae is separated from N. castaneae by 51/490 bp (10.4%) differences in ITS and 12/563 bp (2.1%) differences in LSU, and from P. caryae by 56/490 bp (11.4%) differences in ITS and 6/563 bp (1.1%) differences in LSU.
Reference: [1] Jiang, N. , Yang, Q. , Fan, X. , & Tian, C. . (2021). Micromelanconis kaihuiae gen. et sp. nov. a new diaporthalean fungus from chinese chestnut branches in southern china. MycoKeys, 79.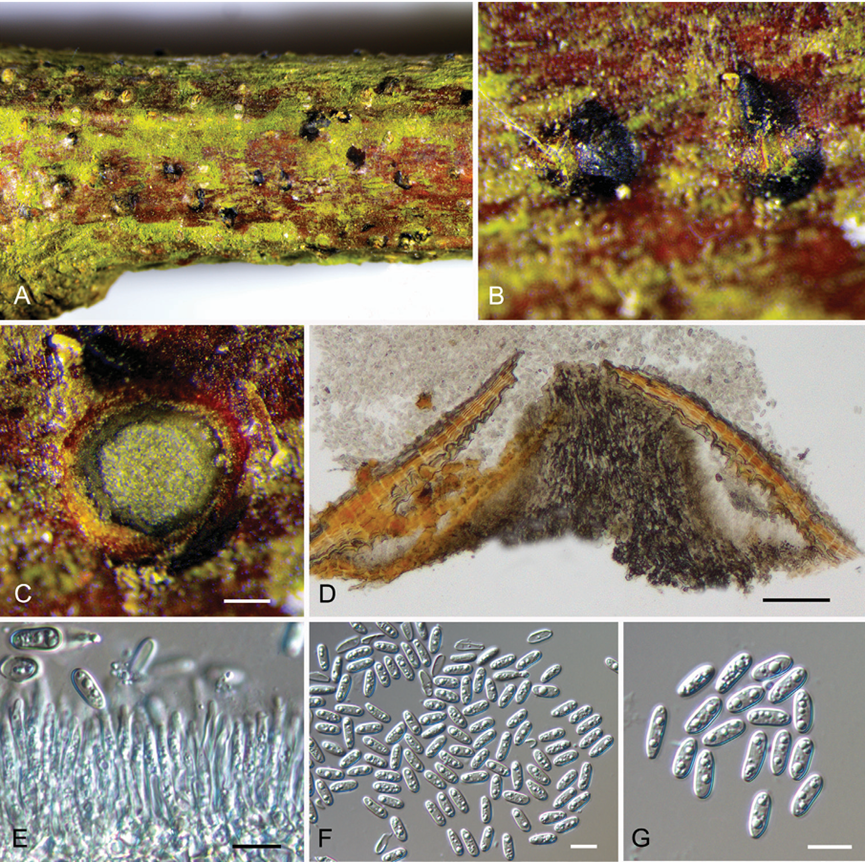
Figure 2. Morphology of Micromelanconis kaihuiae on branches of Castanea mollissima (BJFC-S1831) A, B habit of conidiomata on a branch C transverse section of conidiomata D longitudinal section through co nidiomata E conidiogenous cells attached with conidia F, G conidia. Scale bars: 100 μm (C, D); 10 μm (E–G). 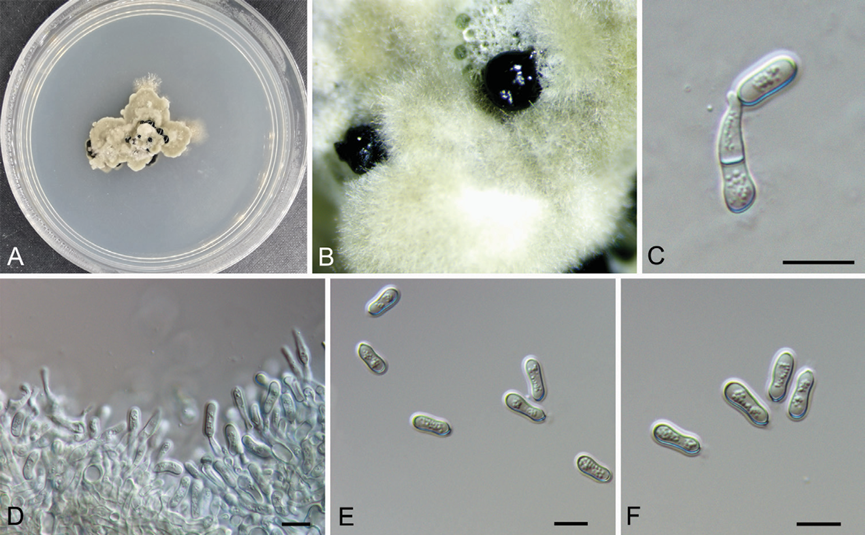
Figure 3. Morphology of Micromelanconis kaihuiae on the PDA plate (CFCC 54572) A colony on PDA B habit of conidiomata formed on PDA C, D conidiogenous cells attached with conidia E, F conidia. Scale bars: 10 μm (C–F).

