Biscogniauxia glaucae Q.R. Li & J.C. Kang, sp. nov.2021
MycoBank Number: MB 835,896
Holotype: GMB0007.
Morphological description
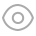
Sexual morph: Stromata 3–5 cm long, 1–2 cm wide and 0.3–0.4 cm high, widely eff used, fl at, black, bipartite, confl uent, with raised margins, perithecium immersed, with black ostioles. Stromatal tissue between perithecia composed entirely of carbonaceous tissue. Ostioles openings punctate, dis cretely encased by carbonaceous stromatal tissue, equal or slightly lower than stromatal surface, black. Perithecia 250–350 μm high, 130–260 μm wide (av. = 285 × 183 μm, n = 10), solitary, black, carbonaceous, immersed, in vertical section, obovoid, globose to subglobose, ostiolate. Perid ium 45–70 μm thick, black. Paraphyses not observed . Asci 131–180 × 10.5–12.5 μm (av. = 152.5 × 11.5 μm, n = 20), 8-spored, unitunicate, cylindrical, short-pedicellate, api cally round, with a J + , wedge apical apparatus in Melz er's reagent, 3–4 μm high, 7.5–9.5 μm wide. Ascospores 13.5–16 × 7.5–9.5 μm (av. = 15 × 8.5 μm, n = 30), uniseri ate, unicellular, dark brown to black, more or less equi lateral with broadly rounded ends, smooth-walled, with a straight germ slit on the more concave side, nearly full spore length, lacking appendages and sheathes.
Asexual morph: Undetermined
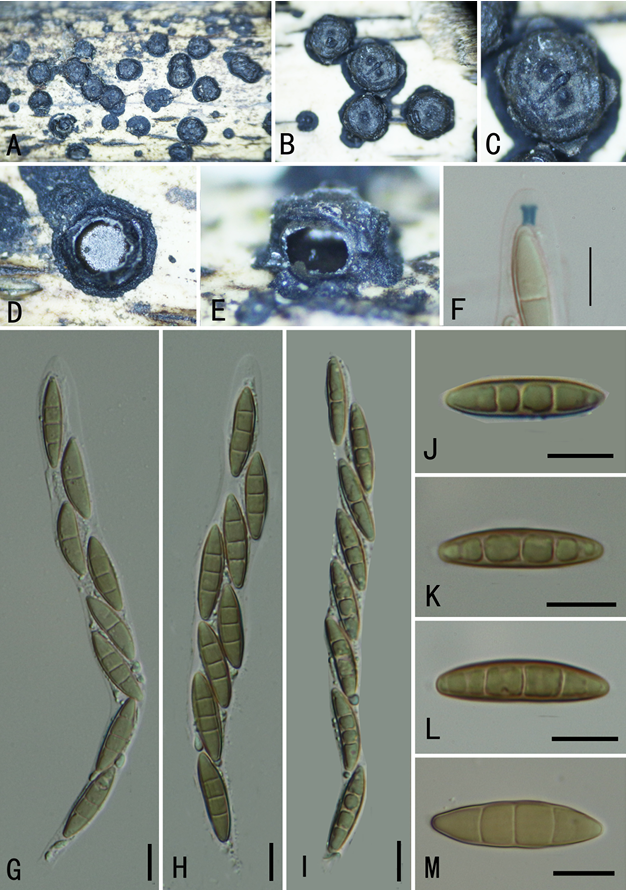
Culture characteristics: Colonies growing on PDA reached 5 cm diam. after 1 week at 25 °C, white, cottony, f l at, low, dense. Fructifi cations were not observed in culture.
Habitat:
Distribution: China
GenBank Accession:
Notes: There were four species collected from China in the examined specimens by Ju et al. ( 1998 ). Most of them were obtained and introduced in Taiwan (Ju and Rogers 2001 ; Kuo et al. 2018 ). Currently, nine species were collected andintroduced from China (Ju and Rogers 2001 ; Vasilyeva et al. 2009 ; Ariyawansa et al. 2015 ; Ma et al. 2020 ). Here, we introduce a new species of Biscogniauxia found from the Chinese mainland. Molecular phylogenetic studies based on ITS, β-tubulin, RPB2 and ACT sequences indicate that B. glaucae forms a distinct branch from other species and supports B. glaucae as a new species of Biscogniauxia . In morphology, this species has a similar ascospores size range to B. atropunctata var. maritima (Lar. N. Vassiljeva) Y.M. Ju & J.D. Rogers, B . citriformis var. macrospora Van der Gucht & Whalley, B. fuscella (Rehm) F. San Martín & J.D. Rogers and B. mediterranea (De Not.) Kuntze. However, the stromata of B. glaucae have clear raised margins, with clear outlines which diff er from those of them (Ju et al. 1998 ; Ju and Rogers 2001 ). Moreover, B. fuscella has a white outer dehiscing layer and nearly equilateral ascospores with a cel lular appendage on immature ascospores and some mature ascospores (Ju et al. 1998 ). Biscogniauxia atropunctata var. maritime shows different characteristics in owning ostioles of slightly higher than the stromatal surface, with openings papillate and ascospores with narrowly rounded ends (Ju et al. 1998 ; Ju and Rogers 2001 ). The ascospores of B. citriformis var. macrospora are almost C-shaped with pinched ends, with spore-length on a more convex side (Ju et al. 1998 ). Biscogniauxia mediterranea readily separates from the B. glaucae in having ostioles higher than stromatal surface, with openings coarsely papillate (Ju et al. 1998 ). The phylogenetic tree (Fig. 2 ) shows that B. glaucae , B. formosana and B. cylindrispora have a close relationship. However, B. formosana (15-22.5 × 8-11 μm) and B. cylindrispora (20-26 × 10-11 μm) and B. cylin 14 μm) has larger ascospores than those of B. glaucae.
Reference: [1] Li, Q. , Gong, X. , Zhang, X. , Pi, Y. , Long, S. , & Wu, Y. , et al. (2021). Phylogeny of graphostromatacea with two new species (biscogniauxia glaucae sp. nov. and graphostroma guizhouensis sp. nov.) and new record of camillea broomeana isolated in china. Archives of microbiology, 203(10), 6119-6129.
Biscogniauxia glaucae (GMB0007, holotype) a Mate rial. b Ascomata on the surface of host. c Section of ascomata. d g Asci with ascospores (stained in Melzer’s reagent). h j Ascospores. l Ascus apex with a J + apical apparatus. Scale bars: b , c = 200 μm, d g = 10 μm, h l = 5 μm.