 116
116
Hirsutella flava X. Zou, J.J. Qu, Z.A. Chen & Z.Q. Liang, sp. nov.2021
MycoBank No: 819552
Holotype: China, Zhejiang Province, Tianmu Mountain National Nature Reserve (30°18'N, 119°28'E, approximately 600–1200 m a.s.l.), 27 June 2010, presented by Prof. Zhuan Chen. The holotype has been deposited at KIB (HKAS112884). Sequenc es from isolated strains (GZUIFR-hir100627-1, GZUIFR-hir100627-2 and GZUI FR-hir100627-3) have been deposited in GenBank.
Morphological description
Sexual morph: Undetermined
Asexual morph: Synnemata extending from the head of insect, 3–10 cm × 0.5 1 mm, simple or irregularly branched, dark brown and changing to faint yellow toward the apex; no conidiation was observed (Fig. 2A). The fungus grows slowly at 22 ± 1 °C on Czapek-Dox agar medium to a diam. of 8–12 mm; the colony surface was flat and flocculent with white aerial hyphae. On PDA agar, fungal colonies grew quickly to a diam. of 15–23 mm after 20 d at 22 ± 1 °C, when the colonies were blanket-like with rough mycelia, radiating beam-like from the centre; centre lunate concave, pale yellow; colony surface with yellowish liquid exudation (Fig. 2B, C). Mycelium hyaline, smooth, septate, 3.6–4.5 μm wide. Conidiogenous cells form direct ly from the mycelial end, monophialidic or polyphialidic, and borne perpendicular or at acute angles (80°–85°) to the subtending hyphae. Phialides slender awl-shaped and tapered, width of the base 24–40.8 × 2.2–2.5 μm, tapering to a narrow neck, 7.2–9 μm long × 0.5 μm wide. Conidia narrow cymbiform, long fusoid or limoni form, 6.5–10 × 2.1–4.3 μm; single- or double-enveloped in a hyaline mucus, thick ness 2.0–3.0 μm (Fig. 2D–K).
Culture characteristics:
Habitat: On decaying leaves in broadleaved forests.
Distribution: Zhejiang Province, China.
GenBank Accession:
ITS KY415598; LSU KY415599; SSU -; RPB1 KY945366; TEF1α KY415601
ITS MF623036; LSU MF623042; SSU -; RPB1 -; TEF1α MF623046
ITS MF623037; LSU MF623043; SSU -; RPB1 -; TEF1α MF623047
Remarks: This species is allied with the H. sinensis and H. strigosa clade. The phi alides of H. flava are subulate, and the necks are slenderer. In particular, the colonymorphology of this fungus is unique among the Hirsutella species. The colony surface appears very rough, and the hyphae are gathered into outwardly radiating filamentous bundles of varying sizes.
Reference: [1] Qu, J. , Zou, X. , Cao, W. , Xu, Z. , & Liang, Z. . (2021). Two new species of hirsutella (ophiocordycipitaceae, sordariomycetes) that are parasitic on lepidopteran insects from china. MycoKeys, 82, 81-96.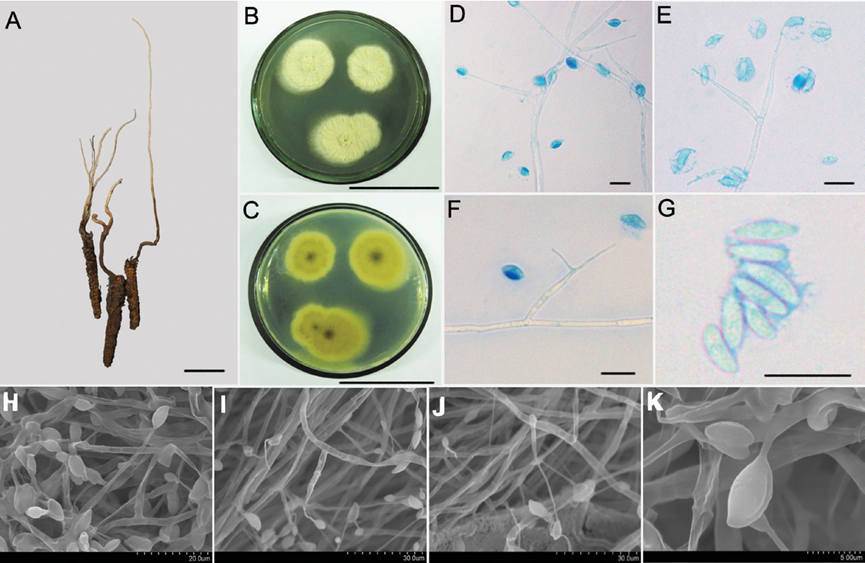
Figure 2. Morphological characteristics of Hirsutella flava A the infected insect specimens with a long and single synnemata (HKAS112884) B, C colonial morphology on PDA agar media for 20 d B shows the front of the colony and C shows the back of the colony D–G LM images of the general morphology of conidiogenous cells and conidia H–K SEM images showing conidiogenous cells and conidial structure; Scale bars: 1 cm (A); 5 cm (B, C), 10 μm (D–G); the rest of the bars are shown in the figure. LM, light microscopy; PDA, potato dextrose agar; SEM, scanning electron microscopy.

