 108
108
Russula subbubalina B. Chen & J. F. Liang, sp. nov.2021
MycoBank No: MB838837
Holotype: China. Guangdong Province, Huizhou City, Boluo County, Luofu Mountain Provincial Nature Reserve, 23°15'43.80"N, 114°3'5.40"E, 220 m asl., in mixed Fagaceae forests of Cyclobalanopsis and Castanopsis, 22 August 2020, leg. CB448 (RITF4710).
Morphological description
Sexual morph: Basidiomata medium-sized to large; pileus 50–100 mm in diam eter; initially hemispheric when young, applanate to convex, convex with a slightly depressed center after mature; margin incurved, cracked with age, striation short and inconspicuous; surface dry, glabrous, peeling to 1/4 of the radius, pruinose in some part; dark salmon with rusty spots when young, blanched almond after maturation, shallower at the margin. Lamellae adnate to slightly adnexed, 3–5 mm deep, 11–13 at 1 cm near the pileus margin, white to cream; lamellulae sometimes present and irregular in length; furcations present especially near the stipe; edge entire and con color. Stipe 30–55 × 5–15 mm, cylindrical, slightly inflated towards the base, white to blanched almond, with rusty tinge towards the base, and medulla initially stuffed becoming hollow. Context 3–4 mm thick in half of the pileus radius, white, unchanging when bruised, taste mild, odor inconspicuous. Spore print white to cream.
Basidiospores (5.2–)5.6–6.2–6.8(–7.2) × (4.5–)4.9–5.3–5.7(–6.2) μm, Q = (1.0–)1.08–1.17–1.25(–1.38), subglobose to broadly ellipsoid; ornamentation of relatively small, moderately distant to dense [6–8(–9) in a 3 μm diameter cir cle] amyloid warts or spines, 0.3–0.5 μm high, locally reticulate, fused in short or long chains [2–3(–4) in the circle], frequently connected by line connections [3–4(–5) in the circle]; suprahilar spot medium-sized, amyloid. Basidia (30.5 )31.7–34.8–37.8(–43.0) × (6.3–)7.5–8.1–8.8(–9.4) μm, mostly 4-spored, some 2- and 3-spored, clavate; basidiola clavate or ellipsoid, ca. 5.5–10 μm wide. Hyme nial gloeocystidia on lamellae sides Moderately numerous, ca. 800–1000/mm2, (41.0)49.1–56.7–64.3(68.5) × (6.5)7.2–8.1–9.0(10.0) μm, clavate or fusiform, apically mainly obtuse, occasionally acute, sometimes with 4–10 μm long append age, thin-walled; contents heteromorphous or granulose, turning reddish black in SV. Hymenial gloeocystidia on lamellae edges Often longer, (40.5–)52.6 63.0–73.5(–83.6) × (4.6–)6.7–8.1–9.6(–10.8) μm, mainly clavate, occasional ly fusiform, apically typically obtuse, sometimes with 3–8 μm long appendage, thin-walled; contents heteromorphous-crystalline, turning reddish black in SV. Marginal cells (14.0–)19.0–23.4–27.7(–34.2) × (3.4–)3.7–4.5–5.3(–5.8) μm, clavate, lageniform or fusiform, often flexuous. Pileipellis Orthochromatic in cr esyl blue, sharply delimited from the underlying context, 400–450 μm deep, two layered; suprapellis180–200 μm deep, hyphal endings composed of inflated or el lipsoid cells with attenuated terminal cells; subpellis 240–260 μm deep, composed of horizontally oriented, relatively dense, intricate, 3–6 μm wide hyphae. Hyphal terminations near the pileus margin sometimes branched, occasionally flexuous, thin-walled; terminal cells (14.8)20.9–26.6–32.3(38.0) × 3.5–4.0–4.6(5.5) μm, mainly narrowly lageniform, occasionally cylindrical, apically attenuated or con stricted; subterminal cells frequently shorter and wider ca. 3–8 μm wide, occasion ally branched. Hyphal terminations near the pileus center similar to those near the pileus margin; terminal cells (14.3–)17.5–22.7–27.8(–33.7) × (3.4–)3.7–4.1 4.6(–5.0) μm, lageniform, clavate or cylindrical, apically attenuated or constricted, sometimes obtuse; subterminal cells often wider, rarely branched, ca. 4–8 μm wide. Pileocystidia near the pileus margin always one-celled, (27.9–)35.1–40.5–45.9( 48.9) × (3.8–)4.2–4.7–5.3(–5.7) μm, mainly clavate, occasionally fusiform, api cally typically obtuse, sometimes with round or ellipsoid 2–6 μm long appendage, thin-walled; contents heteromorphous, turning reddish black in SV. Pileocystidia near the pileus center similar in shape, always one-celled, (23.7–)25.6–31.8 38.0(–46.0) × (3.3–)4.2–4.8–5.4(–6.0) μm, thin-walled, mainly clavate, occasion ally fusiform or subcylindrical, apically typically obtuse, sometimes with 4–6 μm long appendage, contents granulose, turning reddish in SV. Cystidioid hyphae In subpellis and context with granulose contents, oleiferous hyphae frequent in subpellis with yellowish contents.
Asexual morph: Undetermined
Culture characteristics:
Habitat:
Distribution: China
GenBank Accession:
ITS MW646978; nrLSU MW646990; mtSSU MW647001; TEF1 MW650847
ITS MW646979; nrLSU MW646991; mtSSU MW647002; TEF1 MW650848
Notes: Both morphology and phylogeny place R. subbubalina clearly in sub sect. Heterophyllinae. In our phylogenetic tree, R. viridicinnamomea is the sister taxon to R. subbubalina but differs from it by the typically smaller basidiomata (30–50 μm), an emerald green-tinged buff pileus with undulate and tearing mar gin and longer hymenial gloeocystidia on the lamellae edges (36.5–63 × 4–12 μm, Yuan et al. 2019).
Morphologically, R. subbubalina may be confused in the field with two recently re ported new species: R. bubalina and R. pseudobubalina also from Guangdong Province of China. However, R. bubalina has the typically smaller basidiomata (35–54 μm), a striate pileus margin and basidiospores with warty ornamentations not forming re ticulum (Li et al. 2019), whereas R. pseudobubalina possesses the typically smaller ba sidiomata (31–46 μm), never forked lamellae, basidiospores with isolated warts, and often shorter hymenial gloeocystidia on the lamellae edges (23.4–37.8–65.5 × 6.2 8.3–10.0 μm, Li et al. 2019).
Reference: [1] Chen, B. , Song, J. , Chen, Y. , Zhang, J. , & Liang, J. . (2021). Morphological and phylogenetic evidence for two new species ofrussulasubg.heterophyllidiafrom guangdong province of china. MycoKeys, 82, 139-157.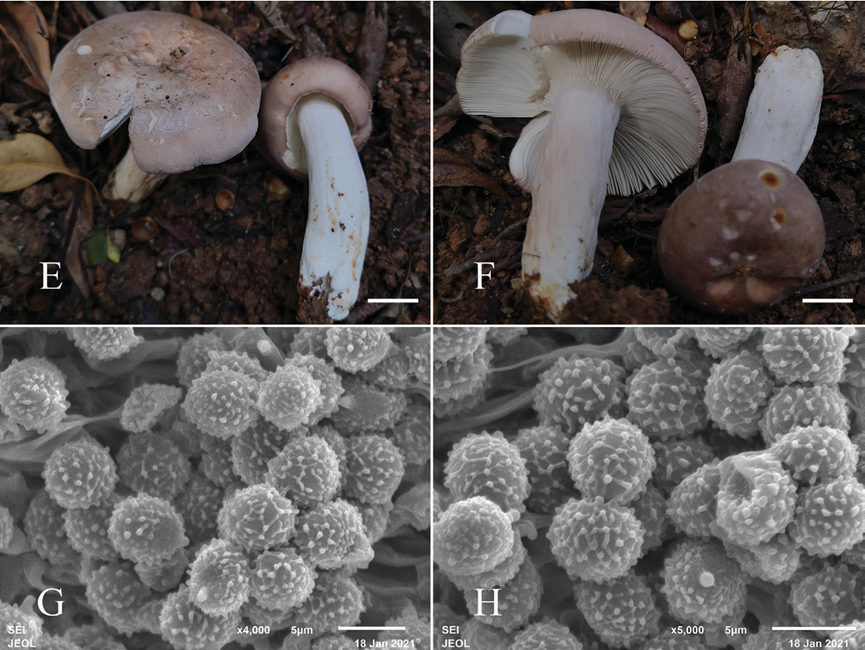
Figure 2. Fruiting bodies (E, F) and basidiospores (G, H) of Russula subbubalina (RITF 3715). Scale bars: 20 mm(E、F) 
Figure 5. Russula subbubalina (RITF 4710) A basidia B basidiola C marginal cells D hymenial gloeocys tidia on lamellae sides E hymenial gloeocystidia on lamellae edges. Scale bar: 10 μm.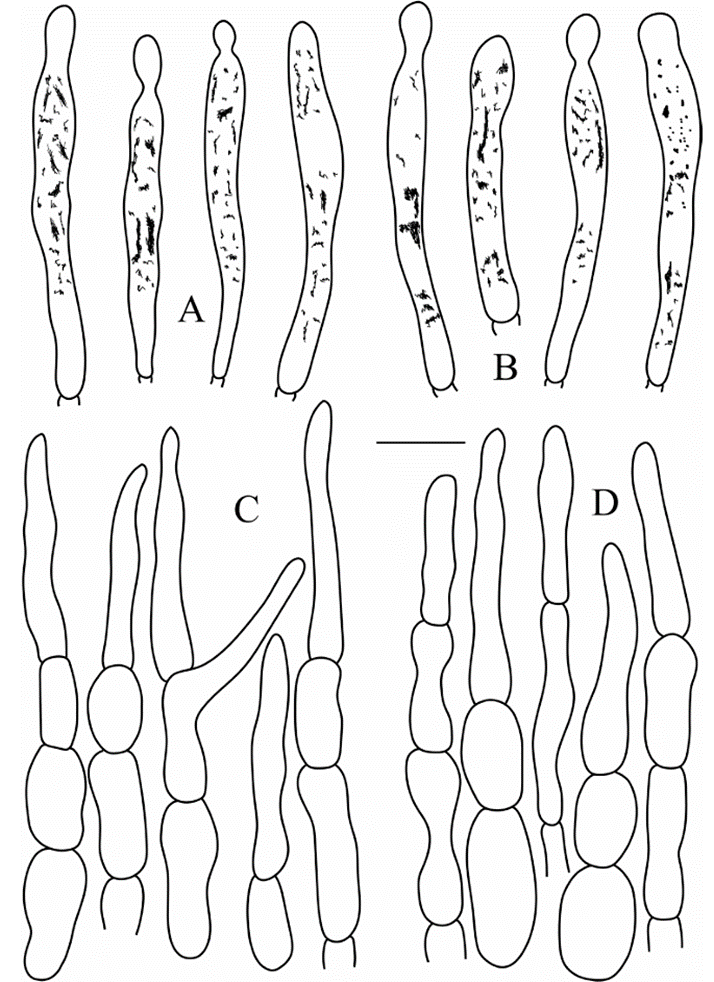
Figure 6. Russula subbubalina (RITF 4710) A pileocystidia near the pileus margin B pileocystidia near the pileus center C hyphal terminations near the pileus margin D hyphal terminations near the pileus center. Scale bar: 10 μm.

