Squamarina kansuensis (H. Magn.) Poelt 2020
MycoBank No:
Holotype Lecanora kansuensis H. Magn., Lichens from Central Asia 1: 116–117 (1940). Type: China, Gansu Province, 1500–1700 m elev., on soil, 1930, Birger Bohlin 202 (S–Holotype!) (Basionym
Morphological description
Thallus terricolous, loosely to tightly adnate on soil, irregular to radiate in outline and with elongate marginal lobes, up to 10 cm in diam.; lobes 2–4(5) mm long, 1–2(3) mm wide, 0.2–0.4 mm thick, with white, thickened and slightly upturned edges, more or less overlapping; upper surface greenish to straw, pruinose and strongly cracked at least in the centre of the thallus; lower surface well delimited, milk-white to pale, without rhizines, margins usually containing sparse white tomentum. Upper cortex filled with yellowish-brown granules, turning colourless in KOH, 26–32 μm thick; epinecral layer grey to brown, 5–15 μm thick; algal layer continuous, well delimited, ca. 50 μm high; medulla grey, filled with calcium oxalate crystals; lower cortex lacking.
Habitat: on soil
Distribution: Growing on soil at 1310–4730 m of elevation. Previously only known from Gansu Prov. and reported here as new to Neimenggu, Ningxia, Sichuan, Xizang, Xinjiang and Yunnan provinces, China.
GenBank Accession: nrITS na nrLSU MK778031 RPB1na RPB2 na mtSSUna
Notes: The holotype consists of several small fragments on soil, bearing a single small apothecium. This species was originally described as a Lecanora by Magnusson (1940) and transferred to Squamarina by Poelt (1958). It is characterised by the pruinose, greenish- to straw-coloured thallus, lobes with white, thickened and slightly upturned edges, exposing a milk-white to pale lower surface, without rhizines and the presence of psoromic and 2’-O-demethypsoromic acids. This species is very common in the deserts and alpine zones of China. In desert regions, the thallus is usually irregular in outline with wider lobes and becomes rosette-like with narrower lobes when growing in the alpine zone.
Reference: : Zhang Y-Y, Wang X-Y, Li L-J, Printzen C, Timdal E, Niu D-L, Yin A-C, Wang S-Q, Wang L-S (2020) Squamarina (lichenised fungi) species described from China belong to at least three unrelated genera. MycoKeys 66: 135–157. https://doi.org/10.3897/mycokeys.66.39057
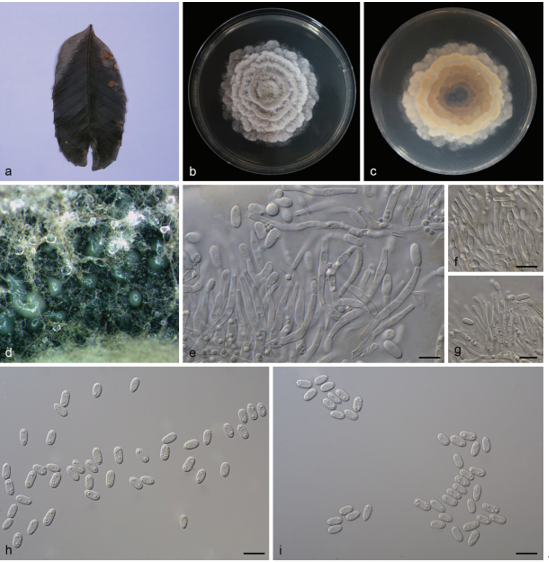
Figure 5. Lecanora chondroderma (A, B KUN-L 18-60317): A habit B apothecial anatomy (LCB) and ascospores (water). Squamarina kansuensis (C–G KUN-L 18-59601): C habit D apothecial anatomy (LCB) e ascus and ascospores (LCB) F apical structure of ascus (Lugol’s) G section of thallus (LCB). S. oleosa (h, i KUN-L 09−30043): h habit i ascus and ascospores (water). Scale bars: 100 μm (B-apothecia, D); 5 μm (B-ascospores, F); 10 μm (e); 20 μm (G); 25 μm (i).