Collodiscula lancangjiangensis Y.P. Wu & Q.R. Li, sp. nov.2021
MycoBank: MB839642
Type:CHINA. Yunnan Province: Baoshan City, Lancang River Nature Reserve (28.72997°N, 99.361083°E), elev. 2674 m, on dead bamboo culms, 10 October 2019, Yinhui Pi 2019LC157 (GMB0030, holotype; KUN-HKAS 112663, isotype; ex-type living culture, GMBC0030).
Morphological description
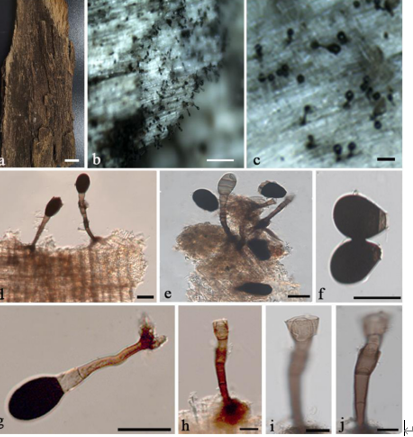
Sexual morph: Stromata scattered or gregarious, solitary, superficial, black, hexagonal prism, 0.5–0.8 mm diam., 0.3–0.6 mm high, containing 1–2 ascomata, with a circle of black tissue at the bottom, with a papillary ostiole. External stromatal layer black, carbonaceous, easily chipped away to reveal the thin, black ascomata. Ostioles papillate in the centre, black. Perithecia subglobose to globose, 0.4–0.8 mm diam., 0.3–0.6 mm high. Asci 145–175 × 9–16 μm (mean 162 × 11.8 μm, n = 30), 8-spored, unitunicate, short-pedicellate, apically rounded with a J+, wedge-shaped apical apparatus, blue staining in Melzer’s reagent, 3.0–3.5 μm (mean 3.2 μm, n = 30) high, 1.5–2.0 μm(mean 1.7 μm, n = 30) broad. Ascospores 26–36.5 × 5–7.5 μm (mean 31 × 6.5 μm, n = 30), overlapping uniseriate, fusiform, equilateral, 3-septate, not constricted at septa, yellowish brown, blunt at both ends, smooth-walled, lacking germ slits or appendages.
Asexual morph: Undetermined
Culture characteristics: Ascospores germinated on PDA within 24 hours at 25 °C, colonies, dense but thinning towards the edge, edge irregular, white from above, reverse similar in colour. No conidia were observed on PDA or oat agar (OA) media.
Habitat: Known to inhabit dead bamboo.
Distribution: Yunnan Province, China.
GenBank Accession:
ITS MW732442; RPB2 N/A; β-tubulin MW755343; α-actin MW755348
ITS MW732443; RPB2 N/A; β-tubulin MW755342; α-actin MW755349
Notes: To date, six species of Collodiscula have been reported (Hino & Katumoto 1955, Li et al. 2015a, b, Hyde et al. 2017, Xie et al. 2020). Collodiscula lancangjiangensis has 3-septate ascospores as does C. fangjingshanensis and C. leigongshanensis, which were collected from China. However, C. lancangjiangensis has larger ascospores than C. fangjingshanensis (19–25.5 × 4.5–6 μm) and C. leigongshanensis (28–35 × 8–10.5 μm). Phylogenetic analyses (Fig. 1) indicates that C. lancangjiangensis is closely related to C. japonica with high bootstrap support and PP values (92% ML, 0.99 BYPP; Fig. 1), but forms a distinct lineage.
Reference: Wu, Y. P., Pi, Y. H., Long, S. H., Lin, Y., Long, Q. D., Kang, J. C., ... & Li, Q. R. (2021). Morphological and phylogenetic study of five species of Astrocystis and Collodiscula on bamboo. Phytotaxa, 522(4), 265-284.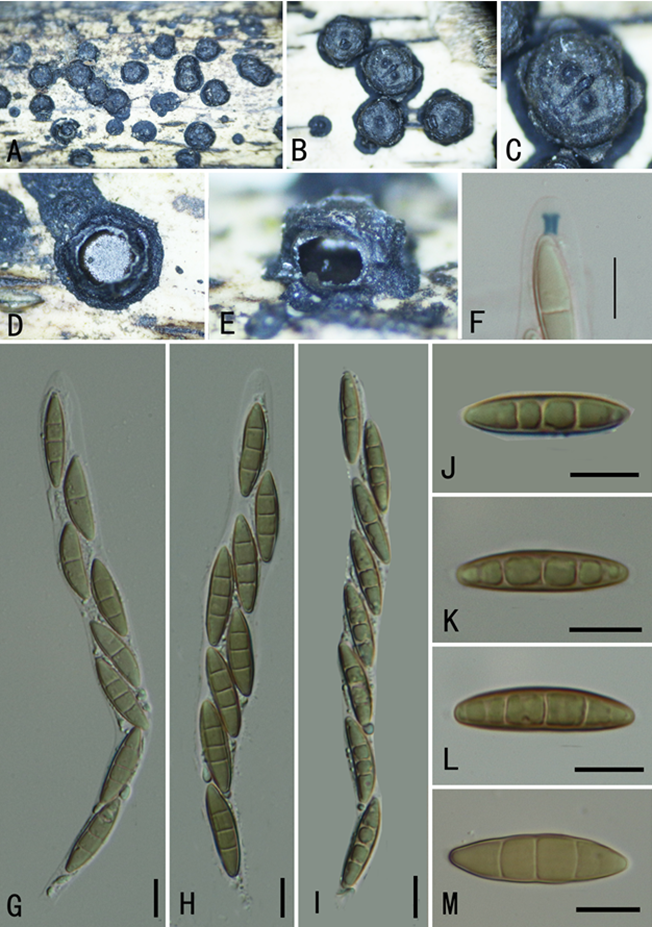
Collodiscula lancangjiangensis (GMB0030, holotype). A–C. Stromata on the surface of host. D. Transverse section of stroma. E. Longitudinal section of stroma. F. Ascus apex with a J+, apical apparatus (stained in Melzer’s reagent). G–I. Asci with ascospores. J–M. Ascospores. Scale bars: B–E = 200 μm, F–M = 10 μm.