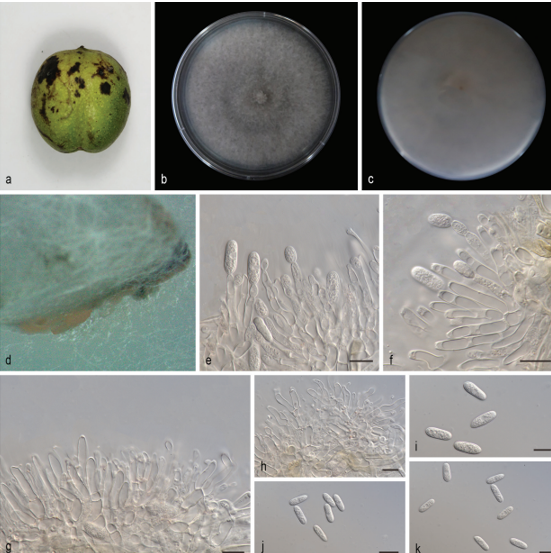
Immersidiscosia eucalypti (Pat.) Kaz. Tanaka, Okane & Hosoya, Persoonia 26: 94 (2011) 2021
(FIGURE 3) Index Fungorum Number: IF519747
Holotype:
Morphological description
Sexual morph: Undetermined.
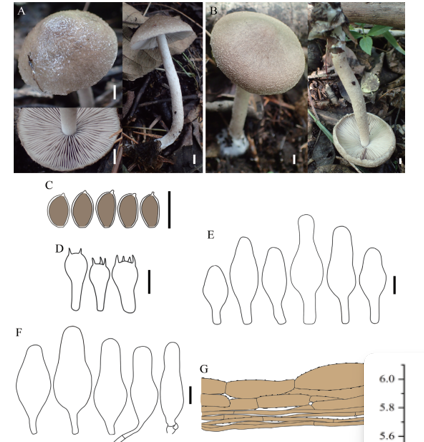
Asexual morph: coelomycetous. Conidiomata 354–522 μm ( x = 427 μm, n = 5) diameter, 287 μm high, conspicuous, pycnidial, subglobose to sometimes lenticular in section view, semi-immersed, scattered, unilocular, with relatively thin stromatic base, black, glabrous. Beak of conidiomata long, 384 μm long, 13 – 61 μm wide. Peridium 18–42 μm wide (upper wall 25–42 μm ( x = 33 μm, n = 7) wide; basal wall 18–26 μm ( x = 27 μm, n = 7) wide), composed of 4 – 7 layers, with outer 3–5 layers light brown and inner layer hyaline, composed of thin-walled cells of textura angularis. Conidiophores up to 45 μm long, cylindrical, branched. Conidia 15.4 – 17 × 2.6 – 3.3 μm ( x = 16.1 × 3 μm, n = 10), cylindrical to subcylindrical, slightly curved, 3-septate, hyaline, with an appendage at both ends; basal cell 2–2.8 μm long ( x = 2.5 μm, n = 10), obconic, truncate at the base; 2 median cells 10.5–12.2 μm long ( x = 11.3 μm, n = 10), cylindrical (second cell from the base 4.7–6.6 μm long ( x = 5.6 μm, n = 10), third cell 4.6–6.7 μm long ( x = 5.7 μm, n = 10)); apical cell 1.7–3.1 μm long ( x = 2.7 μm, n = 10). Appendage single, cellular, unbranched, filiform, flexuous or straight appendage; apical appendage 7.9–9.1 × 0.8–1.1 μm ( x = 8.7 × 1 μm, n = 6); basal appendage 7.8–9.3 × 0.7–1.1 μm ( x = 8.5 × 0.9 μm, n = 6).
Cultures:
Habitat: collected on a fallen leaf of Quercus palustris
Distribution: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Dali; 25°43′27″N 100°6′54″E, 2260 m alt.; 11 August 2019; Hai-Xia Wu leg;
GenBank Accession: (IFRD 500-20)
Notes: —The genus, Immersidiscosia Kaz. Tanaka et al. (2011) was introduced by Tanaka et al. (2011) with I. eucalypti as the type species. The genus, morphologically resembles Discosia but phylogenetically distinct. Immersidiscosia eucalypti was reported from both temperate and tropical countries such as France, Italy, Japan and Tunisia (Tanaka et al. 2011; Hyde et al. 2017; Wijayawardene et al. 2017; Farr & Rossman 2021). This is the first report of I. eucalypti in China. Further collections are essentially required to study whether this taxon is pathogenic on Quercus species
Reference: [1] Chen, C. , Zhao, L. , Zhu, C. , Wang, J. , Jiang, J. , & Yang, S. . (2014). Response of diatom community in lugu lake (yunnan–guizhou plateau, china) to climate change over the past century. Journal of Paleolimnology, 51(3), 357-373.
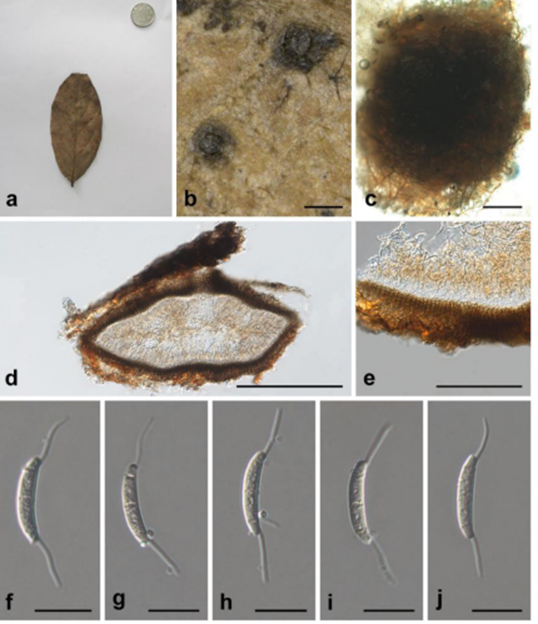 Immersidiscosia eucalypti (IFRD 500-20) a. Host leaves. b. Specimen with conidiomata. c. Conidiomata. d. Section of conidiomata. e. Peridium of conidiomata. f–j. Conidia. Scale bars: b = 300 µm, c, e = 100 µm, d = 200 µm, f–j = 10 µm
Immersidiscosia eucalypti (IFRD 500-20) a. Host leaves. b. Specimen with conidiomata. c. Conidiomata. d. Section of conidiomata. e. Peridium of conidiomata. f–j. Conidia. Scale bars: b = 300 µm, c, e = 100 µm, d = 200 µm, f–j = 10 µm