Chloridium submersum Z.L. Luo, K.D. Hyde & H.Y. Su, sp. nov.2020
Index Fungorum number: IF556752; Facesoffungi number: FoF06866
Holotype: CHINA, Yunnan Province, saprobic on decaying submerged wood in Dulong river, May 2015, H.Y. Su, H D5-13-1, S-510, MFLU 18-1609, holotype; ex-type living culture, MFLUCC 16-1344.
Morphological description
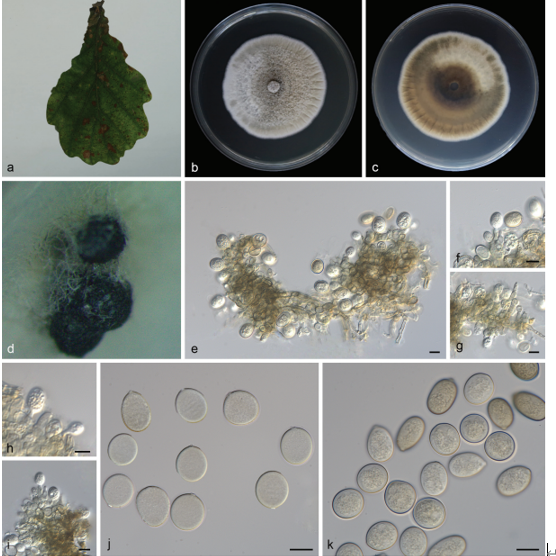
Saprobic on submerged decaying wood. Sexual morph: Undetermined. Asexual morph: Colonies effuse, brown, with long hairy mycelium, with white glistening conidial mass. Mycelium partly immersed, partly superficial, consisting of branched, septate, brown hyphae. Conidiophores 116–264(–350) µm ( x = 190 µm, SD = 74, n = 10) long, 4–6 μm ( x = 5 µm, SD = 1, n = 10) wide, macronematous, mononematous, erect, straight or slightly flexuous, septate, brown at the base, gradually becoming paler towards apex, smooth. Conidiogenous cells integrated, terminal, polyenteroblastic, with a conspicuous outer collarette, hyaline. Conidia 3.5–4.5 µm ( x = 4 µm, SD = 0.5, n = 30) long, 2–3 μm ( x = 2.5 µm, SD = 0.5, n = 30) wide, acrogenous, aggregated in slimy mass at the apex of the conidiophore, ellipsoid, hyaline, aseptate, guttulate, smooth.
Habitat: on decaying submerged wood in Dulong river
Distribution: China.
GenBank Accession: ITS MN860551, LSU MN860556
Notes: Chloridium submersum resembles C. phaeosporum in having macronematous, mononematous, erect, septate conidiophores which are brown at the base, gradually becoming paler towards apex, terminal, hyaline conidiogenous cells and ellipsoid, hyaline, aseptate conidia (Wu & Zhang 2013). However, C. submersum differs from C. phaeosporum by its longer conidiophores (116–264(–350) vs 70–120 µm), polyblastic, denticulate conidiogenous cells and guttulate, hyaline conidia, while the latter species have monophialidic conidiogenous cells constricting abruptly and expanding in a flaring collarette and pale brown conidia without guttules. Chloridium submersum is phylogenetically related to C. aquaticum, C. gonythichii and C. aseptatum (Fig. 8)
Reference: Hyde KD1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 , Norphanphoun C2, 3, 6, 15, 19 , Maharachchikumbura SSN26 et al.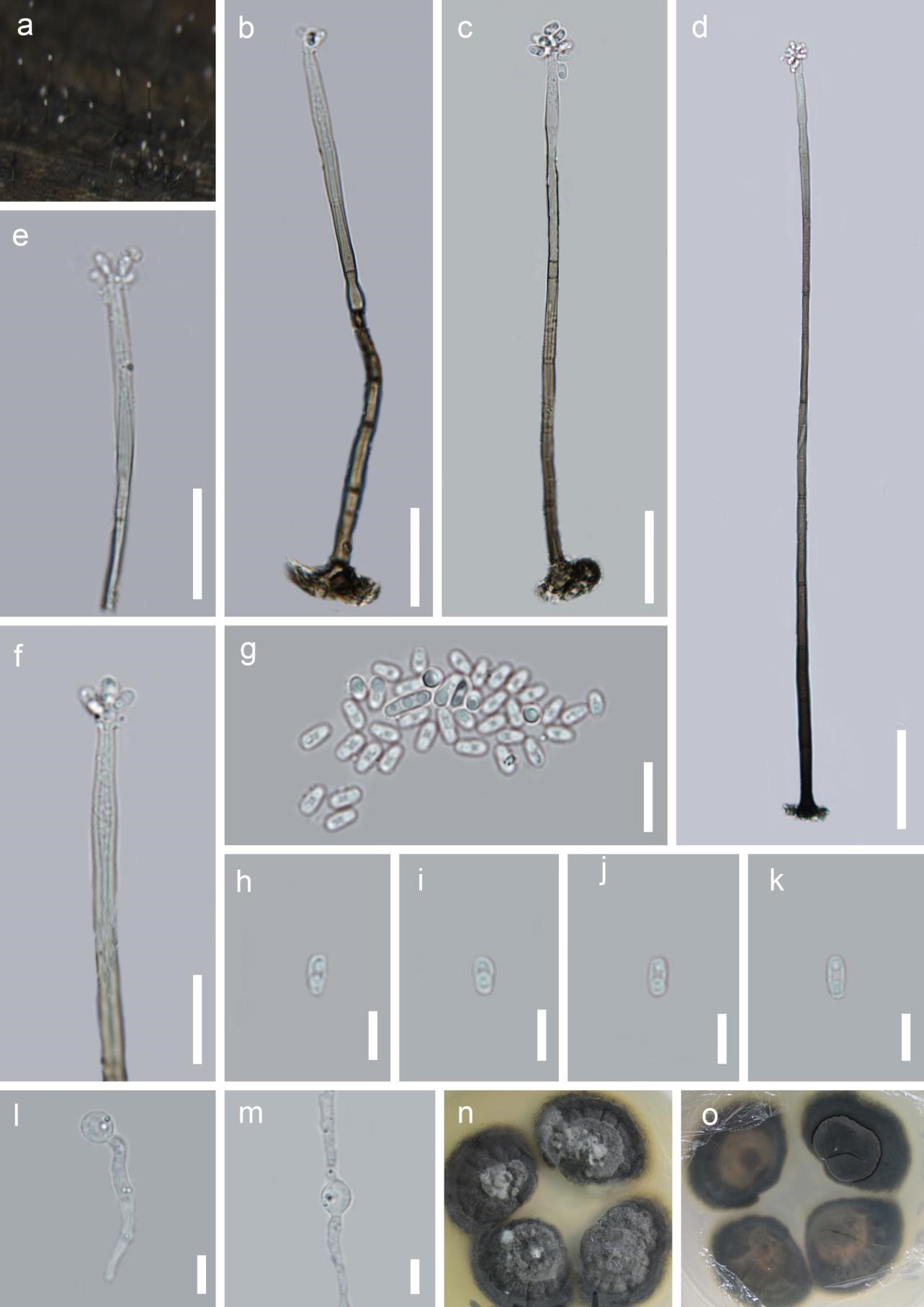
Figure 69 – Chloridium submersum (MFLU 18-1609, holotype). a Colonies on wood. b-d Conidiophores with conidia. e, f Conidiogenous cells. g-k Conidia. l, m Germinating conidia. n, o Culture on PDA from surface and reverse. Scale bars: b-d = 100 μm, e, f = 30 μm, g = 10 μm, h-m = 5 μm