Gnomoniopsis chinensis C.M. Tian & N. Jiang, sp. nov.2020
MycoBank No: 823868
Holotype: China, Hebei Province, Chengde City, chestnut plantation, 40°24'32.16"N, 117°28'56.24"E, 262 m asl, on stems and branches of Castanea mollissima, Ning Jiang, 11 October 2017 (BJFC-S1380, holotype; ex-type culture, CFCC 52286). Hebei Province, Qinhuangdao City, chestnut plantation, 40°22'52.32"N, 119°11'52.18"E, 246 m asl, on branches and twigs of Castanea mollissima, Ning Jiang, 14 October 2017 (BJFC-S1382, paratype; living culture, CFCC 52288). Hebei Province, Tangshan City, chestnut plantation, 40°12'59.76"N, 117°59'7.24"E, 67 m asl, on stems and branches of Castanea mollissima, Ning Jiang, 18 October 2017 (BJFCS1383; living culture, CFCC 52289).
Morphological description:
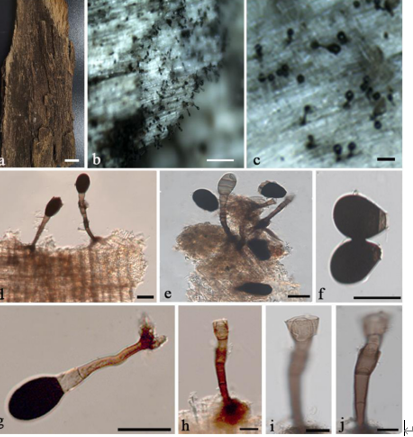
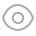
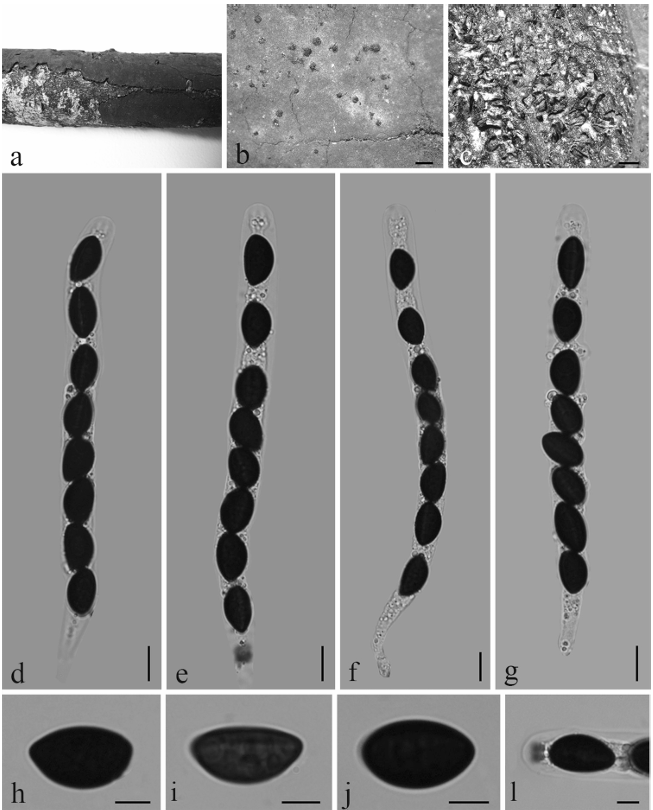
Pathogenic on stems and branches of Castanea mollissima. Conidiomata pseudostromatic, globose to pulvinate, occurring separately, yellow to orange, semi-immersed in bark, 400–1000 µm high, 500–1500 µm diam, unilocular, single ostiolate, forming long, wide orange tendrils, 1500–2000 µm × 400–500 µm. Conidiophores indistinct, often reduced to conidiogenous cells. Conidiogenous cells oval, hyaline, 1-celled, 6–12 µm. Conidia oval, oblate, fusiform, straight to curved, hyaline, 2–3 guttules, (6.0–)6.5–8.5(–9.0) × (2.2–)2.7–3(–3.5) µm (mean = 7.5 × 2.7 µm). Culture characters Colonies on PDA attaining 90 mm after 20 days at 25 °C, flat, velutinous to shortly woolly, dark brown in center, gradually lightening to pale grey at margin; margin diffuse; reverse of almost same colors as surface.
Habitat: on stems and branches of Castanea mollissima
Distribution: China
GenBank Accession: Strain CFCC 52286\ CFCC 52287\ CFCC 52288\ CFCC 52289 GenBank Accession Number ITS MG866032\MG866033\MG866034\MG866035 tub2MH545366\MH545367\MH545368\MH545369 tef1MH545370\MH545371\MH545372\MH545373
Notes: Three Gnomoniopsis species have been discovered from the host genus Castanea. They share similar conidial dimension (6.0–9.0 × 2.2–3.5 µm in Gnomoniopsis chinensis vs. 5.0–8.0 × 2.0–3.5 µm in G. daii vs. 6.0–9.5 × 2.0–4.0 µm in G. smithogilvyi) (Crous et al. 2012; Jiang and Tian 2019). However, we can distinguish them easily by the phylogram of ITS, tef1 and tub2 (Fig. 2). In addition, Gnomoniopsis chinensis and G. daii inhabit the Chinese chestnut (Castanea mollissima), but G. smithogilvyi on the European chestnut (C. sativa) and C. crenata × C. sativa hybrids.
Reference: Jiang N, Liang L-Y, Tian C-M (2020) Gnomoniopsis chinensis (Gnomoniaceae, Diaporthales), a new fungus causing canker of Chinese chestnut in Hebei Province, China. MycoKeys 67: 19–32. https://doi.org/10.3897/ mycokeys.67.51133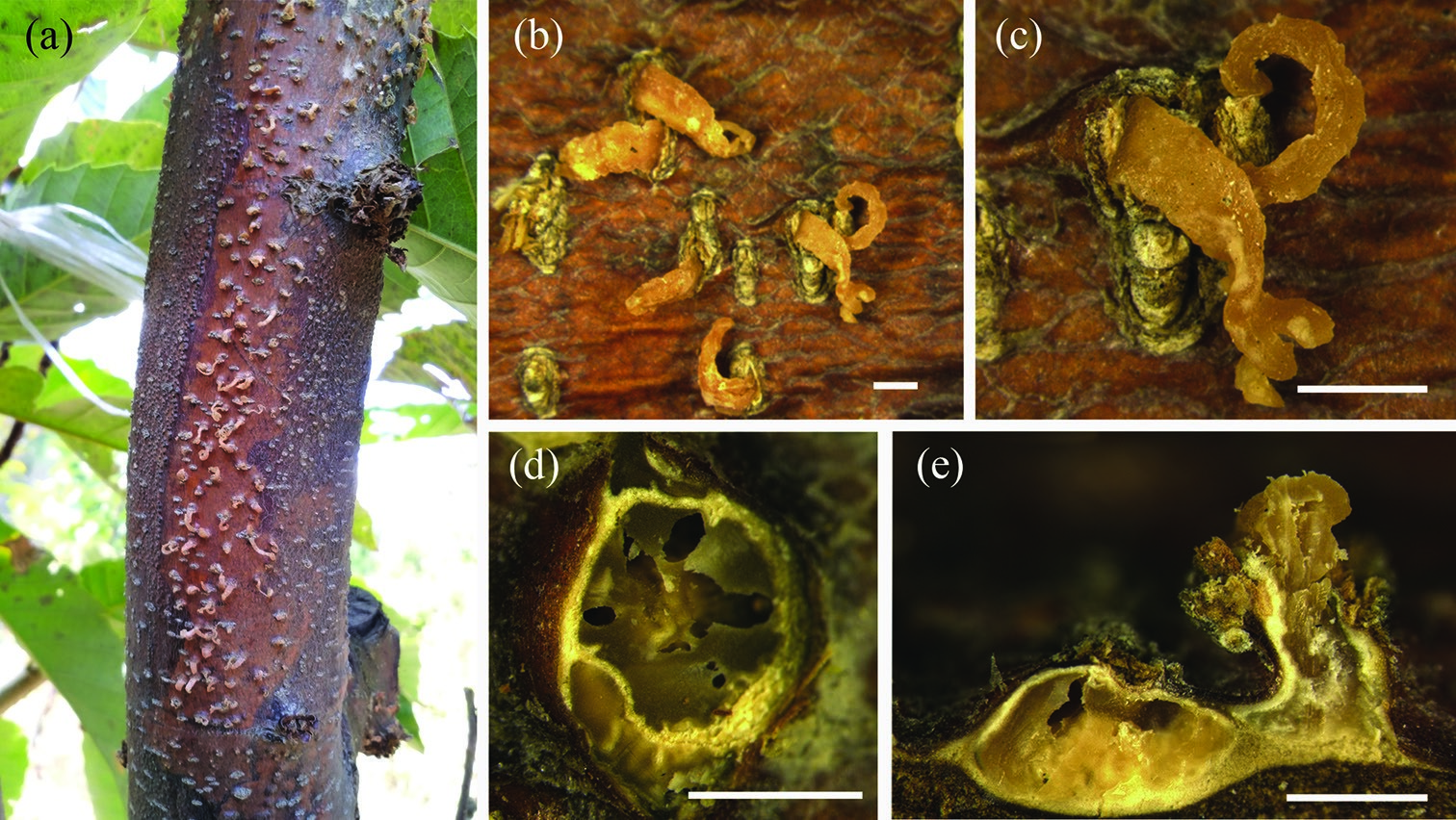
Figure 3. Conidiomata of Gnomoniopsis chinensis from Castanea mollissima (BJFC-S1380, holotype) a–c habit of conidiomata on the chestnut stem d transverse sections through conidiomata e longitudinal sections through conidiomata. Scale bars: 1 mm (b–e).
Figure 4. Morphology of Gnomoniopsis chinensis from PDA (CFCC 52286, ex-type culture) a colonies on PDA b conidiomata formed on PDA c, f conidia d, e conidiogenous cells. Scale bars: 1 mm (b); 10 µm (c–f).