Rhytidhysteron camporesii Ekanayaka & K.D. Hyde 2020
Index Fungorum number: IF556783; Facesoffungi number: FoF 06459
Holotype: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Kunming City, Kunming Institute of Botany, Botanical garden, on dead stems of unidentified woody plant, 14 April 2016, A.H. Ekanayaka, HC 005 (KUN-KHAS 104277, holotype). GenBank numbers: ITS = MN429069, LSU = MN429072, TEF1-α = MN442087.
Morphological description
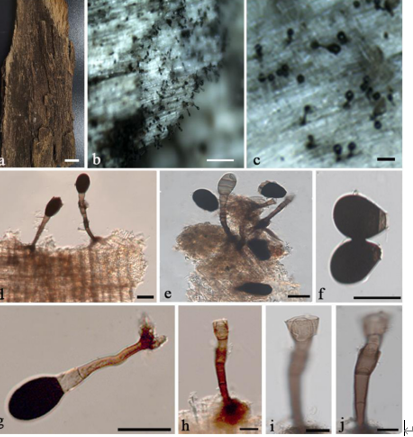
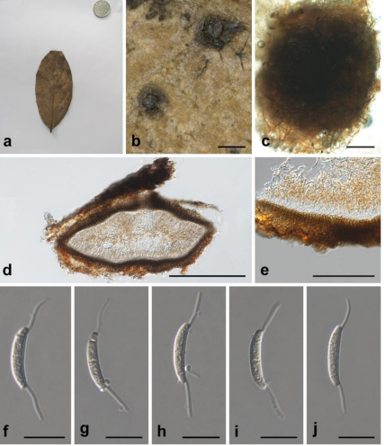
Sexual morph Ascomata 500–650 µm high, 800–1100 µm long ( x̄ = 570.1 × 1002.4 µm, n = 10), apothecial, arising singly or in small groups, short stipitate, erumpent from the substrate. Receptacle cupulate, black, hysteriform. Disc concave covered by margins. Margins black, slightly dentate. Ectal excipulum 65–95 µm ( x̄ = 71.9 µm, n = 10) carbonaceous, composed of blackish cells of textura globulosa to angularis. Medullary excipulum 19–22 µm ( x̄ = 20.4 µm, n = 10), composed of narrow, long, thin-walled, hyaline to brownish cells of textura porrecta. Hymenium hyaline. Paraphyses 3–5 µm wide ( x̄ = 4.4 µm, n = 20) at the apices, numerous, septate, branched at the base, exceed asci in length, apically swollen, slightly branched, slightly granulated and pigmented, pigments are brownish in water, magenta in KOH, apices glued together with gelatinous material to form pseudo-epithecium. Asci 165–175 × 13–15 µm ( x̄ = 171.8 × 13.5 µm, n = 30) 8-spored, short pedicellate, long, cylindrical, rounded at the apex, J-, croziers abscent at the asci base. Ascospores 25–28 × 9–11 µm ( x̄ = 26.1 × 10.4 µm, n = 40), 1-seriate, hyaline to light brown, 1–2-septate when immature, dark brown, 3-septate at maturity, smooth-walled, ellipsoidal to fusiform, slightly rounded or pointed at both ends, guttulate. Asexual morph Undetermined.
Habitat: dead stems.
Distribution:China.
Notes: The new taxon is characterised by short stipitate apothecia, apically swollen, granulated and pigmented paraphyses, ascospores with slightly rounded and pointed ends. In the comparison of ITS sequences, our new strain shows 94% (486/517 bp) similarity to Rhytidhysteron rufulum (Spreng.) Speg. (MFLUCC 12-0568) and 94% (480/510 bp) to R. thailandicum Thambug. & K.D. Hyde (MFLUCC 14-0503) but differs from R. rufulum in 31 base pairs including six gaps and from R. thailandicum in 30 base pairs including five gaps. Phylogenetically this new species formed an independent lineage with strong statistical support (86% ML, 1.00 BYPP; Fig. 8). Rhytidhysteron camporesii is morphologically similar to R. neorufulum Thambug. & K.D. Hyde, but they are different in having sessile apothecia, and longer and highly guttulate ascospores in R. neorufulum (Thambugala et al. 2016). Rhytidhysteron tectonae Doilom & K.D. Hyde is also similar to R. camporesii, but differs in having apically swollen, granulated and pigmented paraphyses (Doilom et al. 2017).
Reference: Kevin D. Hyde1,5,8,22 · Yang Dong2,3 · Rungtiwa Phookamsak1,5,6,7 et al.
Rhytidhysteron camporesii (KUN-HKAS 104277, holotype). a Substrate. b Ascomata on wood. c Cross section of an ascoma. d Vertical section of the ascoma at margin. e Apically swollen paraphyses. f, g Cylindrical asci. h–j Ellipsoid ascospores. Scale bars: b = 500 µm, c = 400 µm, d = 100 µm, e–g = 50 µm, h–j = 10 µm.