Lepteutypa qujingensis L.S. Dissan., J.C. Kang & K.D. Hyde, sp. nov. 2020
Index Fungorum number: IF556877, Facesoffungi number: FoF 06506
Holotype: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Qujing (24.668703oN, 104.24653oE) on recently dead branch of an unknown host, 06 May 2019, L.S. Dissanayake, DW1137–045 (HMAS 290478, holotype; HKAS 107065, isotype), ex-type living culture, KUMCC 19–0187, CGMCC, additional material DW1137–046 (HAMS 290471), living culture KUMCC 19–0186. Additional sequence rpb2: MN729566.
Morphological description
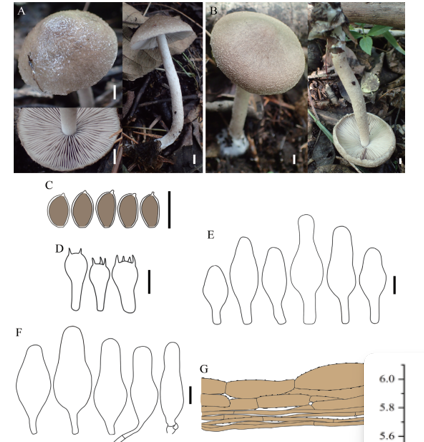
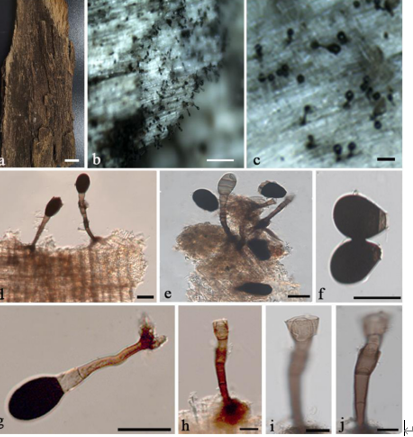
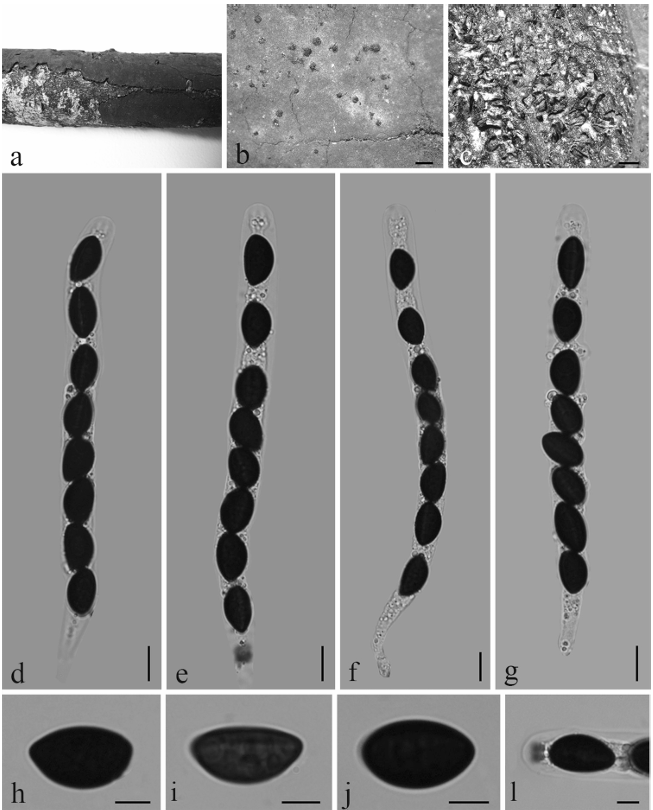
Saprobic on a dead branch. Sexual morph Ascomata 161–222 μm high × 525–550 μm diam. (̄x = 191.5 × 537.5 μm, n = 10), immersed, visible as minute dark black spots, flat on the host surface, solitary, scattered, sub-globose and brown. Peridium 10–25 μm (x = 17.5 μm, n =10), comprising an inner layer of hyaline cells of textura angularis, the outer layer of reddish brown cells of textura angularis. Paraphyses 6.5–12 μm wide (x = 9.3 μm, n = 15), hyaline, few, longer than asci, cellular, constricted at septum, guttulate, embedded in a gelatinous matrix. Asci 100–140 × 4.5–8.5 μm (x = 120 × 6.5 μm, n = 20), 8-spored, unitunicate, cylindrical, with long pedicel, apically rounded, with a J+ apical ring. Ascospores 19–26 × 4–6 μm (x = 22.5 × 5 μm, n =35), overlapping uniseriate, straight to slightly curved, fusiform, multi-guttulate, hyaline turning light brown when mature, 5–6-septate, smooth-walled Asexual morph Undetermined.Culture characteristics:—Colonies on PDA, reaching 15–20 mm diam., after 2 weeks at 20–25oC, circular, flat, smooth surface, entire edge, slightly wooly, smooth margin, with concentric rings of wooly from above: ash white at the center; from below: light brown at the margin, dark brown at the center; mycelium ash white.
Habitat: on recently dead branch of an unknown host
Distribution: Yunnan Province, China.
GenBank Accession: LSU MN556316, MN707567; ITS MN477033, MN707568
Notes: Both of our specimens (HAMS 290478 and HAMS 290471) share characteristics typical to Lepteutypa in having long, cylindrical asci with J+ apical ring and uniseriate, multiseptate, brown ascospores. Lepteutypa qujingensis differs from other Lepteutypa species by having thin asci and smaller ascospores (19–26 × 4.3–6.3 μm). Lepteutypa qujingensis is similar in morphology to L. fuckelii in having immersed ascomata, J+ apical ring and multiguttulate, hyaline to brown ascospores. However, L. fuckelii has ascomata surrounded by grey clypeus and 4septate, yellowish brown ascospores with a sheath, while L. qujingensis has 5–6-septate, brown ascospores without a sheath. Phylogenetic analyses show that L. qujingensis is sister to L. fuckelii Petr. (79% MP, 84% ML, 0.99 PP, Fig. 1). Significant characteristics among similar taxa are given in TABLE 3. Based on phylogenetic evidences and morphological differences, we introduce L. qujingensis as a new species.
Reference: LAKMALI S. DISSANAYAKE1,7, MILAN C. SAMARAKOON2,3,8, PETER E. MORTIMER4,9 et al.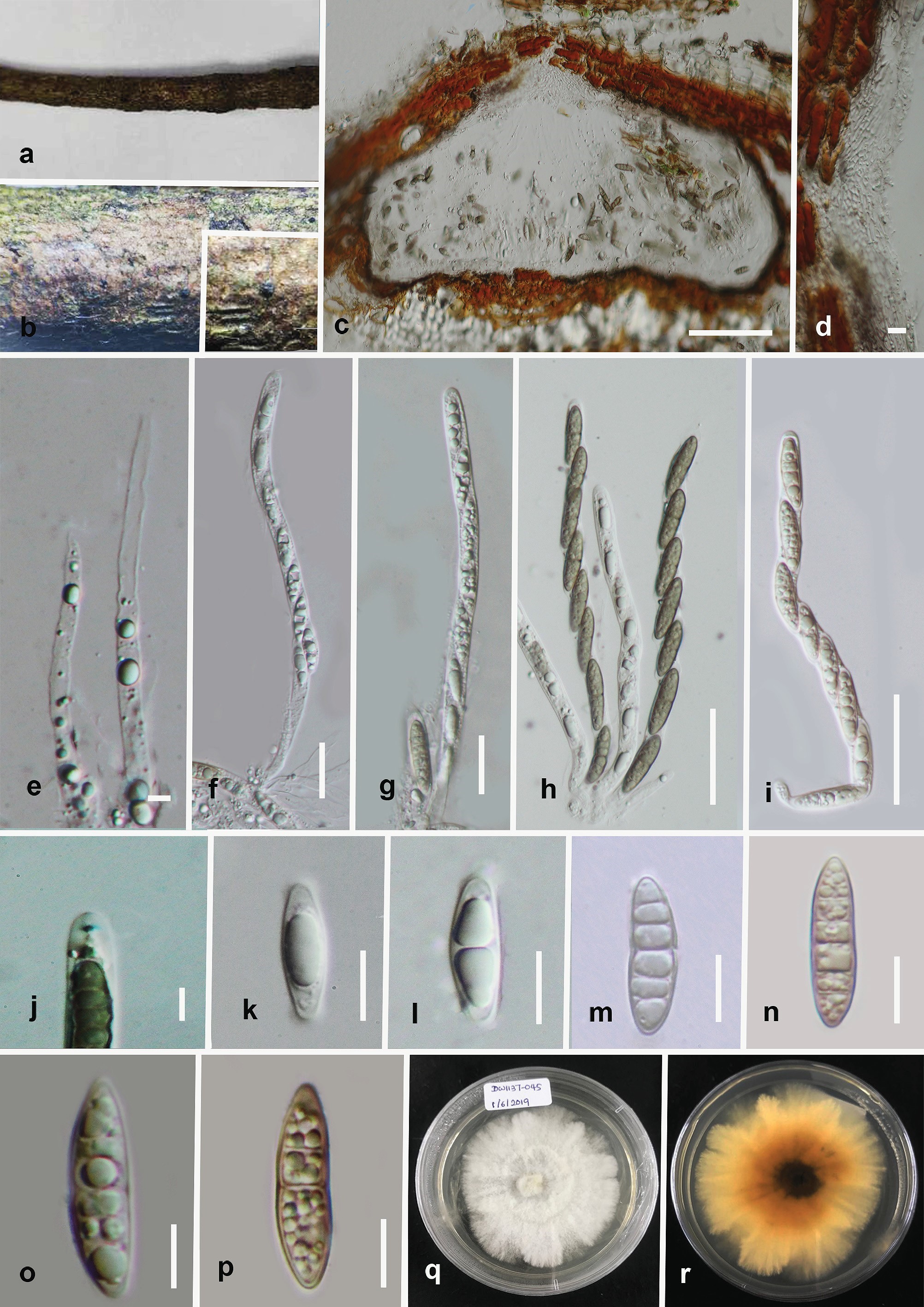
Lepteutypa qujingensis (HMAS 290478). a,b. Ascomata on the substrate. c. Vertical section of ascoma. d. Peridium. e. Paraphyses. f–i. Asci. j. Apical ring bluing in Melzer’s reagent k–p. Ascospores. Culture on PDA from, q. above, r. below after 6 weeks.
Scale bars: c = 100 μm, d, e = 5 μm, f–i = 20 μm, j = 5 μm, k–p = 10 μm.