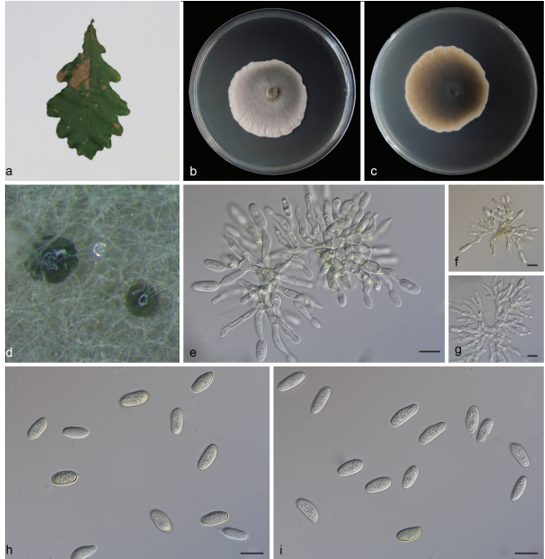
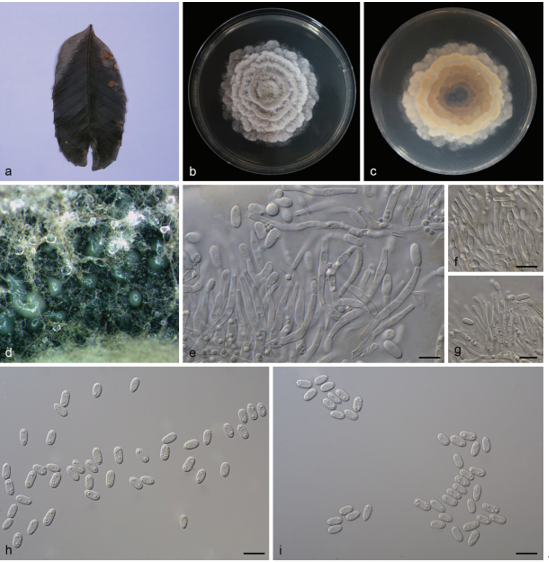
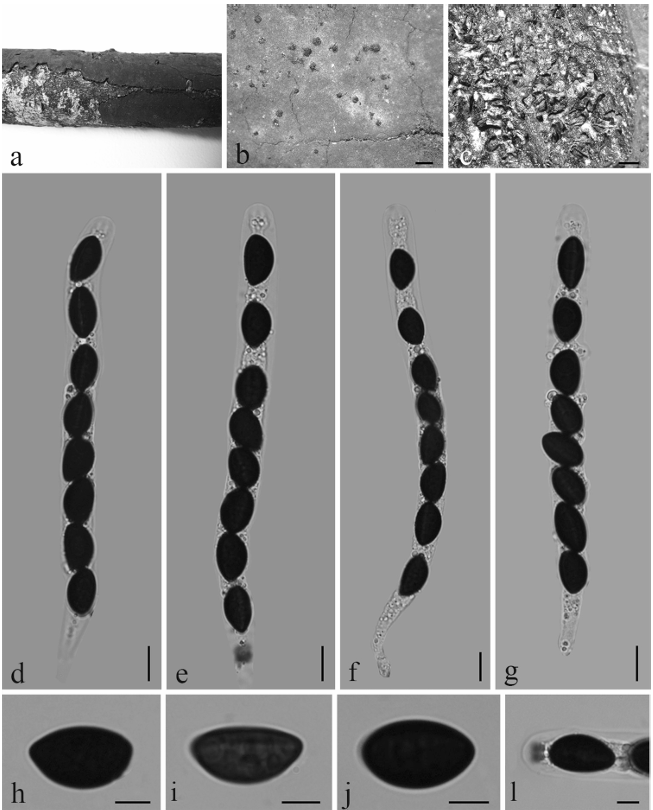
Colletotrichum gloeosporioides (Penz.) Penz. & Sacc., Atti Reale Ist. Veneto Sci. Lett. Arti., ser. 6, 2: 670. 1884.2021
MycoBank No:
Holotype:
Morphological description
Asexual morph: developed on PDA. A mass of orange conidia grows in the white m celium of PDA after 14 days in light at 25 °C. Conidia, hyaline, smooth-walled, subcylindrical, both ends round, 1–3-guttulate, contents granular. Conidia on PDA (10.6–16.5 × 4.3– 5.3 µm, mean ± SD = 14.9 ± 1.5 × 4.9 ± 0.3 μm, L/W ratio = 3.0, n = 40). Sexual morph not observed. Conidiogenous cells subcylindrical, straight to curved, 4.7–12.7 × 3.1–4.0 µm, opening 1.5–2.0 μm diam. Conidiophores hyaline, smooth walled, septate, branched.
Sexual morph: Undetermined.
Cultures: . Colonies on PDA flat with entire margin, aerial mycelium white, floccose cottony; surface and reverse grayish in the center and white margin. PDA attaining max 81 mm in diameter after 7 days, at 25 °C, growth rate 8.7–11.5 mm/day. Colonies on SNA sparse hyphae, slow growth
Habitat: on diseased fruit of Juglans regia
Distribution: . China, Shandong Province: Mengyin County, Mengshan, on diseased fruit of Juglans regia, 25 July 2020, T.C. Mu, paratype HSAUP200952, ex-paratype living culture SAUCC200952. China, Shandong Province: Mengyin County, Mengshan, on diseased fruit of Juglans regia, 25 July 2020, T.C. Mu, paratype HSAUP200954, ex-paratype living culture SAUCC200954. China, Shandong Province: Mengyin County, Mengshan, on diseased fruit of Juglans regia 25 July 2020, T.C. Mu, paratype HSAUP201001, ex-paratype living culture SAUCC201001.
GenBank Accession: its JX145145 ;tub2 JX145196.
Notes: Colletotrichum gloeosporioides was originally described as Vermicularia gloeosporioides on fruit of Citrus sinensis in Italy and this species placed in Colletotrichum by Corda (Weir et al. 2012; Cannon et al. 2008). In the present study, three strains (SAUCC200952, SAUCC200954 and SAUCC201001) are clustered to C. gloeosporioides clade in the combined phylogenetic tree (Fig. 1). Morphologically, our strains were similar to C. gloeosporioides by conidia (10.6–16.5 × 4.3–5.3 vs. 12.0–17.0 (–23.5) × 4.5–6.0 μm, mean:14.9 × 4.9 vs. 14.4 × 5.6 μm). We therefore consider the isolated strain as C. gloeosporioides
Reference: [1]Toyozo SatoJouji MoriwakiShihomi UzuhashiYousuke DegawaTsuyoshi OnoKazuko Nishimura. (2012). Molecular phylogenetic analyses and morphological re-examination of strains belonging to three rare colletotrichum species in japan. 日本微生物資源学会誌: Official Publication of the Japan Society for Culture Collections, 28(2
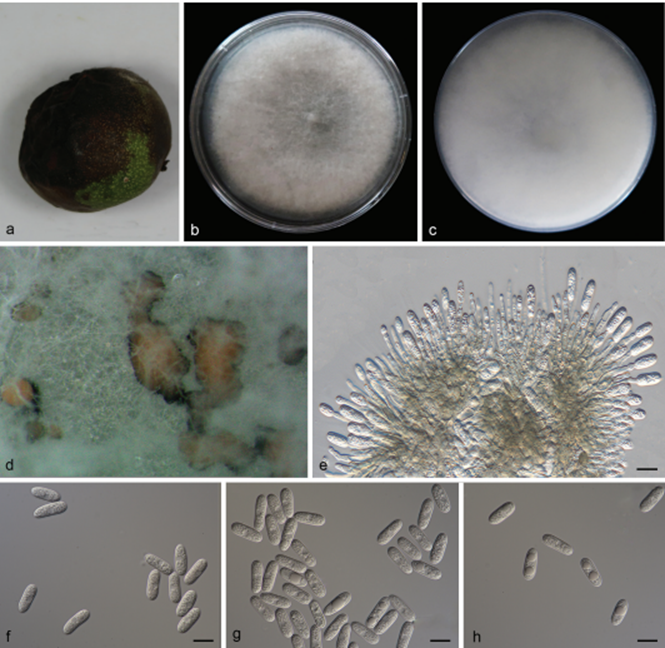 Colletotrichum gloeosporioides (SAUCC201001) a lesion fruit of host plant b, c surface (b) and reverse (c) sides of colony after incubation for 7 days on PDA d conidiomata e conidiophores, conidiogenous cells and conidia f–h conidia. Scale bars: 10 μm (e–h)
Colletotrichum gloeosporioides (SAUCC201001) a lesion fruit of host plant b, c surface (b) and reverse (c) sides of colony after incubation for 7 days on PDA d conidiomata e conidiophores, conidiogenous cells and conidia f–h conidia. Scale bars: 10 μm (e–h)