Trichomerium leigongense W. Sun, L. Su and M.C. Xiang, sp. nov.2020
MycoBank MB 817688
Holotype: China: Guizhou Province: Leishan County, Leigong Mountain, 26◦230 N, 108◦120 E,2112 m a.s.l., from rock surrounded by vegetation, 13 October 2014, Meichun Xiang, (HMAS 246977 (dried culture)–holotype and CGMCC 3.17983–ex-type culture).
Morphological description
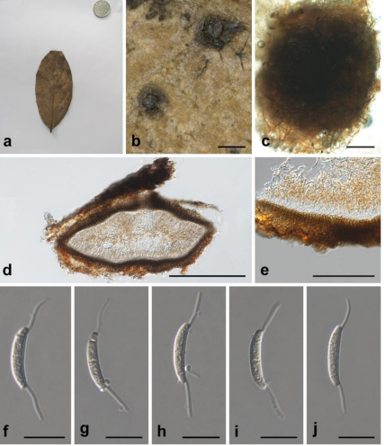
Hyphae cylindrical, occasionally toruloid, branched, septate, constricted at the septa, 1.9–4.8 µm (x = 3.3 µm, n = 20), yellowish brown to mid-brown, the lateral branched moniliform hyphae normally developed by enteroblastic proliferation (Figure 16C–G). Swollen cells globose, ellipsoidal, or sub-globose, light brown to yellowish brown, produced at the hyphal apex, 6.5–7.4-µm-long,5.3–9.8-µm-wide (x = 6.8 × 7.5 µm, n = 10) (Figure 16H,I).Culture characters: Colonies on MEA growing slowly, attaining 21-mm-diam. after 20 weeks at 25 ◦C, regular margins, dark brown to black, covered by a sparse, velvety, aerial mycelium, black brown in reverse (Figure 16A,B). Minimum 4 ◦C, optimum at 20–25 ◦C, and maximum 28 ◦C.
Habitat: from rock surrounded by vegetation
Distribution: Leishan County (Guizhou Province, China).
GenBank Accession:
Notes: T. leigongense (CGMCC3.17983) phylogenically resembles T. lapideum (CGMCC3.17311)(96% identity in ITS, 99% in nucLSU, 70% in RPB1, and 90% in TUB) (Figure 3). However, swollen cells (6.5–7.4 µm × 5.3–9.8 µm) were present in T. leigongense but lack in T. lapideum, while Tripospermum-like conidia were present in T. lapideum but not in T. leigongense.
Reference: Wei Sun , Lei Su , Shun Yang et al.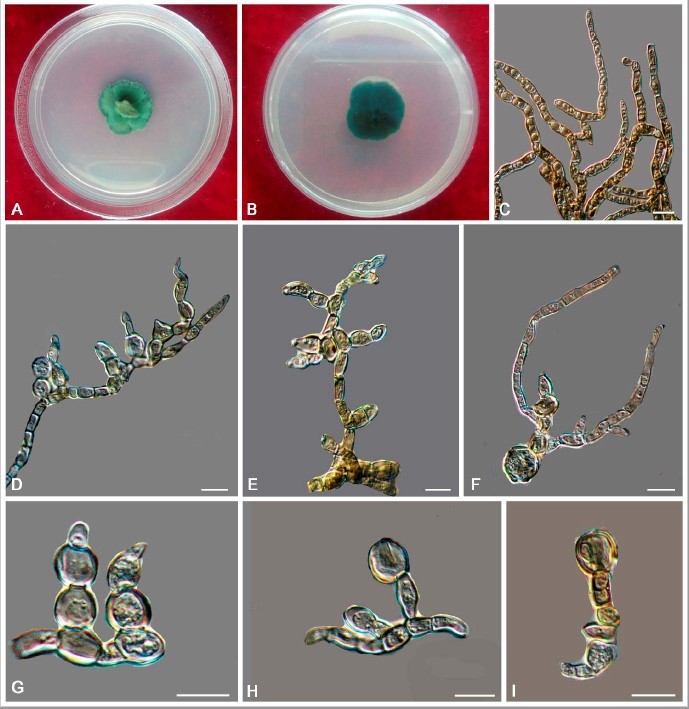
Trichomerium leigongense (CGMCC 3.17983). (A,B) Colony forward and reverse after 20 weeks on MEA. (C) Cylindrical, septate hyphae with constricted septa. (D–G) Moniliform hyphae with blastic proliferation on the lateral branches. (H,I) Apical unicellular body. Scale bars: (C–I) = 10 µm.