Trichomerium lapideum L. Su, W. Sun and M.C. Xiang, sp. nov. 2020
MycoBank MB 810891
Holotype: China: Jiangxi Province: Jiujiang City, Guling Town, Lushan Mountain, 29◦350 N, 115◦590 E, 952 m a.s.l., from granite in tropical climate, 19 May 2013, Lei Su, (HMAS245387 (dried culture)–holotype and CGMCC 3.17311–ex-type culture).
Morphological description
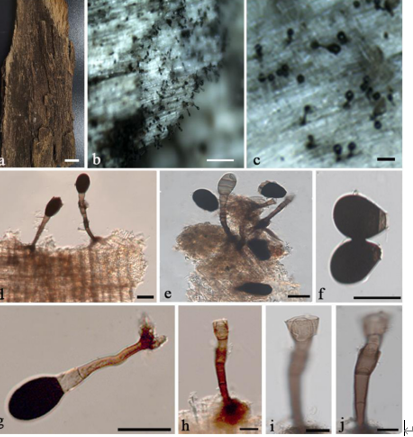
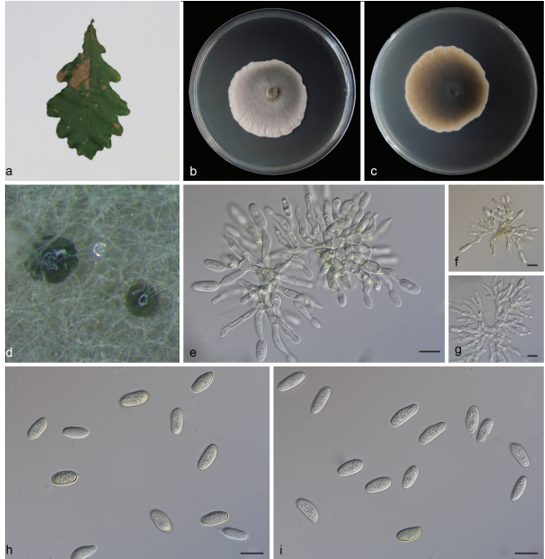
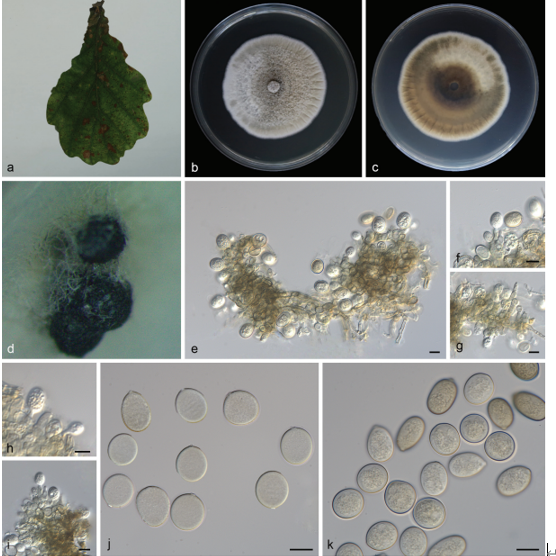
Hyphae cylindrical, branched, constricted at the septa, dark brown, 2.6–4.9-µm-wide
(x = 3.8 µm, n = 10) (Figure 15C–E). Conidia Tripospermum-like, pale brown to dark brown, consisting of a subcylindrical basal cell, 1–3-septate, 12.5–19.8 × 2.2–4.8 (x = 15.8 × 3.8 µm, n = 5), with truncate hilum, giving rise to three lateral arms, arms one to two septate, subcylindrical with obtusely rounded ends, 7.8–13.5 × 2.2–4.8 (x = 10.5 × 3.9 µm, n = 5) (Figure 15F–H).Culture characters: Colonies on MEA slow-growing, attaining 22-mm-diam. after 20 weeks at 25 ◦C, dark brown to black, slightly raised in the center, with a flat margin, aerial mycelia sparse; black in reverse (Figure 15A,B). Minimum 4 ◦C, optimum at 20–25 ◦C, and maximum 29 ◦C.
Habitat: from granite in tropical climate
Distribution: China
GenBank Accession:
Notes: Phylogenetic analyses showed that T. lapideum is the closely related species to T. deniqulatum. T. lapideum can be distinguished from T. deniqulatum in having Tripospermum-like conidia, whereas T. deniqulatum has ascostromata with sub-globose to globose, brown, 154–175-µm-diam., 163–180-µm-high [27].
Reference: Wei Sun , Lei Su , Shun Yang et al.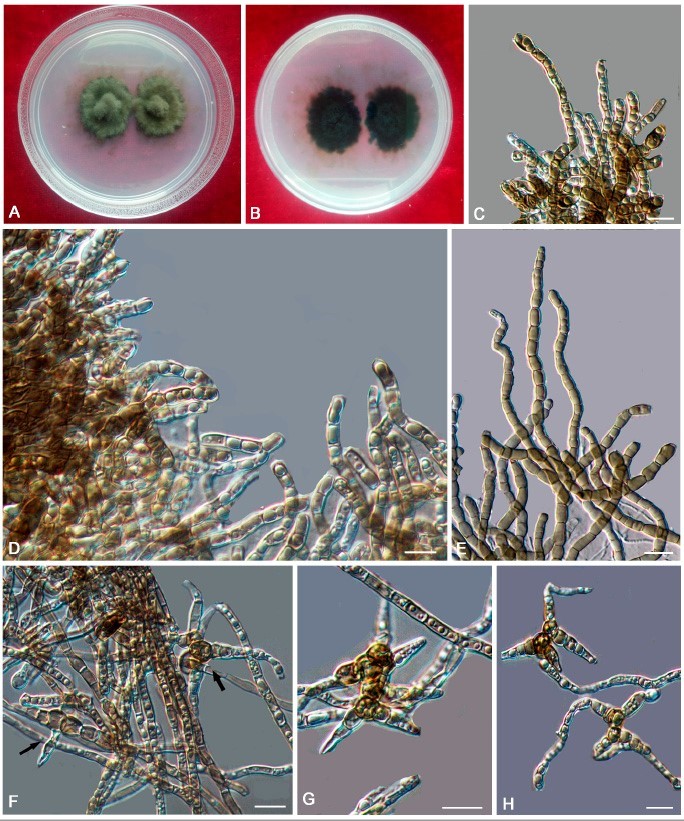
Trichomerium lapideum (CGMCC 3.17311). (A,B) Colony forward and reverse after 20 weeks on MEA. (C–E) Moniliform hyphae with constricted septa. (F–H) Branched conidia (arrows). Scale bars: (C–H) = 10 µm.