 109
109
Yamadazyma paraaseri C.Y. Chai & F.L. Hui, sp. nov..2021
MycoBank No: 840101
Holotype NYNU 1811114T
Morphological description :
Asexual morph: The cells are ovoid to elongate (2–2.5 × 3–8.5 µm) and occur singly or in pairs after being placed in YM broth for three days at 25 °C (Figure 4A). Budding is multilateral. After three days of growth on YM agar at 25 °C, the colonies are white to cream-colored, buttery, and smooth, with entire margins. After two weeks at 25 °C on a Dalmau plate culture with CM agar, pseudohyphae consisting of elongated cells with lateral buds are formed (Figure 4B). True hyphae are not observed. Asci or signs of conjugation are not observed on sporulation media. Fermentation of sugars is absent. Glucose, galactose, l-sorbose, d-glucosamine, d-ribose, d-xylose, l-arabinose, d-arabinose, sucrose, maltose, trehalose, methyl α-d-glucoside, cellobiose, salicin, arbutin, lactose, melezitose, inulin, glycerol, erythritol, ribitol, d-glucitol, d-mannitol, d-gluconate, dl-lactate, succinate, citrate, and ethanol are assimilated. No growth is observed in lrhamnose, melibiose, raffinose, xylitol, galactitol, myo-inositol, d-glucono-1, 5-lactone, 2-keto-d-gluconate, d-glucuronate, or methanol. In nitrogen-assimilation tests, growth is present on ethylamine, l-lysine, glucosamine, and d-tryptophan, while growth is absent on nitrate, nitrite, cadaverine, creatine, creatinine, and imidazole. Growth is observed at 37 °C but not at 40 °C. Growth in the presence of 0.01% cycloheximide, 10% NaCl with 5% glucose and 1% acetic acid is absent. Starch-like compounds are not produced. Urease activity and diazonium blue B reactions are negative
sexual morph :not observed.
Culture characteristics:
Habitat: in rotting wood from a tropical rainforest
Distribution :China, Yunnan Province, Jinghong City, Meng yang Town
GenBank: Holotype NYNU 1811114T (ITS: MK682794; D1/D2 LSU: MK682805); additional isolate NYNU 181033 (ITS: MZ318421; D1/ D2 LSU: MZ318460)
Reference:[1] Limkaisang, S. , Kom-Un, S. , Furtado, E. L. , Liew, K. W. , Salleh, B. , & Sato, Y. , et al. (2005). Molecular phylogenetic and morphological analyses of oidium heveae, a powdery mildew of rubber tree. Mycoscience, 46(4), 220-226.
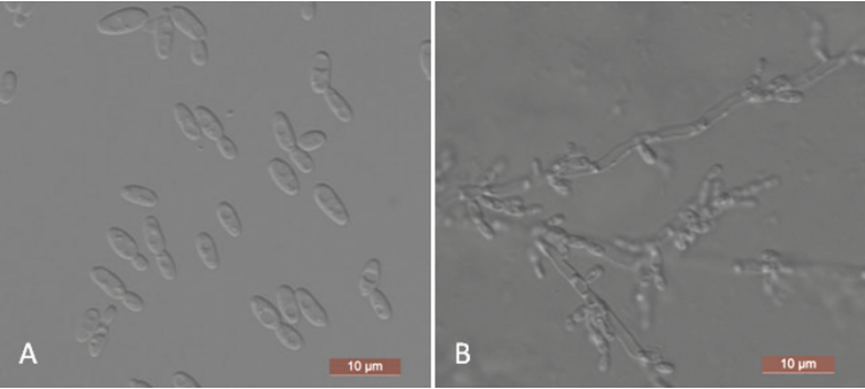
Yamadazyma paraaseri (NYNU 1811114, holotype) A budding cells after three days in YM broth at 25 °C B pseudohyphae on cornmeal agar after two weeks at 25 °C. Scale bars: 10 µm

