Distoseptispora chinensis X. Tang& Jayaward, sp. nov.2021
MycoBank Index Fungorum number: IF558531; Facesoffungi number: FoF 09941
Holotype: GZAAS21-0380.
Morphological description
Sexual morph:
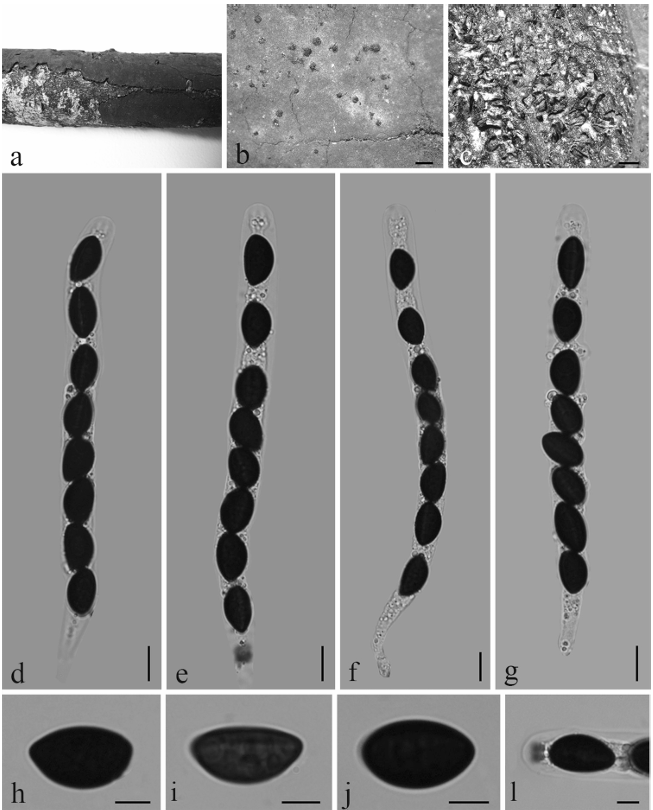
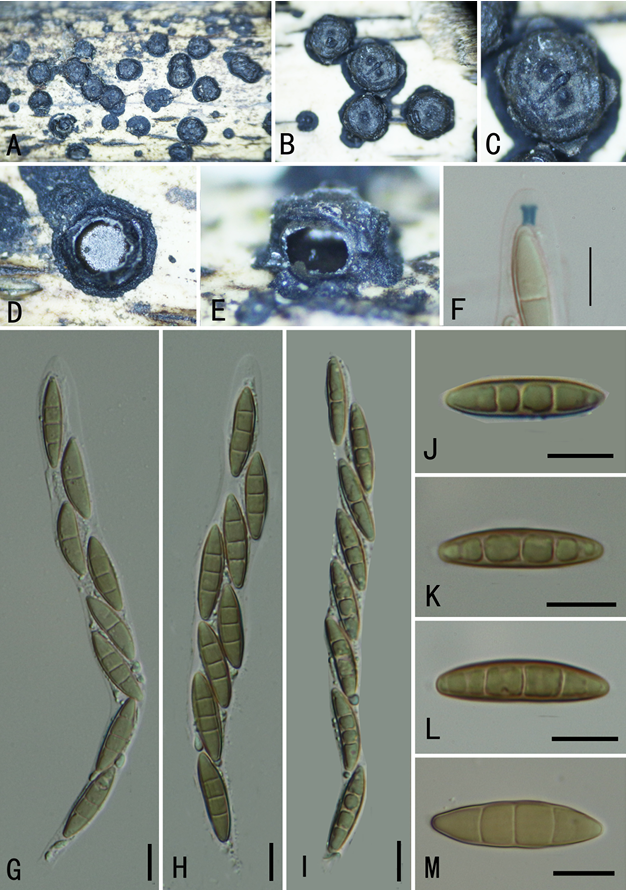
Asexual morphs: Colonies effuse, brown or dark brown, hairy. Mycelium mostly immersed, branched, septate, smooth, pale brown to brown. Conidiophores 16.5–44 × 5.5–9 μm (x̅= 34 × 7 μm, n = 30), macronematous, mononematous, mid-olivaceous to brown, solitary, 1–4-septate, erect, straight or flexuous, unbranched, smooth, cylindrical, truncate at the apex. Conidiogenous cells holoblastic, monoblastic, integrated, terminal, determinate, brown to dark brown, smooth, cylindrical. Conidia1125 81–283 × 10–19 μm (x̅ = 201 × 15 μm, n = 30) acrogenous, solitary, obclavate or lanceolate, rostrate, straight or slightly curved, multi-distoseptate, up to 40-distoseptate, guttulate, olivaceous to dark brown, tapering towards the rounded apex 4.5–9 μm (x̅= 7 μm, n = 30), truncate at the base, slightly constricted at septa, smooth-walled, rounded at apex, with a truncate base and faintly to heavily pigmented scar.
Cultures: Colony grown on PDA, circular, fluffy, white, dense, white mycelium, but olivaceous in the center, slightly pigmented. In reverse, olivaceous, brown at the center, lightly brown at the entire margin, breaking in the center.
Habitat: on decaying wood submerged in a freshwater stream.
Distribution: China, Guizhou Province, Longli.
GenBank Accession: (ITS) MZ474871, (LSU) MZ474867, (SSU) MZ474874 and (tef-1) MZ501609.
Notes: Distoseptispora chinensis forms a sister clade to D. tectonigena with 88% ML, 71% MP and 0.99 PP support values (Fig. 17). However, D. chinense differs from D. tectonigena in having smaller conidiophores (16.5–44 × 5.5–9 μm, 1–4-septate vs 110 × 5–11 μm, 2–6-septate) and larger conidia (81–283 × 10–19 μm vs 148–225 × 11–12 μm). Distoseptispora tectonigena is distinct from D. chinensis by its unique characters on percurrently proliferating 5–10 times at apex. Based on a pairwise nucleotide comparison of ITS and LSU, D. chinensis differs from D. tectonigena in 11/ 562 bp (1.9%) for ITS and 3/ 837 bp (0.3%) for LSU. Based on morphology and phylogeny can be considered as a distinct species according to the guidelines of Jeewon & Hyde (2016).
Reference: Hyde KD, Suwannarach N, Jayawardena RS, Manawasinghe IS, Liao CF, Doilom M, Cai L, Zhao P, Buyck B, Phukhamsakda C, Su WX, Fu YP, Li Y, Zhao RL, He MQ, Li JX, Tibpromma S, Lu L, Tang X, Kang JC, Ren GC, Gui H, Hofstetter V, Ryoo R, Antonín V, Hurdeal VG, Gentikaki E, Zhang JY, Lu YZ, Senanayake IC, Yu FM, Zhao Q, Bao DF 2021 – Mycosphere notes 325-344 – Novel species and records of fungal taxa from around the world. Mycosphere 12(1), 1101–1156, Doi 10.5943/mycosphere/12/1/14

Distoseptispora chinensis (Holotype: GZAAS21-0380). a, b Colonies on submerged wood. c–f Conidiophores, conidiogenous cell bearing conidia. g–k Conidia. l Germinated conidium. m, n Colony on PDA (from above, from below). Scale bars: c–e, h–l = 50 μm, f = 20 μm.