Sanguinoderma rugosum (Blume & T. Nees) Y.F. Sun, D.H. Costa & B.K. Cui, comb. nov. 2020
MycoBank MB828447
Holotype: China, Guangdong Province, Shaoguan, Chebal ing Nature Reserve, on ground of angiosperm forest, 25 June 2010, B.K. Cui, Cui 8795 (BJFC); Zhaoqing, Heishiding Nature Reserve, on ground, 1 July 2010, B.K. Cui, Cui 9011 (BJFC); ibid., Cui 9012 (BJFC); Guangxi Autonomous Region, Nanning, Liangfengjiang National Forest Park, on ground, 3 Aug. 2017, J.L. Zhou, Cui 16337 (BJFC); ibid., 4 Aug. 2017, Cui 16166 (BJFC). – indonesia, West Java, Banten, on Acacia mangium, Bougher, E7079 (PERTH).
Morphological description
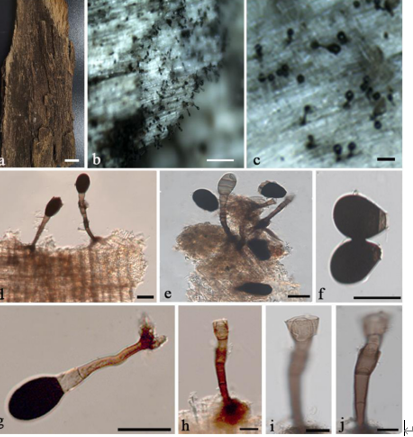
Basidiomata annual, centrally to laterally stipitate, corky to woody hard. Pileus single, suborbicular to flabelliform, up to 12 cm diam and 8 mm thick. Pileal surface dark brown to near black, dull, glabrous, with obviously concentric furrows and radial wrinkles, centre navel-shaped; margin acute to obtuse, entire, wavy and incurved when dry. Pore surface greyish white when fresh, colour changing to blood red when bruised, then quickly darkening; pores circular to angular, 5–7 per mm; dissepiments slightly thick, entire. Context cinnamon to dark brown, with two black resinous lines, corky, up to 5 mm thick. Tubes concolorous with pore surface, woody hard, up to 3 mm long. Stipe concolorous with pileal surface, cylindrical and hollow, slightly swollen at base, up to 12 cm long and 1 cm diam. Hyphal system trimitic; generative hyphae with clamp connections, all hyphae IKI–, CB+; tissues darkening in KOH. Generative hyphae in context colourless, thin-walled, 4–6 μm diam; skeletal hyphae in context yellowish brown to dark brown, thick-walled with a wide to narrow lumen or subsolid, arboriform branched and flexuous, 4–6 μm diam; binding hyphae in context pale yellow, subsolid, branched and flexuous, 1–2 μm diam. Generative hyphae in tubes scanty; skeletal hyphae in tubes dark brown, thick-walled with a wide to narrow lumen or subsolid, arboriform branched and flexuous, 3–7 μm diam; binding hyphae in tubes pale brown, subsolid, branched and flexuous, 1–2 μm diam. Pileal cover composed of clamped generative hyphae, thin- to thick-walled, apical cells clavate with obvious septa at the base, inflated, dark brown, about 20–50 × 6–10 μm, forming a regular palisade. Cystidia absent; cystidioles clavate and apexes constricted, colourless, thin-walled, 20–28 × 3–5 μm. Basidia barrel-shaped to clavate, colourless, thin-walled, 18–25 × 9–20 μm; basidioles in shape similar to basidia, colourless, thin-walled, 15–20 × 10–16 μm. Basidiospores broadly ellipsoid, pale yellow, IKI–, CB+, with double and slightly thick walls, exospore wall smooth, endospore wall with conspicuous spinules, (9.9–)10.2–11.3(–11.7) × (8–)8.3–9.2(–9.5) μm, L = 10.75 μm, W = 8.86 μm, Q = 1.21–1.22 (n = 60/2). Under SEM, exospore wall alveolate to semi-reticulate, endospore wall with short and thin columnar spinules tightly arranged.
Habitat: on ground of angiosperm forest
Distribution: China. tropical and subtropical areas of South East Asia.
GenBank Accession: ITS MK119843a; nLSU MK119922a; RPB1 MK119865a; RPB2 MK121516a; TEF MK121593a; TUB MK125004a
Notes: Amauroderma rugosum is a widespread species distributed in tropical and subtropical areas of South East Asia. It seems to be a species of difficult delimitation due to its great spectrum of morphologic variation (colour, texture and basidiospores size), exhibiting a broadly distribution (although some of the records are dubious), being one of the most cited Amauroderma species (Furtado 1981, Corner 1983). Based on its colour-changing pore surface when bruised and good phylogenetic support, it is proposed as a new combination in Sanguinoderma. It is similar to S. microporum in the dark brown pileal surface with obvious concentric furrows and radial wrinkles, but S. microporum differs from S. rugosum by the extremely thick dissepiments and slightly bigger basidiospores (11–12 × 8.7–9.8 μm) with long and thin endospore coniform spinules (Fig. 8i–j). The distinction between S. rugosum and S. rude is difficult, but the latter has a softer pileus and slightly larger spores (9.5–12.5 × 8–10.7 μm).
Reference: Y.-F. Sun1,2, D.H. Costa-Rezende3, J.-H. Xing1 et al.
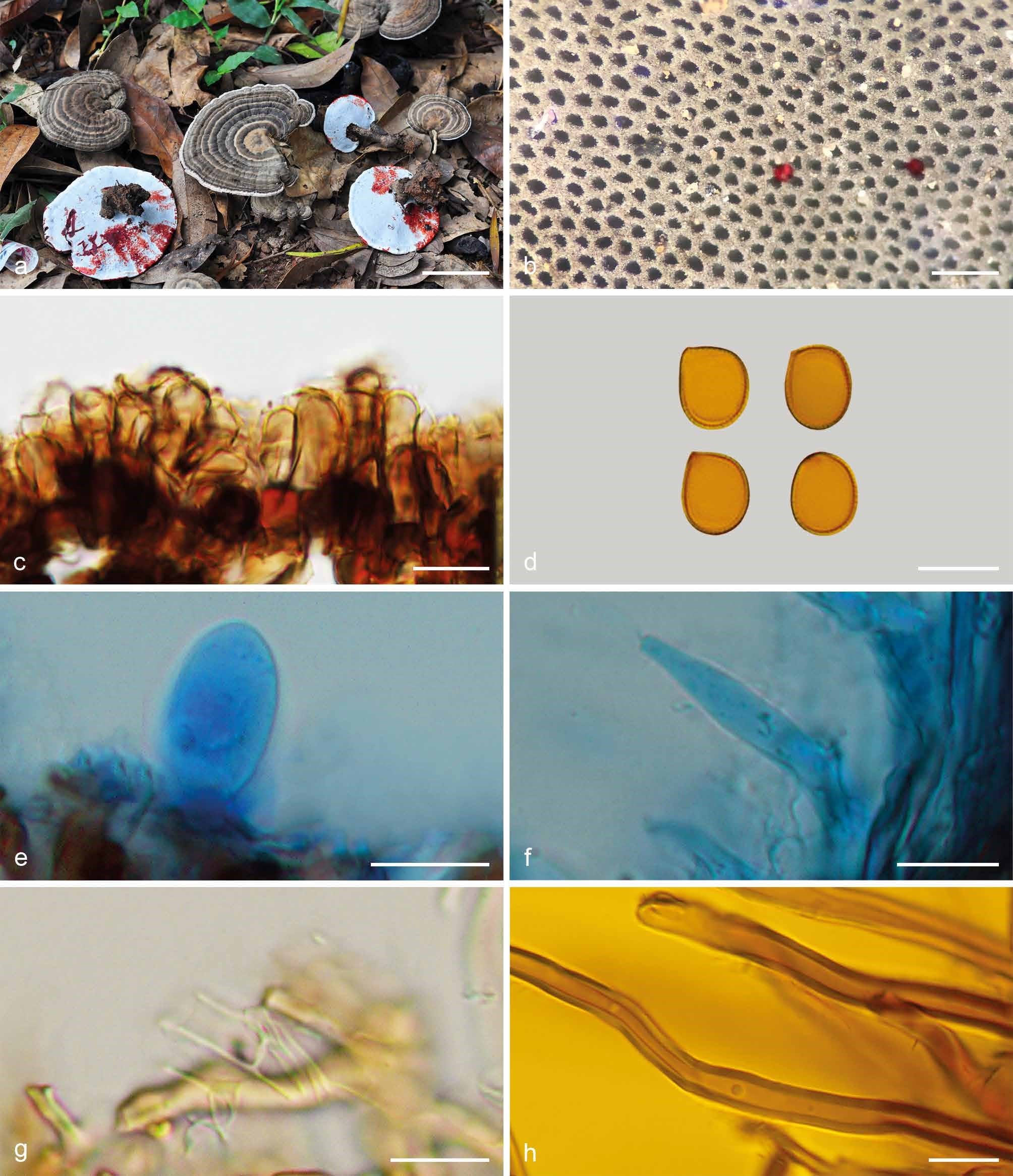

Basidiomata and microscopic structures of Sanguinoderma rugosum (Cui 16337). a. Basidiomata; b. pores; c. apical cells from pileal cover; d. basidiospores; e. basidioles; f. cystidioles; g. generative hyphae from tubes; h. skeletal hyphae from context. — Scale bars: a = 4 cm; b = 0.5 mm; c–h = 10 µm.