Phanerochaete cinerea Y.L. Xu & S.H. He, sp. nov2020
MycoBank: MB 835446; Facesoffungi number: FoF 08032
Holotype China, Hainan Province, Changjiang County, Bawangling Nature Reserve, on small diameter bamboo, 4 July 2019, He 5998 (BJFC 030874, holotype).
Morphological description
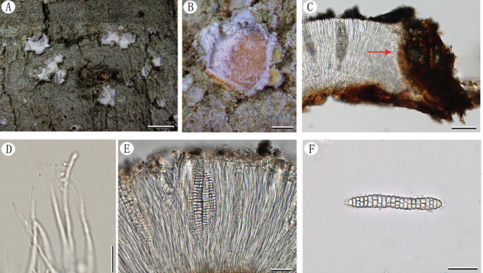
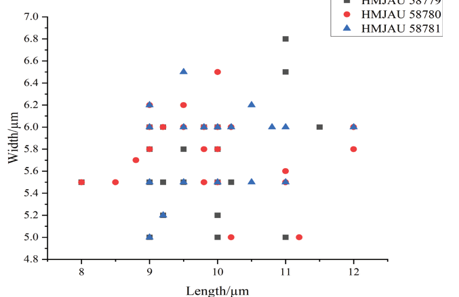
Fruiting body – Basidiomata annual, resupinate, effused, adnate, detachable from substrate, membranaceous to coriaceous, first as many small patches, later confluent up to 15 µm long, 3 cm wide. Hymenophore smooth, grey (6C1–6D1), brownish grey (6C2–6D2) to greyish brown (6D3), slightly darkening in KOH, uncracked; margin thinning out, velvety, distinct, white (6A1), usually with a dark line near hymenophore when juvenile, becoming indistinct, concolorous or darker with hymenophore surface with age. Microscopic structures – Hyphal system monomitic; generative hyphae simple-septate. Subicular hyphae yellowish brown, thick-walled to distinctly thick-walled, smooth, moderately branched and septate, tightly interwoven, more or less parallel to substrate, 3–5 µm in diam. Cystidia absent. Hyphida present, yellowish brown, thick-walled, branched. Basidia clavate, colorless, thin-walled, with a basal simple septum and four sterigmata, 20–30 × 4–5 µm; basidioles numerous, similar to basidia but smaller. Basidiospores subcylindrical, colorless, thin-walled, smooth, IKI–, CB–, 4.8–5.6 (–6) × 2–2.5 (–2.8) µm, L = 5.2 µm, W = 2.2 µm, Q = 2.4 (n = 30/1)
Habitat: on small diameter bamboo
Distribution: – Hainan Province, southern tropical China.
GenBank Accession: nLSU MT248171\ MT248172 Literature This study\ This study
Notes: Phanerochaete cinerea is characterized by grey basidiomata on small diameter bamboo, absence of cystidia, brown subicular hyphae, and subcylindrical basidiospores. Phanerochaete stereoides Sheng H. Wu is similar to P. cinerea by sharing grey hymenophore and brown subicular hyphae, but differs in having effuse-reflexed and tough basidiomata and leptocystidia (Wu 1995). Phanerochaete brunnea Sheng H. Wu also has brown subicular hyphae and lacks cystidia, but differs from P. cinerea in having soft basidiomata and loosely interwoven subicular hyphae and lacking hyphidia (Wu 1990). Phanerochaete porostereoides S.L. Liu & S.H. He differs from P. cinerea in having brown, tough, coriaceous basidiomata, slightly wider basidiospores (4.7–5.3 × 2.5–3.1 µm) and a distribution in temperate regions (Liu & He 2016). Phanerochaete thailandica Kout & Sádlíková differs from P. cinerea in having leptocystidia and larger basidiospores (7–8 × 4–4.5 µm, Sádlíková & Kout 2017). In the phylogenetic tree, two samples of P. cinerea formed a distinct lineage from morphologically similar species (Fig. 1).
Reference: Xu YL1 , Cao YF1 , Nakasone KK2 et al.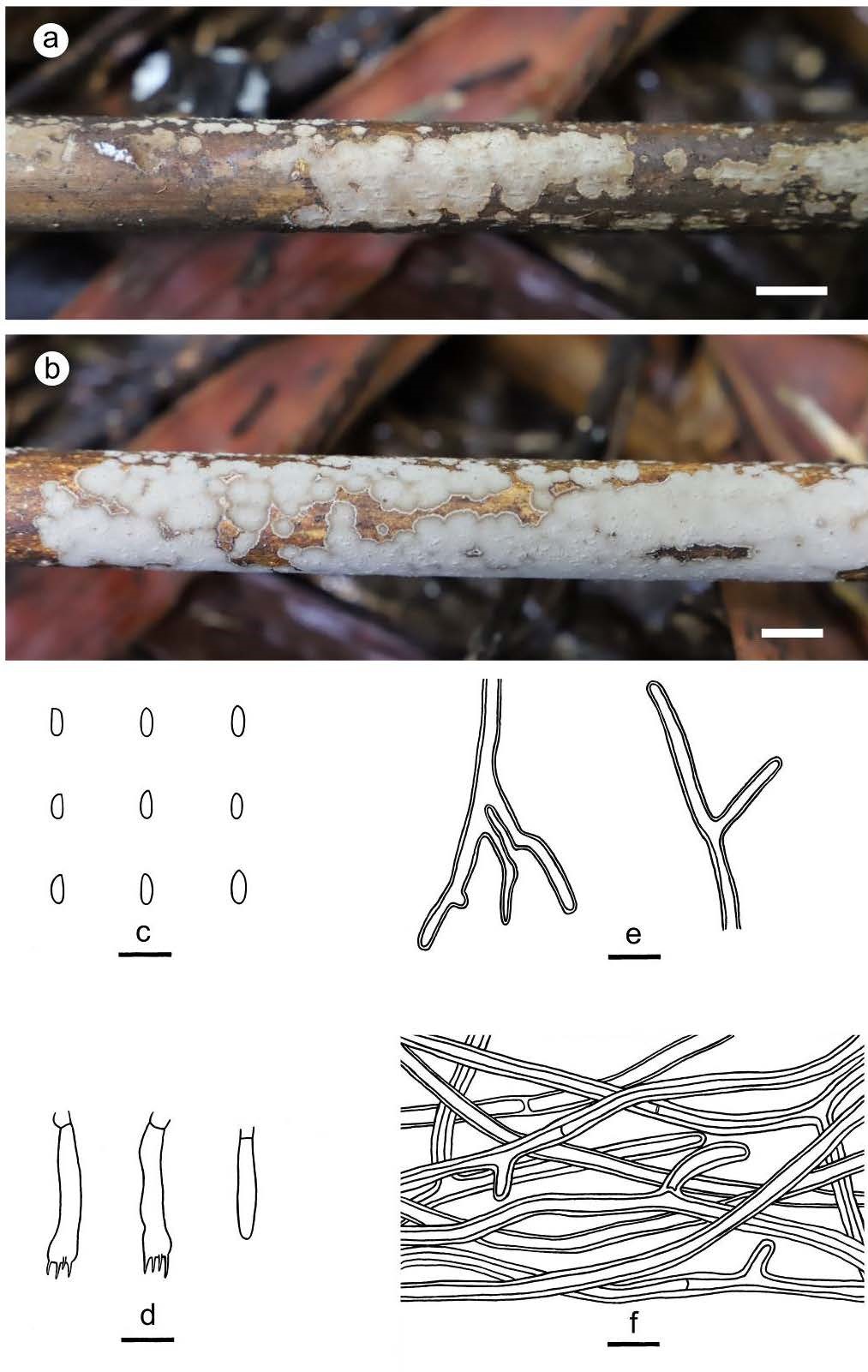
Figure 3 – Phanerochaete cinerea (a, c–f: from the holotype He 5998, b: from He 6003). a–b basidiomata. c basidiospores. d basidia and a basidiole. e hyphidia. f hyphae from subiculum. Scale bars: a–b = 1 cm, c–f = 10 µm