Tetraploa aquatica W.L. Li & H.Y. Su, sp. nov. 2020
Index Fungorum number: IF556723; Facesoffungi number: FoF 06215
Holotype: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Dulong river, on submerged decaying wood, 18 October 2016, Z.L. Luo, S-910 (MFLU 19–0995, holotype), ex-type living culture MFLUCC 19–0389; saprobic on decaying wood submerged in a stream of Gaoligongshan mountain, 21 August 2018, W.L. Li, S–1235 (MFLU 19–0996).
Morphological description
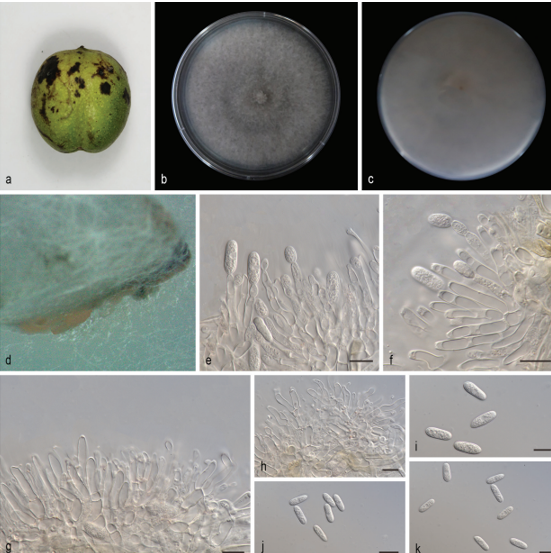
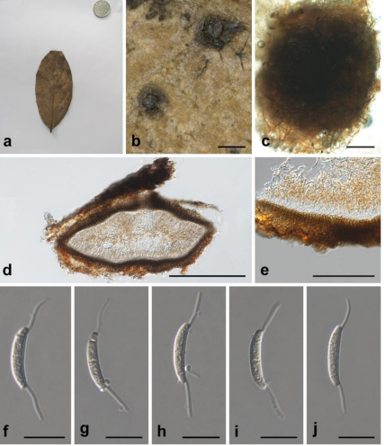
Saprobic on submerged decayed wood in freshwater habitats. Asexual morph: Hyphomycetous. Colonies effuse, brown or dark greyish brown. Mycelium partly immersed, composed of septate, branched, subhyaline, 2.5–3 μm wide, hyphae. Conidiophores indistinct, when present micronematous. Conidiogenous cells holoblastic, monoblastic or occasionally polyblastic, integrated, terminal or intercalary, determinate, cylindrical. Conidia solitary, dry, unbranched, septate, straight, verrucose, composed of a conidial body at the base and 4 brown to pale brown, setose, septate, apical appendages. Conidial body 22.5–27 μm long (x = 25 μm, SD = 2.3, n = 30), 20–24 μm wide (x = 22 μm, SD = 2, n = 30), pale brown, smooth, narrowly ovate or ovate, composed of 4 closely-adhered vertical columns of cells, with each column 2–3-septate. Appendages 98–134 μm long, (x = 116 μm, SD = 18, n = 30), 6–9 μm wide (x = 8 μm, SD = 1, n = 30) , pale brown at the base, almost hyaline at the apex, 6–10-pseudoseptate. Mature conidia with shallow furrows between 4-columns of cells which develop independently and later get compacted and tend to remain vertically to one another apically. Sexual morph: Undetermined. Culture characteristics:—Conidia germinating on PDA within 24 h and germ tubes produced from both ends. Colonies on PDA reaching 10 mm diam. at two weeks at room temperature 25 °C, in natural light, colonies on PDA irregular, with undulate edge, umbonate surface, obviously wrinkeled, paler brown in the umbone, dark gray in the periphery; in reverse dark brown to black.
Habitat: on submerged decaying wood
Distribution: China
GenBank Accession: SSU MT530454; LSU MT530452, MT530453; ITS MT530448, MT530449
Notes: Phylogenetic analyses of combined ITS, LSU and SSU sequence data indicates that our new species belongs to the genus Tetraploa and is close to Tetraplosphaeria nagasakiensis. Morphologically, Tetraploa aquatica shares some similar features with the asexual morph of Tetraplosphaeria nagasakiensis in having conidia with closely adhered cell columns, which are short-cylindrical, brown, verrucose at the base and euseptate with 4 setose appendages at the apex. However, Tetraploa aquatica differs from the latter in having smaller conidia (22.5–27 × 20–24 vs. 32.5–42 × 20–33 μm) and shorter appendages (98–134 × 6–9 vs. 95–225 × 2–3 μm). Moreover, the vertical columns of Tetraploa aquatica are 2–3-septate, aguttulate, constricted at septa; setose appendages are 6–10-septate and tend to remain parallel to one another apically, whereas Tetraplosphaeria nagasakiensis has cell columns of conidial body that are 4-septate, often with 5 large guttules, and 3–13-septate appendages, with divergent apical arms.
Reference: WEN-LI LI1,2,6, DAN-FENG BAO1,3,4,7, D. JAYARAMA BHAT5,8 et al.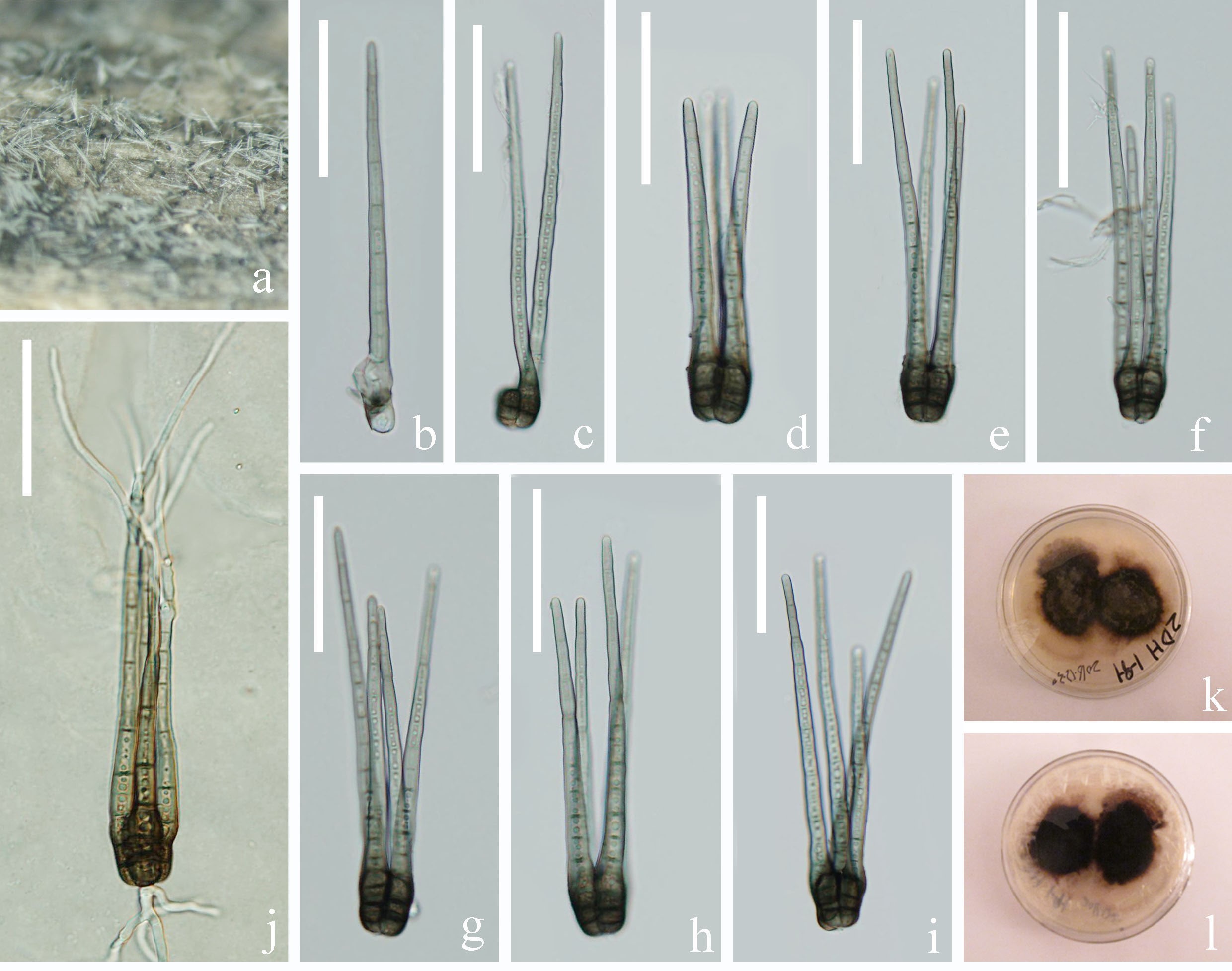
Tetraploa aquatica (MFLU 19–0995, holotype). a Colonies on substrate. b, c Conidia with separable columns. d–i Conidia. j Germinating conidium. k, l Colonies on PDA from surface and reverse at 45 days. Scale bars: b–i = 50 µm.