Russula guangxiensis G.J. Li, H.A. Wen & R.L. Zhao, sp. nov. 2020
Index Fungorum number: IF551492; Facesoffungi number: FoF01007
Holotype: CHINA. Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Wuzhou City, Tengxian County, Xiangqi Township, Xiangqi Village, 21 August 2013, Xin-Hua Chen 35 (HMAS 267867).
Morphological description
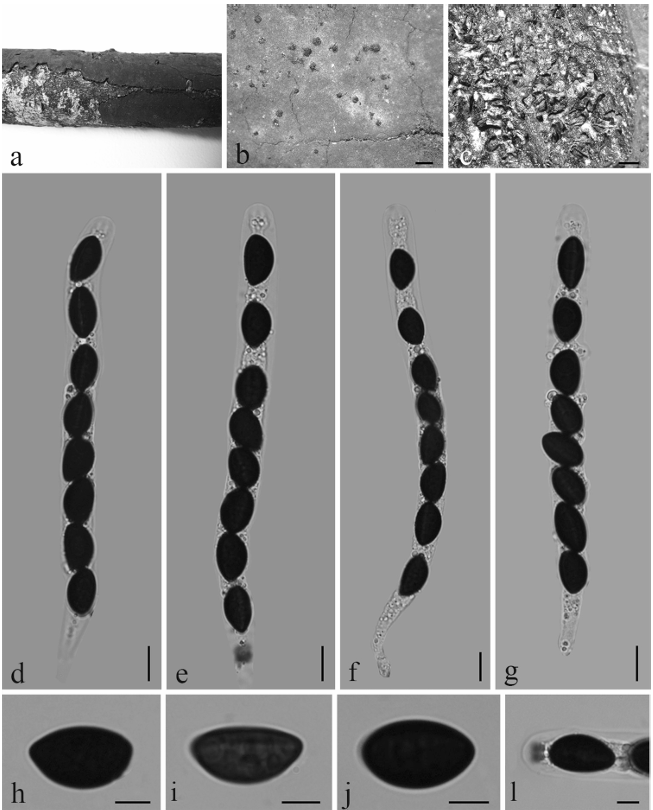
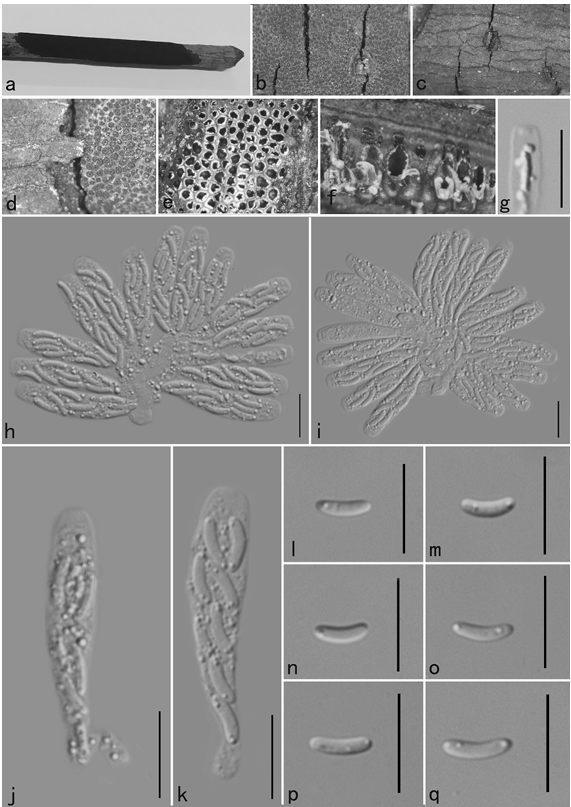
Basidiomata small to medium sized. Pileus 30–65 mm diam., first hemispheric to plano-convex, then expanding to applanate, finally slightly depressed in center to concave, smooth, viscid when wet, slightly glabrous when young, peeling 1/3–1/2 from the edge, sometimes desquamated in small patches, margin sometimes undulate, not striate, rarely cracked; pale pinkish red tinged with Begonia Rose (I1b) to Geranium Pink (I3d), intermixed with Strawberry Pink (I5d) in center, Hermosa Pink (I1f), Shrimp Pink (I5f), or even White (LIII) towards the margin. Lamellae adnate, equal to sub equal, 2–4 mm in height, 15–21 pieces per cm at the edge, rarely forked near the stipe and pileal edge, often interveined, White when fresh, slowly turning Orange Cinnamon (XXIX13″) to Mikado Brown (XXIX13″i) when injured, lamellulae absent. Stipe central, 6–9×0.8–1.5 cm, subcylindrical, surface dry, smooth, rarely rugulose longitudinally, dull, sometimes slightly attenuate upwards or downwards, white, a tinge of when injured and dry, first stuffed, becoming hollow at last. Context 2–4 mm at the center of the pileus, white, fragile, odour indistinct, taste mild. Spore print White (RomagnesiIa).
Habitat: in broadleaved forests (dominated by Lithocarpus spp.).
Distribution: China
GenBank Accession:
Notes: The combination of white spore print, mild taste, bright red pileus, pileipellis with primordial hyphae but without pileocystidia, pseudoparenchymatic subpellis, and the topology of phylogenetic analysis of ITS sequences clearly place R. guangxiensis within subgenus Incrustatula Romagn. Subsection Roseinae Singer ex Sarnari. Two new taxa, R. guangxiensis and R. hakkae, clustered together with strong support (BS 92 %, PP 1.00) with most members of subsection between the two new taxa through a fairly good support (BS 80 %, PP 1.00). The two Roseinae involved in this study. Our phylogenetic analysis also indicated a close relationship new taxa have context without distinctive odour, amyloid and distinct basidiospores uprahilar area, and habitat of Lithocarpus forest. However, R. hakkae has an acrid tasted context, larger basidiospores with dense ornamentation up to 1.2 μm in height, and a palisade epipellis.
Reference: Hiran A. Ariyawansa1,3 & Kevin D. Hyde1,2,3,15 & Subashini C. Jayasiri1,3 et al.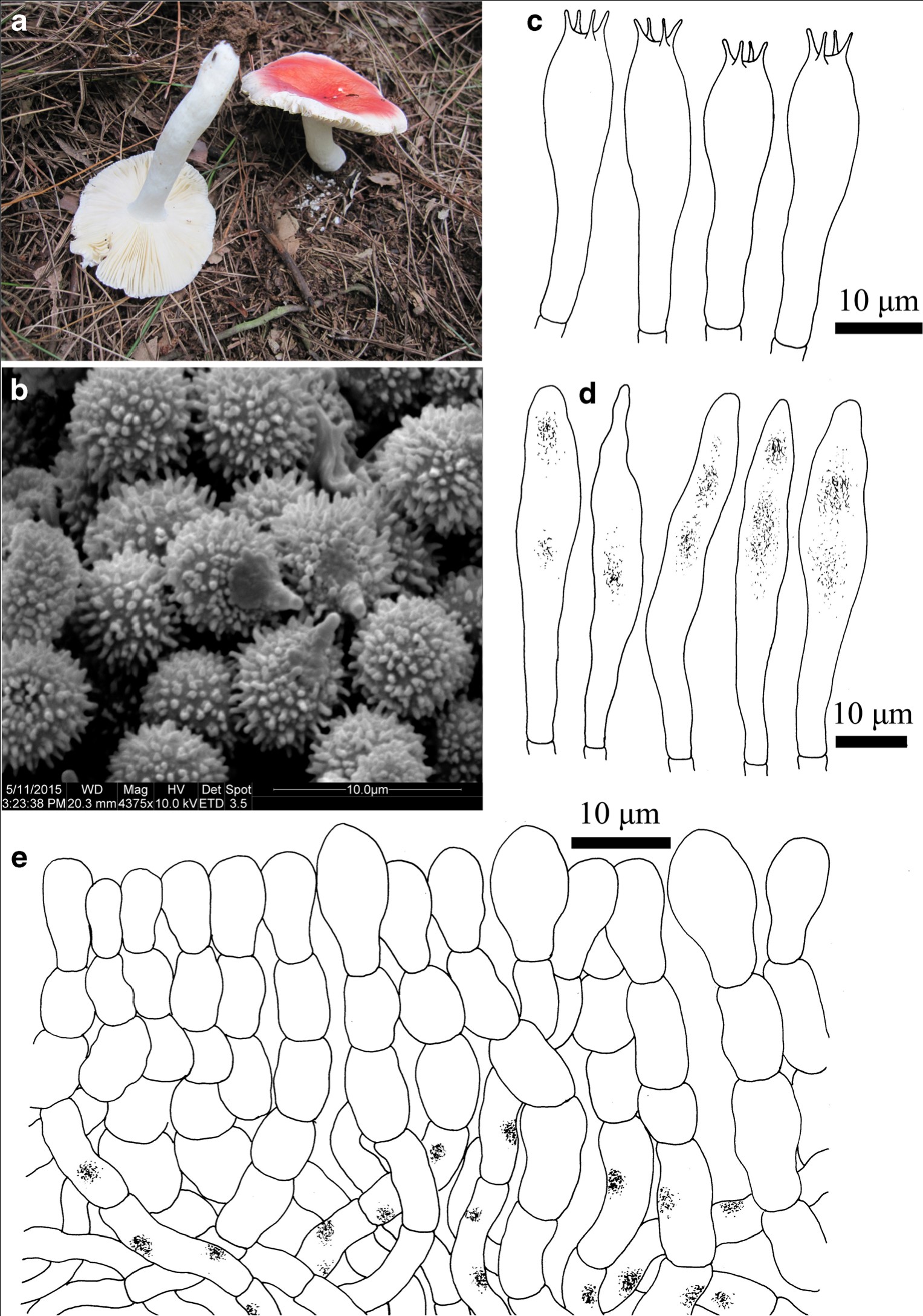
Russula guangxiensis (holotype) a Basidiocarps b Basidiospores c Basidia d Pleurocystidia e Pileipellis