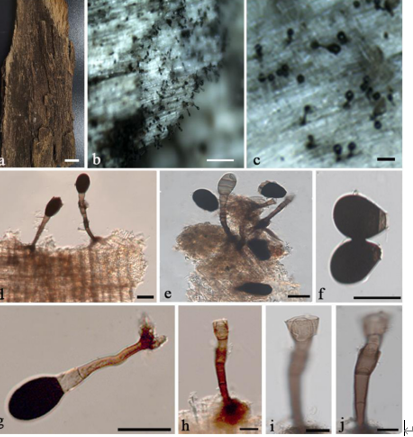
Arthrinium biseriale Y. Feng and Z.Y. Liu, sp. nov.2021
Index Fungorum number: IF558136
Holotype: HKAS 111961
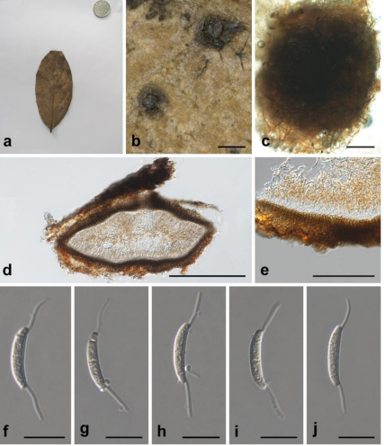
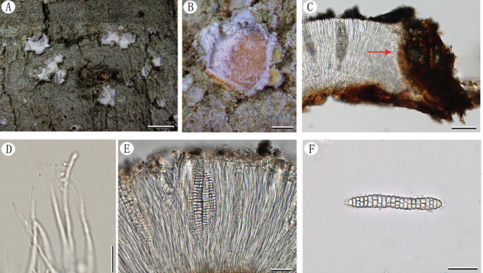
Sexual morph:Stromata scattered to gregarious, immersed to erumpent, later becoming superficial, dark brown to black, fusiform, forming a slit-like opening at the apex, multi-loculate, membranous, with a periphysate ostiole. Ascomata 122–153 μm high, 138–207 μm diam, arranged in rows, dark brown to black. Peridium 11–19 μm wide, composed of several layers of dark brown to hyaline cells of textura angularis. Hamathecium 3–4 μm wide, comprising dense, hyaline, septa paraphyses. Asci 84–116 μm × 18–25 μm (x¯ = 97 μm × 21 μm, n = 20), 8-spored, unitunicate, clavate, apically rounded, with an indistinct pedicel. Ascospores 22–28 μm × 7–11 μm (x¯ = 25 μm × 9 μm, n = 30), biseriate, fusiform, curved at the bottom, obtuse at both ends, slightly wider in the middle, hyaline, 1-septate, constricted at the septum, mostly curved at the lower cell, rarely straight, with a large upper cell and a small lower cell, smoothwalled. The lower cell has 1-guttulate, the upper cell has 1–3 big guttulate in the middle surrounded by multiple small guttulate with a shallow 4–7 μm thick gelatinous sheath in the early. Growing to a later stage, the guttulate filled the entire spore, and the gelatinous sheath dissolves easily. Asexual morph: On WA, Hyphae 2.5–6.0 μm diam, hyaline, branched, septate, some curled in a ring structure. Conidiophores 12.0–44.0 μm × 2.5–5.0 μm (x¯ = 20.0 μm × 3.5 μm, n = 20), straight or flexuous, smooth, thin-walled, unbranched, hyaline to pale brown, cylindrical, cyathiform, having transverse septa, often reduced to conidiogenous cells. Conidiogenous cells 5.0–22.0 μm × 2.5–5.0 μm (x¯ = 10.0 μm × 3.5 μm, n = 20), integrated, hyaline to pale brown, doliiform to ampulliform, or lageniform. Conidia 7–9 μm long (n = 30), brown, smooth in surface view, and 7–11 μm long (n = 30), lenticular, with a paler equatorial slit in side view, globose to ellipsoid with many guttules.
Culture characters :Ascospores germinated on WA within 24 h and germ tubes produced from middle and lower end. Colonies fast grown on PDA at 25◦C, reached 7 cm in 7 days at 25◦C. Colonies evenly tiled, with a large number of aerial hyphae, white, velvety, thin, gray-white on the reverse side and dirty white in the center
Habitat:on dead culms of bamboo
Distribution:china, Guizhou Province, Chishui City, Zhuhai National Forest Park,
GenBank Accession:CGMCC 3.20135 lsu MW478885;its MW481708; tef MW522938;tub MW522955.GZCC 20–0099 lsu MW478886; its MW481709;tef MW522939;tub MW522956.GZCC 20–0100 lsu MW478887;its MW481710;tef MW522940;tub MW522957.
Notes:Three strains representing Arthrinium biseriale clustered in a well-supported clade which are closely related to A. gelatinosum, but phylogenetically distinct and can be recognized as two different species (99% sequence similarity in ITS; 99% in TEF; 98% in TUB2). Morphologically, Arthrinium biseriale has smaller stromata (122–153 μm × 138–207 μm vs. 144–199 μm × 184–214 μm) and the spores of A. biseriale are more curved than those of A. gelatinosum.
Reference: Feng, Y. , Liu, J. K. J. , Lin, C. G. , Chen, Y. Y. , & Liu, Z. Y. . (2021). Article additions to the genus arthrinium (apiosporaceae) from bamboos in china. Frontiers in Microbiology, 12, 661281.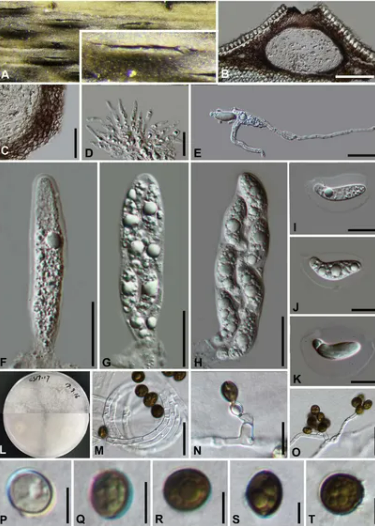
Arthrinium biseriale (HKAS 111961, holotype). (A) Appearance of stromata on bamboo host. (B) Vertical section of stroma. (C) Peridium. (D) Paraphyses. (E) Germinating ascospore. (F–H) Asci. (I–K) Ascospore. (L) Culture. (M) Hyphae. (N,O) Conidiophore and conidiogenous cells. (P–T) Conidia. Scale bars: (B) = 50 μm. (C) = 20 μm. (D) = 10μm. (E–H) = 20 μm. (I–K) = 10 μm. (M) = 20 μm. (N) = 10 μm. (O) = 20 μm. (P–T) = 5 μm.