Neocryphonectria chinensis C.M. Tian, N. Jiang & Crous 2020
MycoBank MB831777
Holotype: CHINA. Beijing City, Fangshan District, on branches of Carpinus turczaninowii, 5 Oct. 2018, N. Jiang & C.M. Tian (holotype BJFC-S1737, extype living culture CFCC 53025, living culture CFCC 53026); ibid., paratype BJFC-S1738, living ex-paratype culture CFCC 53029; ibid., BJFC-S1739, living culture CFCC 53030.
Morphological description
Sexual morph: Unknown.
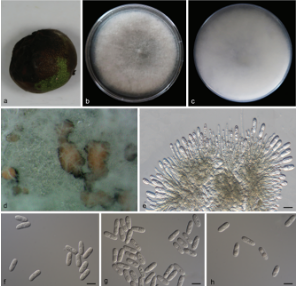
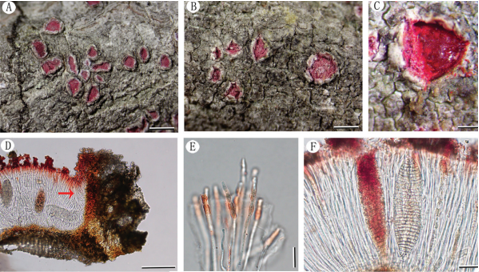
Asexual morph: Conidiomata multiloculate, pulvinate; necks short or absent, semi-immersed, orange, 800–3000 μm wide, 100–250 μm high. Conidiophores cylindrical, aseptate, hyaline, sometimes reduced to conidiogenous cells. Conidiogenous cells lining inner cavity of conidiomata, phialidic, ampulliform, inconspicuous, with attenuated or truncate apices, hyaline, smooth, 4.5–35 × 1.5– 10.5 µm. Conidia dimorphic, microconidia minute, cylindrical, aseptate, hyaline, (3.5–)4–4.5(–5) × 1.5–2.5 µm; macroconidia fusoid, aseptate, hyaline, (22–)25–27.5 (–29) × (10.5–)11.5–12.5(–14) µm.
Culture characteristics: Cultures incubated on PDA and OA at 25 C in darkness. On PDA effuse, first white and turning to pale brown after 10 d, reverse dark brown. On OA profuse cottony, with concentric rings, white to pale brown on surface, and gray in reverse.
Habitat: On branches of Carpinus turczaninowii.
Distribution: In China.
GenBank Accession: ITS: MN172413; 28S: MN172396; tef1-α: NA; rpb2: NA
Notes: Neocryphonectria chinensis is presently known from its asexual morph, which can be easily distinguished from other species of Cryphonectriaceae and Foliocryphiaceae. Neocryphonectria chinensis occurs on the same host with N. carpini and has the same geographic distribution. Neocryphonectria chinensis is known in only asexual morph and N. carpini in sexual morph. However, they can be distinguished by 33 bp differences in ITS and 6 bp differences in 28S.
Reference: Ning Jiang a, Xinlei Fana, Chengming Tian a et al.
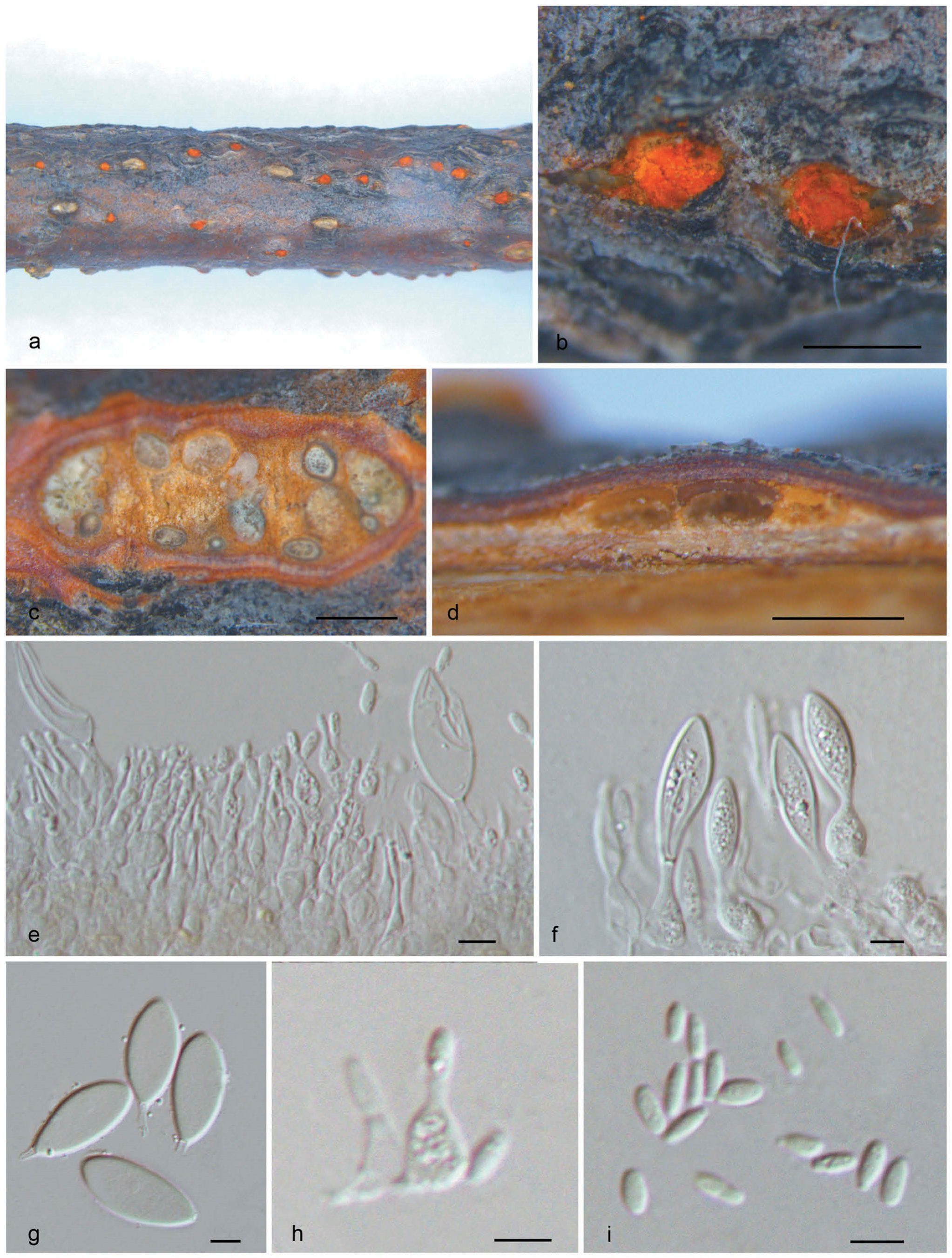
Morphology of Neocryphonectria chinensis on Carpinus turczaninowii (holotype, BJFC-S1737). a, b. Habit of conidiomata on branch. c. Transverse section of conidiomata. d. Longitudinal section through conidiomata. e, f, h. Conidiogenous cells with attached conidia. g. Macroconidia. i. Microconidia. Bars: b–d = 0.5 mm; e–i = 5 μm.