Clitocella orientalis S.P. Jian & Zhu L. Yang, sp. nov. 2020
MycoBank MB831313
Holotype: CHINA. HUBEI PROVINCE: Shennongjia Forestry District, Muyu Town, Shennongding Scenic Area, gregarious, growing on rotten wood in broadleaved (Quercus) forest, alt. 1960 m, 13 Jul 2012, Q. Zhao 1504 (holotype KUN-HKAS78763).
Morphological description
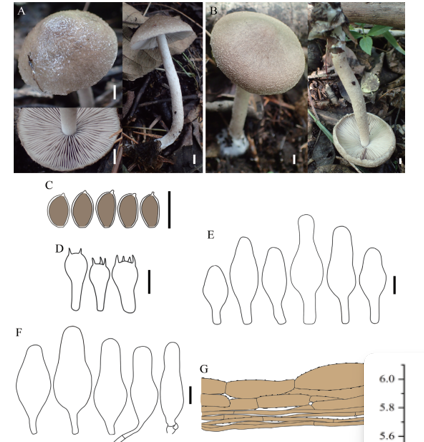
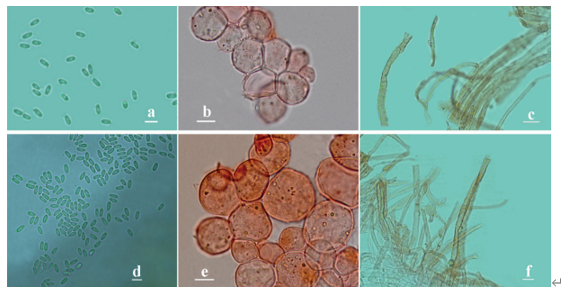
Basidiospores (4–)4.5–6 × 4–5 μm, Lm × Wm = 5.08 (± 0.37) × 4.48 (± 0.35) μm, Q = 0.96–1.32 (Qavg = 1.14 ± 0.10) [88/4/4], globose to subglobose, sometimes broadly ellipsoid in profile view, slightly angled in polar or face view with obscure minute pustules or bumps. Basidia 20–28 × 5–7 μm, clavate, hyaline, 4-spored, rarely 2-spored; sterigmata 3–5 μm long. Lamellar trama more or less regular, composed of 3–6 μm wide, hyaline hyphae; subhymenium consisting of filamentous hyphal segments. Lamellae edges fertile. Pleurocystidia and cheilocystidia absent. Pileipellis a cutis composed of more or less radially and loosely arranged, slightly gelatinized, hyaline, smooth, cylindrical hyphae, 2–6 μm wide; terminal hyphae subcylindric, fusiform or narrowly clavate, 3–5 μm wide; subcutis made up of compactly arranged, thin-walled, hyaline, smooth, cylindrical hyphae, 3–6 μm wide, usually interweaved by somewhat filamentous, hyaline hyphae. Stipitipellis a gelatinized cutis composed of compactly arranged, gelatinized, thin-walled, hyaline hyphae, 3–5 μm wide, with some upturned terminal hyphae. Caulocystidia absent. Clamp connections absent.
Habitat: on rotten wood in broadleaved (Quercus) forest.
Distribution: central China at mid- to high altitudes (1500–2000 m).
GenBank Accession: ITS/LSU MK748199; β-tubulin gene MN896026; EF-1α MN896074; calmodulin gene MN896102
Notes: Clitocella orientalis is similar to Clc. obscura (Pilát) Vizzini et al., Clc. mundula, Clc. popinalis, Clc. himantiigena (Speg.) Silva-Filho & Cortez, and Clc. pallescens Silva-Filho & Cortez. However, according to Baroni (1981; as Rhodocybe), both Clc. obscura or Clc. popinalis produce a distinctly reddish reaction when 3% KOH is placed on the pileus surface. Clitocella orientalis exhibits no such reaction. Moreover, the pileus of Clc. orientalis is paler, and both the pileus and stipe are usually viscid when wet. Clitocella himantiigena and Clc. pallescens, originally described from the South America, differ from Clc. orientalis by pileal color and basidiospore size (Singer 1949; Silva-Filho et al. 2018).
Reference: Si-Peng Jian, Tolgor Bau, Xue-Tai Zhu et al. (2020): Clitopilus,Clitocella, and Clitopilopsis in China.

Basidiomata of Clitopilus, Clitocella, and Clitopilopsis. A–C. Clitopilus umbilicatus (A. KUN-HKAS80370. B. KUN-HKAS104509. C. KUN-HKAS80310, holotype). D–E. Clitopilus yunnanensis (D. KUN-HKAS59712. E. KUN-HKAS82076). F. Clitocella mundula (HMJAU7275). G–H. Clitocella orientalis (G. KUN-HKAS78876. H. KUN-HKAS78763, holotype). I. Clitopilopsis albida (KUN-HKAS104519, holotype). Bars = 10 mm