Tomentella dimidiata H.S. Yuan, X. Lu & Y.C. Dai 2020
Index Fungorum number: IF555738; Facesoffungi number: FoF 05614
Holotype: CHINA, Liaoning Province, Qingyuan County, Experimental Station of Forest Ecology, on fallen angiosperm branch, 3 August 2016, Yuan 11205 (IFP 019265, holotype); Jilin Province, Changbaishan Nature Reserve, on fallen angiosperm branch, 7 August 2016, Yuan 11267 (IFP 019266).
Morphological description
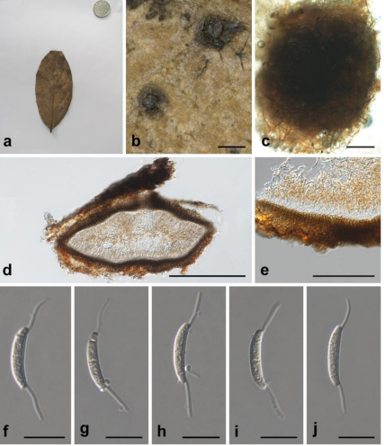
Basidiocarps annual, resupinate, adherent to the substrate, mucedinoid, without odour or taste when fresh, 0.2–0.4 mm thick, continuous. Hymenophoral surface smooth, golden brown to brown (5D7–6F5) and turning lighter than the subiculum when dry. Sterile margin often determinate, byssoid, concolorous with hymenophore. Rhizomorphs present in subiculum and margins, 12–50 μm diam; rhizomorphic surface more or less smooth; hyphae in rhizomorph dimitic, highly differentiated, of type G (this a new type, see in the notes); central hyphae usually simple septate, thick-walled, unbranched, 2–4 μm diam, pale brown in KOH, cyanophilous, inamyloid; skeletal hyphae from outer part of rhizomorphs thick-walled, unbranched, 1.5–2.5 μm diam, pale brown in KOH, cyanophilous, inamyloid. Subicular hyphae monomitic; generative hyphae clamped, thick-walled, 4–6 μm diam, without encrustation, pale brown in KOH, acyanophilous, inamyloid. Subhymenial hyphae clamped, thin-walled, 4–6 μm diam; hyphal cells short and not inflated, pale brown in KOH, cyanophilous, inamyloid. Cystidia absent. Basidia 10–40 μm long and 4.5–12.5 μm diam at apex, 3.5–5.5 μm at base, with a clamp connection at base, utriform, not stalked, sinuous, without transverse septa, pale brown in KOH and in distilled water, 4-sterigmate; sterigmata 5.5–11.5 μm long and 2–3 μm diam at base. Basidiospores slightly thick-walled, (6.5– )7–7.5(–8) × (5–)5.5–7(–7.5) μm, L = 7.07 μm, W = 5.99 μm, Q = 1.15–1.26 (n = 60/2), subglobose to bi-, tri- or quadralobed in frontal and lateral views, echinulate, pale brown in KOH and distilled water, cyanophilous, inamyloid; echinuli usually grouped in 2 or more, up to 2 μm long.
Habitat: On fallen angiosperm branch.
Distribution: In China.
GenBank Accession: ITS: MK211704, MK211705; LSU: MK446355, MK446356.
Notes: Some species of Tomentella have been reported to have dimitic rhizomorphs, for instance, T. botryoides, T. brunneorufa M.J. Larsen, T. fungicola (Litsch.) M.J. Larsen, T. pilosa, T. punicea (Alb. & Schwein.) J. Schröt. and T. umbrinospora M.J. Larsen (Kõljalg 1996; Daemmrich 2006; Peintner and Dämmrich 2012). In addition, some species of Pseudotomentella Svrček and Odontia Pers. also have dimitic rhizomorphs (Agerer et al. 2001; Tedersoo et al. 2014; Yuan et al. 2018). Agerer recognized six different types (type A–F) of the rhizomorphic hyphal organization, but all these types are monomitic hyphal systems (Agerer 1987–2008). Yorou mentioned the presence of dimitic rhizomorphs in T. punicea and T. umbrinospora, but he treated this kind of structure as type C. However, the dimitic hypal system of rhizomorphs is significantly different from the monomitic hyphal structure. We name this kind of structure in rhizomorphs as type G.
Reference: Hai‑Sheng Yuan1,2· Xu Lu1,2 · Yu‑Cheng Dai3 ·
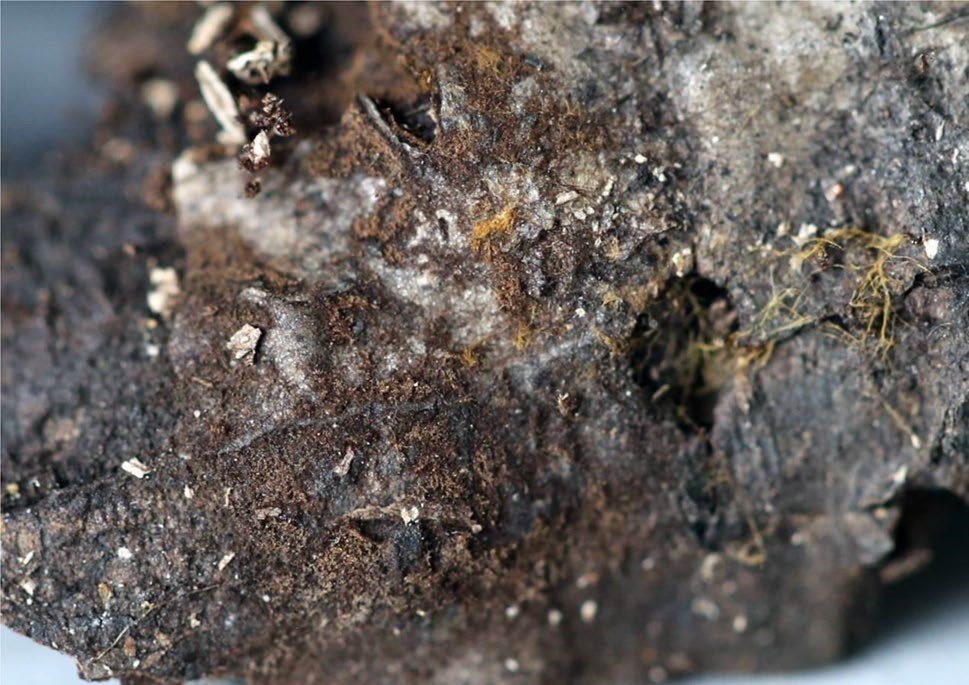

A basidiocarp of Tomentella dimidiata (IFP 019265, holotype)