Chrysosporium pallidum Z.F. Zhang & L. Cai, sp. nov. 2020
Index Fungorum number: 556418; Facesoffungi number: FoF 08437
Holotype: CHINA, Guangxi, Guilin, E’gu Cave, N 24.942°, E 110.511°, on animal faeces, May 2016, Z.F. Zhang, HMAS 247992 (holotype designated here), ex-type living culture CGMCC3.19575 = LC12583; ibid., LC12670.
Morphological description
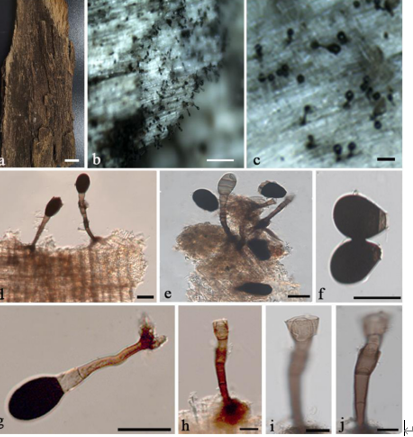
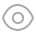
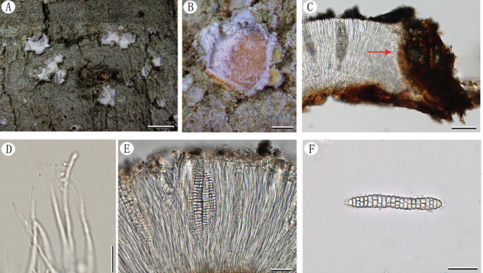
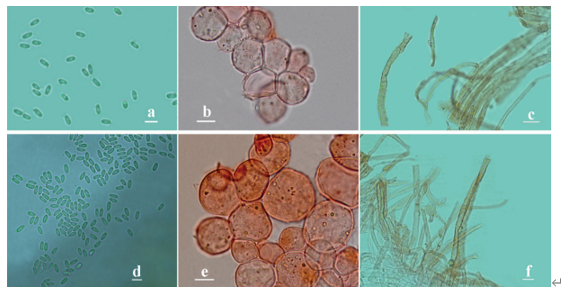
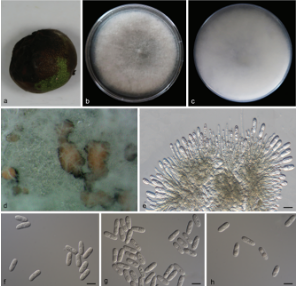
Hyphae hyaline, septate, branched, smooth, 2.0–3.0 μm diam., racquet hyphae present, up to 6 μm wide. Sexual morph Ascomata abundant, solitary, or in clusters, cottony, globose, white initially, becoming pale yellow when aging, with conidia produced on surface, up to 750 μm diam. Peridial hyphae difficult to distinguished from aerial hyphae, septate, branched and anastomosed, terminated by short blunt prominences, smooth, thick-walled, hyaline, 2.5–4.0 μm diam. Asci 8-spored, pyriform, subglobose or globose, hyaline, 8.0–13.0 × 7.5–10.5 µm. Ascospores oblate, globose in front view, hyaline, smooth, 2.5–3.5 µm ( x̄ ± SD = 3.0 ± 0.21 µm, n = 70). Sexual morph Arthroconidia abundant, intercalary, lateral or terminal, unicellular, hyaline; intercalary conidia cylindrical or ellipsoidal with truncated base, 3.5–6.5 × 2.0–3.5 µm (mean = 6.6 ± 1.28 × 2.9 ± 0.46 µm, n = 40); lateral or terminal conidia arising from aerial hyphae directly, pyriform or clavate with truncated base, 4.0–7.0 × 2.5–4.0 µm (mean = 5.3 ± 0.73 × 3.4 ± 0.43 µm, n = 40). Culture characteristics—Colonies on PDA attaining 28–34 mm diam. after 4 weeks, flat, felty, annular, margin with fimbriate, ivory (1A1) to white from margin to center. Colonies on OA attaining 27–30 mm diam. after 4 weeks, flat, felty, annular, white. Reverse white to beige (30A2). Colonies on SNA attaining 26–29 mm diam. after 4 weeks, margin rhizoids, floralwhite (1A2), aerial mycelia sparse. Reverse floralwhite (1A2). Sporulation within 3 weeks on SNA.
Habitat: on animal faeces.
Distribution: Guangxi, Guilin, E’gu Cave, China.
GenBank Accession:
Notes: Chrysosporium pallidum is phylogenetically allied to C. carmichaelii Oorschot and Myriodontium keratinophilum Samson & Polon (Fig. 15). C. pallidum differs from C. carmichaelii by its more abundant intercalary conidia and sessile lateral conidia. Conidia of Myriodontium keratinophilum are lateral with short stem (conidiogenous cell), comparing with sessile lateral conidia and the presence of intercalary, lateral or terminal of C. pallidum. In addition, neither C. carmichaelii nor myriodontium keratinophilum sexual stage.
Reference: Zhi‑Feng Zhang ,Shi‑Yue Zhou ,Lily Eurwilaichitret al.
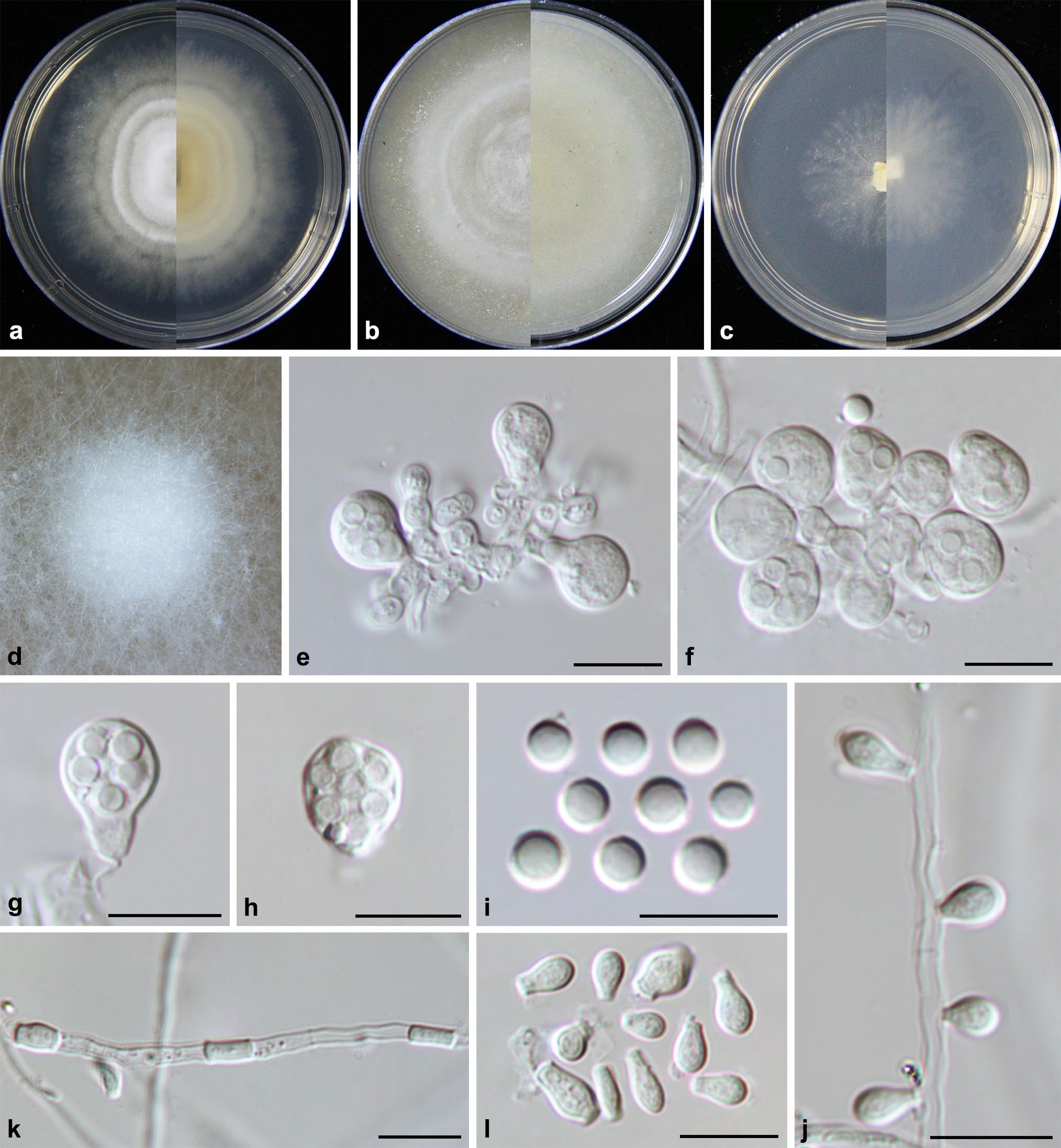
Chrysosporium pallidum (from ex-holotype CGMCC3.19575). a–c Upper and reverse views of cultures on PDA, OA and SNA 4 weeks after inoculation; d ascomata; e–h asci; i ascospores; j–l arthroconidia. Scale bars: e–l 10 μm.