Agaricus luteopileus R.L. Zhao & B. Cao, sp. nov. 2020
Fungal Names: FN 570670
Holotype: CHINA. TIBET: Nyingchi, Mainling, scattered on ground in coniferous forest, 29 Jul 2012, Ruilin Zhao ZRL2012604 (holotype HMAS 253907).
Morphological description
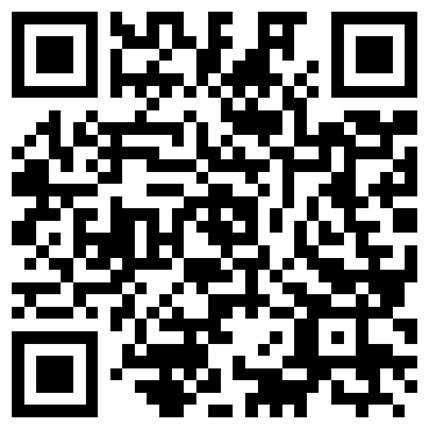
Pileus 80–140 mm wide, at first broadly parabolic, then convex, and finally applanate with uplifted margin; surface dry, covered by yellowish squamulose against the white background; edge slightly exceeding. Lamellae free, up to 6 mm broad, crowded, with intercalated lamellulae, at first pink or light grayish red, brown, finally dark brown. Stipe 110–130 × 10–20 mm, cylindrical, clavate, hollow, white, smooth above the annulus, fibrillose below the annulus, becoming yellowish when bruised. Annulus superior, membranous, fragile, white, smooth on the upper surface and fibrillose on the lower surface. Context white when exposed. Odor of almond. KOH reaction yellow;
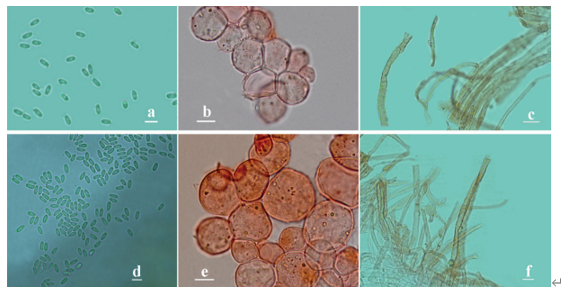
Schäffer’s reaction reddish orange on pileus and stipe. Basidiospores (7.5–)8–9 × 4.5–5(–5.5) μm [x¯= 8.2 × 4.8 μm, Q = 1.6–1.8(–1.9), Qm = 1.7, n = 30], oblong ellipsoid, and rarely ovoid, smooth, thick-walled, brown. Basidia 23.5–26 × 8–9 μm, 4-spored, clavate or slightly truncate at the apex, hyaline, smooth. Cheilocystidia
17.5–26 × 8–16 μm, hyaline, simple or sometimes catenulate, pyriform, capitulum or with median constriction. Pileipellis a cutis of cylindrical hyphae, 3.5–8 μm wide, not or slightly constricted at septa hyaline.
Habitat: on ground in coniferous (Abies) forest.
Distribution: southwest China.
GenBank Accession: ITS KT951375; 28S KT951515; tef1 KT951620
Notes: Agaricus luteopileus is represented by two specimens from Tibet in a well-supported clade (95/0.96 BS/PP) (FIG. 1). Agaricus luteopileus is similar to A. augustus, but the latter has a larger pileus and larger basidiospores (Parra 2013; Kerrigan 2016).
Reference: Bin Cao , Mao-Qiang He , Zhi-Lin Ling et al. (2020): A revision of Agaricus section Arvenses with nine new species from China.
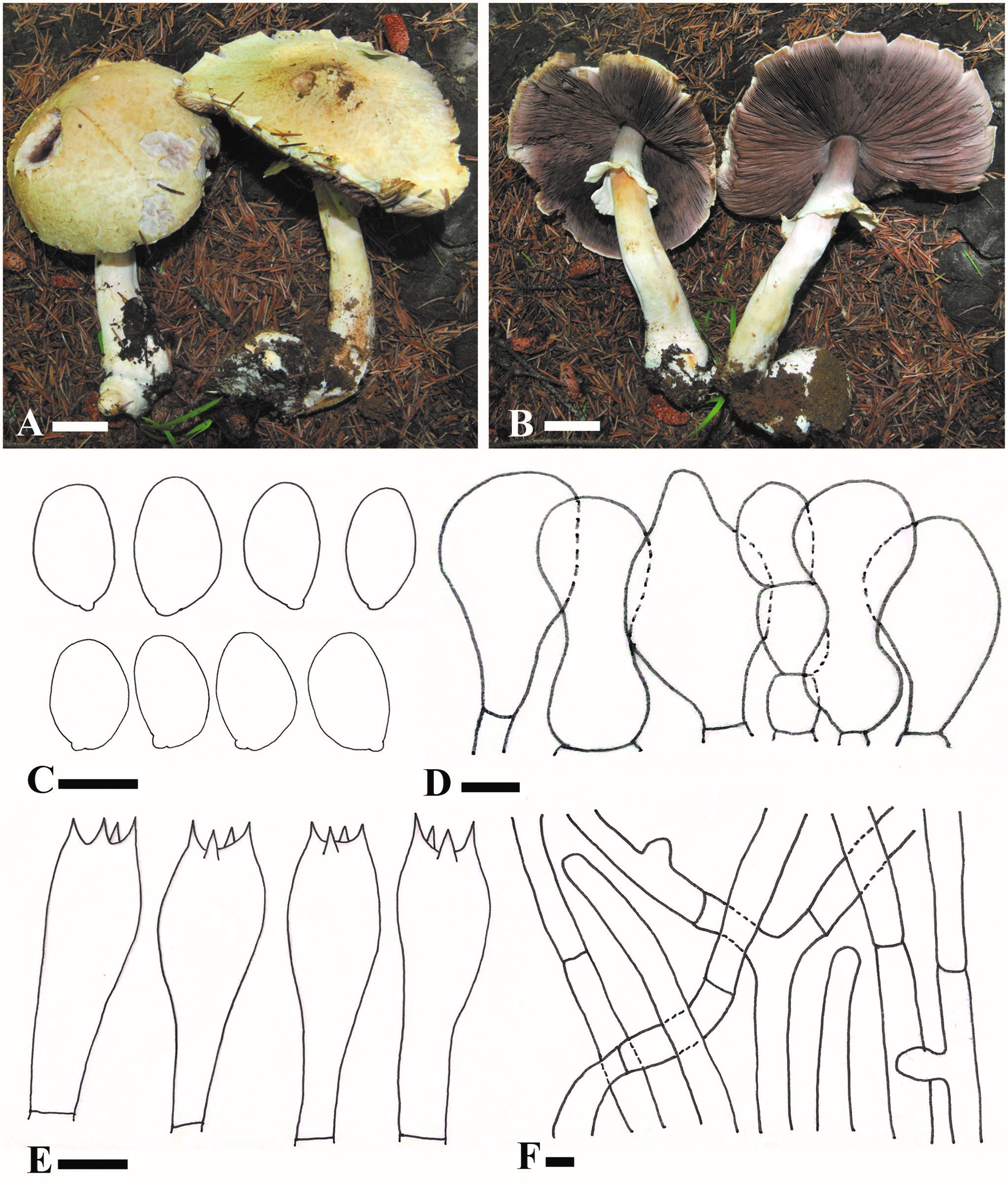
Agaricus luteopileus (ZRL2012604, holotype). A, B. Basidiomes. C. Basidiospores. D. Cheilocystidia. E. Basidia. F. Pileipellis hyphae. Bars: A, B = 2 cm; C–F = 5 μm.