Acrogenospora basalicellularispora D.F. Bao, Z.L. Luo, K.D. Hyde & H.Y. Su, sp. nov. 2020
Index Fungorum number: IF 557596; Facesoffungi number: FoF 07981
Holotype: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Gaoligongshan Mountain, on decaying wood submerged in a stream, August 2015, A.L. Shi, S-431 (MFLU 20–0288, holotype); ex-type culture, MFLUCC 16–0992.
Morphological description
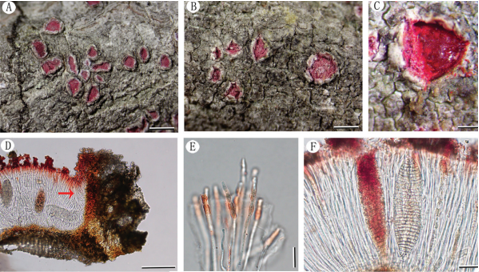
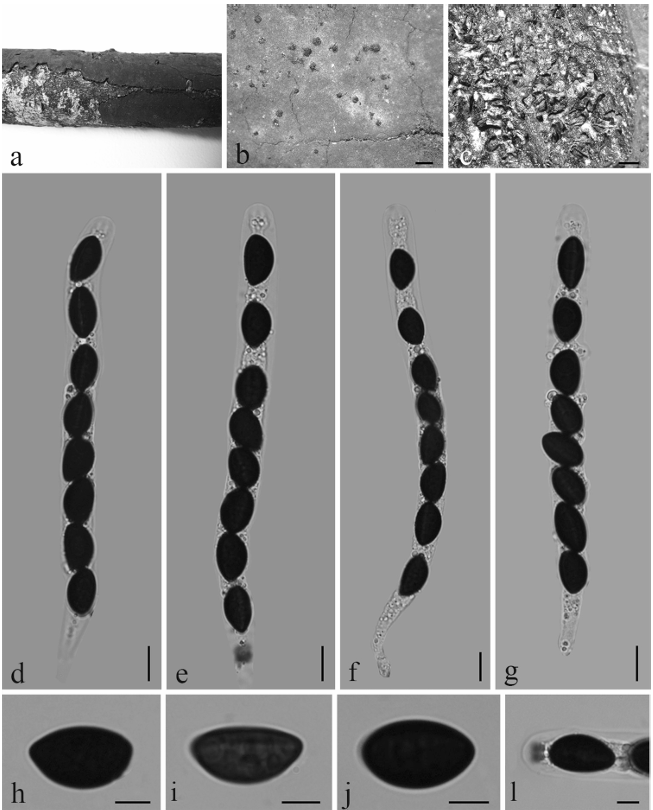
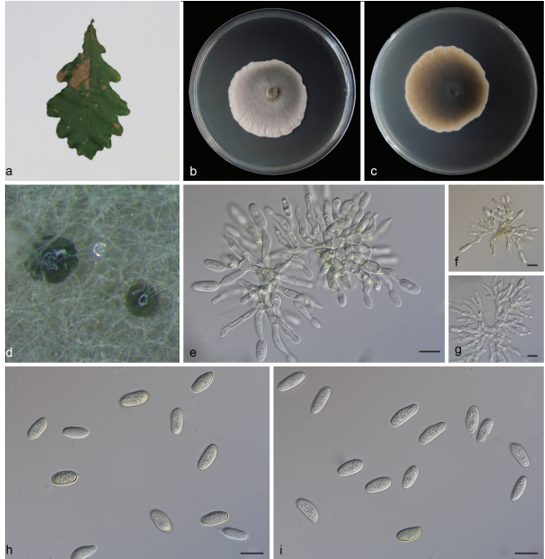
Saprobic on submerged decaying wood. Sexual morph: Undetermined. Asexual morph: Colonies effuse on natural substrate, hairy, dark brown. Mycelium mostly immersed, composed of grayish brown, septate, branched, smooth hyphae. Conidiophores 260–395 × 8–12 µm (x¯ = 327 × 10 µm, n = 20) wide, mononematous, macronematous, solitary, cylindrical, erect, straight or slightly flexuous, mostly unbranched, septate, brown to dark brown, slightly paler toward apex, smooth.
Conidiogenous cells holoblastic, monoblastic, integrated, initially terminal, later becoming intercalary, cylindrical, smooth, pale brown, proliferating percurrently. Conidia 27.5–33.7 × 21.7–25.8 µm (x¯ = 30.6 × 23.7 µm, n = 30) wide, acropleurogenous, solitary, dry, broadly obovoid to spherical, smooth, pale orangebrown to olivaceous brown, aseptate, with several small or large guttules, with a small, hyaline, subcylindrical to subglobose basal cell, germinating from basal cell.
Habitat: on decaying wood submerged in a stream.
Distribution: Yunnan Province, Gaoligongshan Mountain, china.
GenBank Accession: LSU MT340729
Notes: In the phylogenetic analysis, Acrogenospora basalicellularispora clustered with A. sphaerocephala (CBS206.36) with low support (66% ML and 0.98 BYPP). Unfortunately, CBS 206.36 lacks a morphological description and only LSU sequence data is available in GenBank. Morphologically, our new isolate can be distinguished from other Acrogenospora species by its pale orange-brown to olivaceous brown, broadly obovoid to spherical conidia with several small to large guttules and a small, hyaline, subcylindrical to subglobose basal cell. In our study, A. aquatica also has conidia with a basal cell. However, we can distinguish them by the shape (broadly obovoid to spherical vs. subprolate to broadly ellipsoidal) and color (pale orange-brown to olivaceous brown vs dark brown to black) of conidia and size (260–395 × 8–12 vs. 200–250 × 7.5–9.5 µm) of conidiophores.
Reference: Dan-Feng Ba1,2,3, Eric H. C. McKenzie4, D. Jayarama Bhat5 et al.
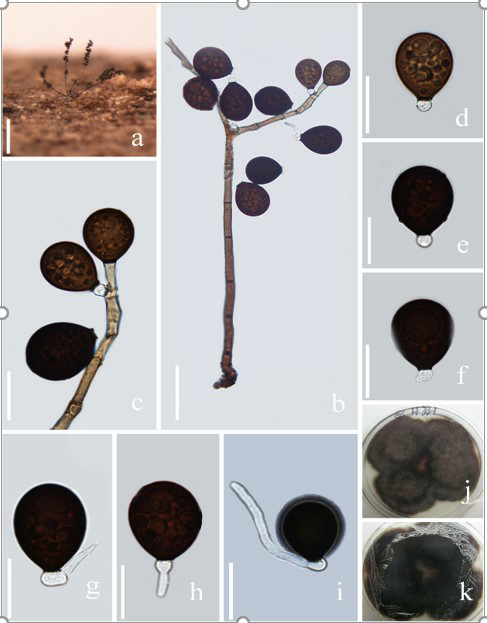

Acrogenospora basalicellularispora. (MFLU 20–0288, holotype) (a) Colony on wood. (b) Conidiophores, conidiogenous cells and conidia. (c) Conidiogenous cells and conidia. (d-h) conidia. (i) Germinating conidium. (j-k) Culture on MEA (upper and lower view). Scale bars. (a)200µm. (b)50µm. (c-i)20µm.