 264
264
Rhytidhysteron magnoliae N.I. de Silva, Lumyong S & K.D. Hyde 2020
Index Fungorum number: IF 557220; Facesoffungi number: FoF 07369
Holotype: China, Yunnan Province, Xishuangbanna, dead twigs (attached to the tree) of Magnolia grandiflora (Magnoliaceae), 26 April 2017, N. I. de Silva, NI154 (MFLU 181021 holotype, HKAS100657 isotype), ex-type living culture, MFLUCC 18-0719 = KUMCC 170189.
Morphological description
Sexual morph: Hysterothecia 1200–2300 μm long, 430–550 µm high, 540–600 µm diameter (x̅ = 1750 × 490 × 570 µm, n = 15), apothecioid, with a longitudinal slit, sometimes elliptic or irregular in shape, with lenticular or irregular opening, dark brown to black, coriaceous, solitary to aggregated, semi-immersed to superficial, with striations perpendicular to the long axis, dark brown at the center. Exciple 80–100 μm, comprising of two cell layers; outer layer comprising black to dark brown, thick-walled cells of textura angularis, inner layer comprising hyaline, thin-walled, somewhat flattened cells of textura angularis to textura prismatica. Hamathecium comprising 2–3 µm wide, cylindrical to filiform, septate, hyaline pseudoparaphyses, slightly swollen at the apex and enclosed in a gelatinous matrix. Asci (148–)160–200 (–210) × (11–)13–15(–16) µm (x̅ = 176 × 14 µm, n = 30), 8-spored, bitunicate, fissitunicate, clavate to cylindrical, with a short pedicel. Ascospores (25–)28–30(–32) × (8–)10– 11(–12) µm (x̅ = 29 × 10 µm, n = 30), uniseriate, slightly overlapping, pale brown to dark brown, initially ellipsoidal, hyaline, aseptate, becoming fusiform, 1–3-septate, slightly rounded or pointed at both ends, constricted at the central septum, with large guttules and without a mucilaginous sheath. Asexual morph: Undetermined.
Culture characteristics – Colonies on PDA reaching 30 mm diameter after 7 days at 25°C in the dark, colonies circular, flat, margin wavy, fairly, fluffy appearance in margins, colony from above: light brown and; reverse: pale brown centre and dark brown margin.
Habitat: on dead twigs of Magnolia grandiflora.
Distribution: China.
GenBank Accession: LSU: MN989384;SSU:MN989382;tef1:MN997309;ITS:MN989383
Notes: The morphological features of Rhytidhysteron magnoliae are in accordance with the generic concept of Rhytidhysteron as they have large, conspicuously navicular hysterothecia, which open by a longitudinal slit and become irregularly apothecioid when wet. Ascospores are pigmented, sparsely septate (Boehm et al. 2009b, Thambugala et al. 2016, Soto & Lucking 2017). In the present multi-gene analyses (LSU, ITS, SSU and tef1), R. magnoliae (MFLU 18-1021) nested with other Rhytidhysteron species (Fig. 1), in particular, it was closely related to R. tectonae Doilom & K.D. Hyde and formed a well- supported clade (87% ML, 93% MP, 1.00 BYPP). However, R. magnoliae is distinct from R. tectonae in having elliptic or irregular ascomata with distinct striations. Further details are given in Table 2.
Rhytidhysteron magnoliae also differs from R. tectonae in having slightly larger asci (176 × 14 µm) and ascospores (25–32 × 8–12; x̅ = 29 × 10 µm), whereas R. tectonae has slightly smaller asci (155 × 13 µm) and ascospores (19–31 × 8−13; x̅ = 27 × 10 µm). In contrast to R. tectonae, R. magnoliae initially has ellipsoidal, hyaline ascospores becoming fusiform, pale brown to dark brown when mature with large guttules, whereas R. tectonae initially has subglobose, hyaline to pale brown ascospores becoming ellipsoidal to fusiform, pale brown to dark brown when mature and without guttules (Doilom et al. 2017). Rhytidhysteron magnoliae also differs from R. tectonae in terms of host association and locality, as the latter has been reported from the dead branches of Tectona grandis in Thailand (Doilom et al. 2017).
Reference: De Silva NI, Tennakoon DS, Thambugala KM et al. 2020 – Morphology and multigene phylogeny reveal a new species and a new record of Rhytidhysteron (Dothideomycetes, Ascomycota) from China. Asian Journal of Mycology 3(1), 295–306, Doi 10.5943/ajom/3/1/4 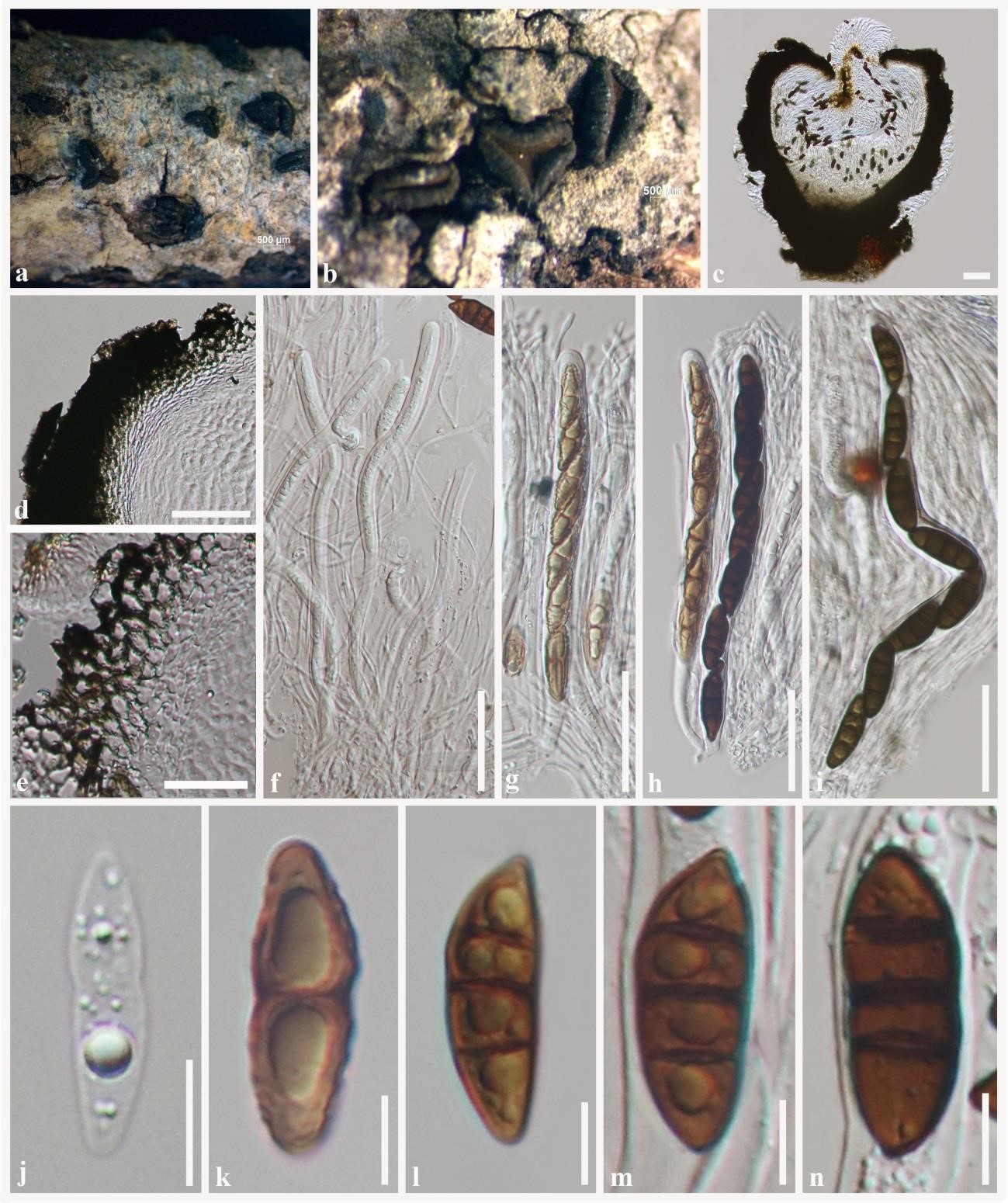
Rhytidhysteron magnoliae (MFLU 18-1021, holotype). a, b Appearance of hysterothecia on the host surface. c Vertical section through hysterothecium. d, e Exciple. f Pseudoparaphyses with immature asci. g–i Asci. j–n Ascospores. Scale bars: c = 80 μm, d = 50 μm, e = 20 μm, f–i = 50 μm, j–n = 10 μm.

