 214
214
MycoBank No 834962
Morphological description
Ascomata subglobose to irregularly subglobose, 3–14 × 2–12 mm in fresh, reddish brown when fresh, usually with some superficial furrows, surface covered with verrucose or fine warts, warts obtuse or pointed, 270–400 μm wide and 150–300 μm high. Odor light, mushroom flavor. Gleba solid, white to cream white, with numerous irregular canals and chambers of around 1 mm width. Peridium 150–350 μm thick, two-layered, outer layer pseudoparenchymatous, 90–190 μm thick, composed of 3–5 layers of reddish brown polygonal cells with 4-6 sides, cells 15–35 × 10–27 μm, walls 4.0–8.0 μm thick, the outermost cells reddish-brown, and gradually light-yellow to hyaline towards inner side; inner layer 60–150 μm thick, composed of interwoven hyphae, that is more or less parallel to the surface of peridium, hyphae hyaline, 2.5–6.0 μm wide. Paraphyses line the surface of chamber, arranged like a fence, 3–4 × 50 μm, but disorganized in the mature ascomata, usually not well-defined. Asci 8-spored, hyaline, citriform or fusiform, 55–80 × 27–38 μm (not including stalk), inamyloid, with a slender-stalk of 13.5–35 × 5–10 μm, spores irregularly arranged in ascus. Ascospores ellipsoid, smooth, hyaline, inamyloid, 20.6–25.6 × 12.9–15 μm (av. 23.5 × 14.0 μm), Q (L/I) = 1.55–1.80 (Qm = 1.68) (n = 30), usually containing one large oil drop and several small droplets.
Habitat: unidentified
Distribution: Shanxi, China
GenBank Accession: ITS MT232907; 28S MT232902
Notes: Balsamia lishanensis was diagnosed by the combination of reddish brown ascomata covered with fine warts, the whitish gleba with numerous small chambers open to 1 mm, 3–5 layers peridium reddish brown polygonal cells and the smooth and regular ellipsoid ascospores with one large oil drop. There are four Balsamia species similar to B. lishanensis in morphology. Of them, B. vulgaris differed by its large ascospores of (23–) 26–32 (–36) × 11.5–14 (–16) μm, Balsamia lazyana and B. trappei by their narrow ascospores, which are 19.5–27 × 8–11.5 μm in B. lazyana and 24–26 × 11.5–13.5 μm in B. trappei, B. platyspora by its short-ellipsoid ascospores of 19–22–28 × 12–13–16 μm (ca. 20 × 13 μm). Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the sequences of B. lishanensis were grouped into an independent clade with strong support value (Figs 1, 2). DNA analysis showed that B. lishanensis shared less than 87.19% identity in ITS sequence with other Balsamia species. These supported the erection of the new species.
Reference: Xu Y-Y, Yan X-Y, Li T et al. (2020) A taxonomic reassessment of the genus Balsamia from China.
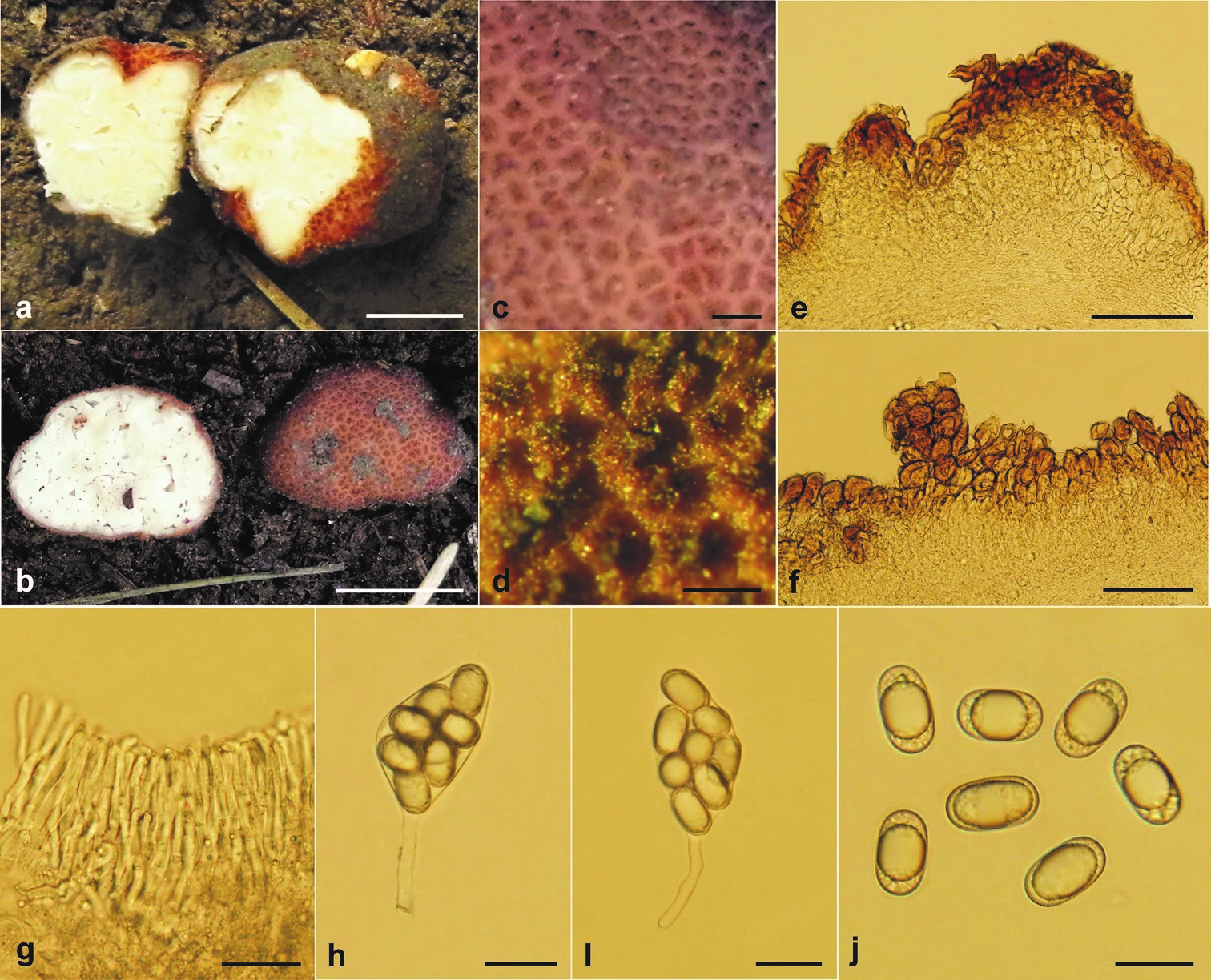
Balsamia lishanensis (BJTC FAN676, holotype) a, b ascomata c warts (when fresh) d warts (when dry) e, f peridium g paraphyses h, i mature ascus j ascospores. Scale bars: 5 mm (a, b); 500 μm (c); 300 μm (d); 100 μm (e, f); 25 μm (g, h, i); 20 μm (j).

