Hypsostroma thailandicum J.Y Zhang, Y.Z. Lu & K.D. Hyde, sp. nov.2021
Index Fungorum number: IF558529, Faces of fungi number: FoF 09900
Holotype: MFLU 21−0086
Morphological description:
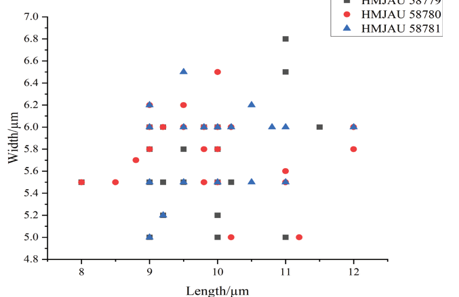
Sexual morph: Ascomata 340–460 μm high × 360–460 μm diam, superficial, clustered, numerous, subglobose to globose, black. Setae / hyphal filaments 150–650 μm long, 4.5–7.5 μm wide, abundant, cylindrical, brown to dark brown, 3–10 septate, straight or bent, apex rounded. Peridium 55–80 μm thick, composed of several layered cells of textura prismatica, with inner cells pale brown and outer cells dark brown. Pseudoparaphyses 1–2.5 μm wide, numerous, hyaline, septate, branched, filiform. Asci 180–440 × 8.5–14 μm (x = 247 × 11 μm, n = 20), polysporous, unitunicate, elongate clavate, very long-stalked, thin walled, apically rounded. Ascospores 7–14.5 × 2.5–6 μm (x = 9.5 × 4 μm, n = 50), 2-seriate, olivaceous when young, brown to dark brown when mature, oblong, long triangular to cuneiform, with acute end cells, aseptate, straight to slightly curved, end cells slightly longer than central cells, guttulate..
Asexual morph: Undetermined
Culture characteristics: Ascospores germinated on PDA within 12 hours from single-spore isolation. Colonies diameter reaching 35–40 mm after 4 weeks at 26°C on PDA media. Mycelia superficial, irregular, filiform, umbonate, dark brown from above and below.
Habitat:Undetermined
Distribution: China
GenBank Accession Numbers:LSU MZ435867 ITS MZ435865.;
Notes:Hypsostroma thailandicum shares the same morphology with other species of Hypsostroma in having clustered, superficial ascomata, abundant pseudoparaphyses, numerous elongate clavate, very long-stalked asci and oblong ascospores (Huhndorf 1992). Hypsostroma caimitalensis is the closest species based on a BLAST search of the LSU region with 94.7% similarity. A multi-loci phylogenetic analyses showed that H. thailandicum is a distinct species and sister to the type species, H. caimitalensis with 89% MP, 1.00 PP support. Our collection differs from H. caimitalensis in the absence of an ostiolar neck, abundant, long setae, smaller ascomata (340–460 μm high × 360–460 μm diameter vs 650–900 μm diameter, 1500–1800 μm high) and smaller ascospores (7–14.5 × 2.5–6 μm vs 40–4 7 × 5.5–6.5μm) (Huhndorf 1992). Therefore, we introduce H. thailandicum as a new species. Only two species are accepted in Hypsostroma; H. caimitalensis and H. saxicola, and both only have LSU sequence data. Therefore, sequence data and new collections are needed for this genus.
Reference:[1] Karim, M. , Kavosi, M. R. , Mosazadeh, S. A. , & Hajizadeh, G. . (2013). New fungal records for the iran mycota from hyrcanian forests. Middle East Journal of Scientific Research, 14(5), 729-733.
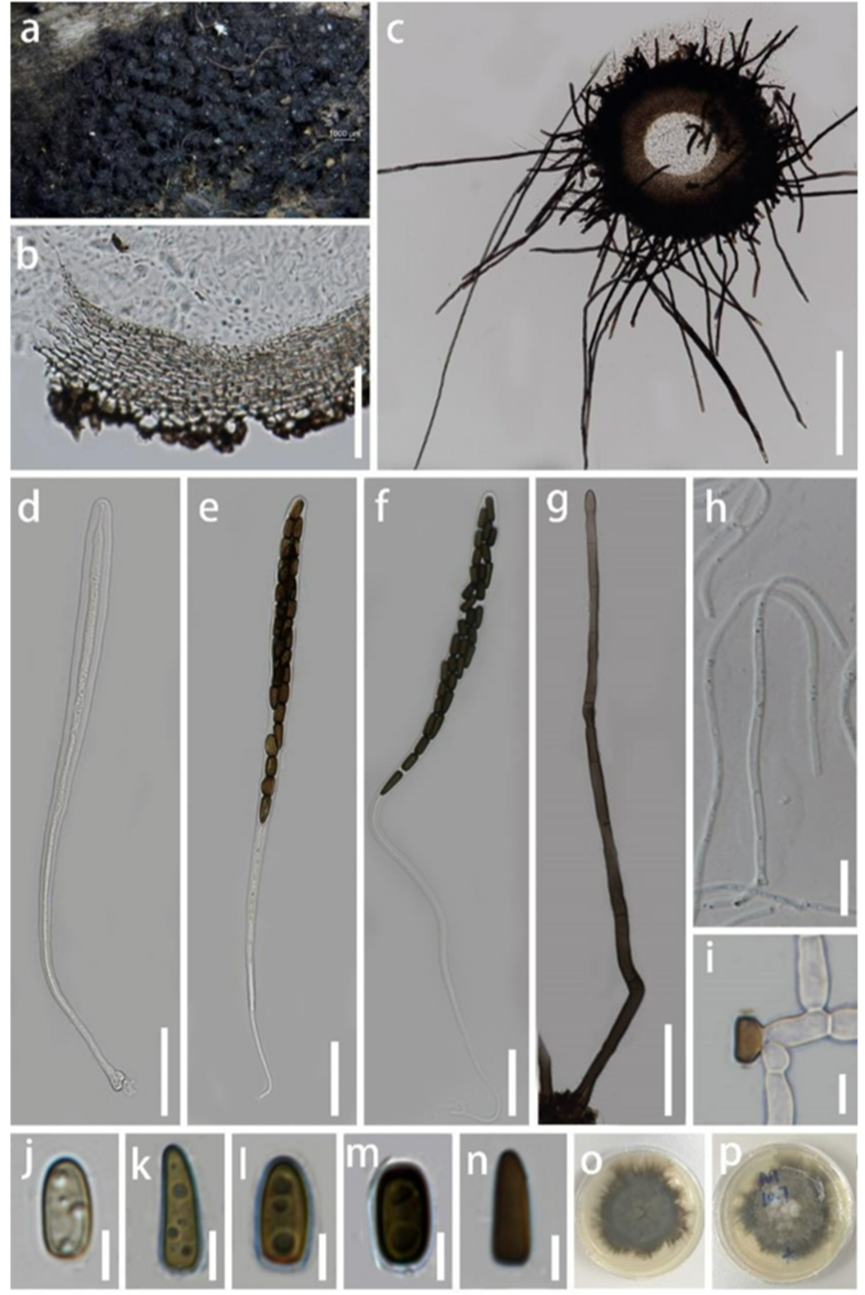

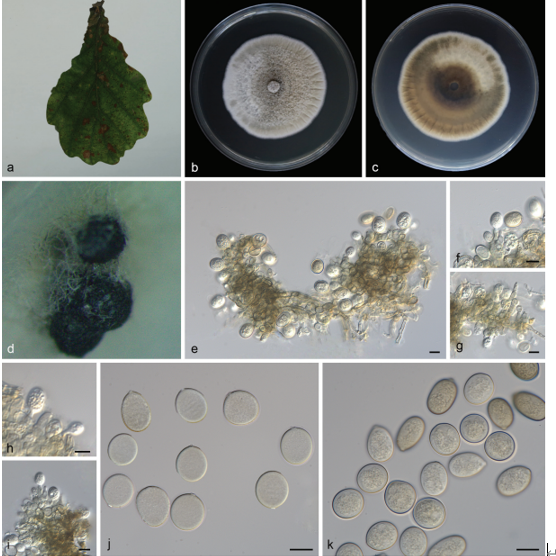
a Superficial ascomata on substrate, note ascomata surrounded by black setae. b Peridium. c Section of ascoma. d–f Asci. g Seta. h Pseudoparaphyses. i Germinating ascospores. j–n Ascospores. o, p Colonies on PDA. Scale bars: b, g = 50 μm, c = 200 μm, d–f = 20 μm, h, i = 10 μm, j–n = 5 μm.