Megasporia bambusae Y.C. Dai & Yuan Yuan, sp. nov. 2021
MycoBank Index Fungorum number: IF558811; Facesoffungi number: FoF10470
Holotype: Dai22106.
Morphological description
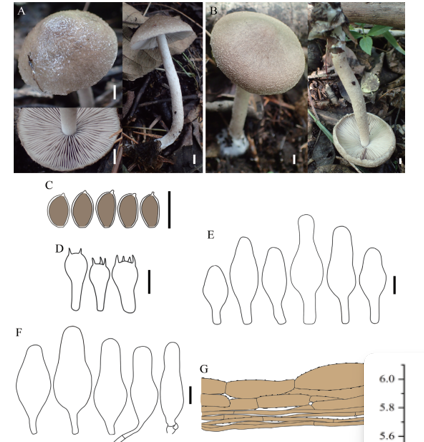
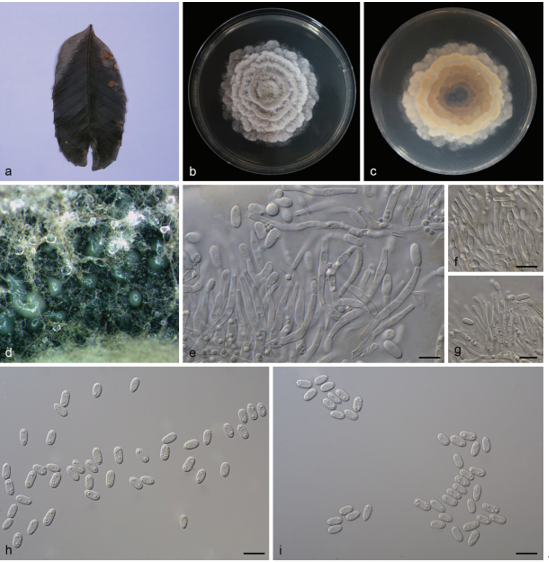
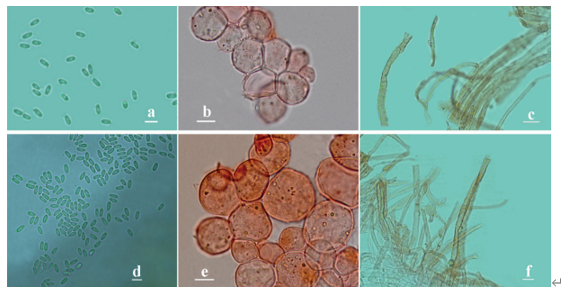
Sexual morph:Basidiocarps annual, resupinate, corky, without odor or taste when fresh, becoming hard corky upon drying, up to 2.7 cm long, 2.2 cm wide, and 0.2 mm thick at center; sterile margin distinct, white, up to 1 mm wide. Pore surface white to cream when fresh, cream to buff when dry; pores angular, 4–5 per mm; dissepiments thick, entire; subiculum pale buff, corky, up to 0.05 mm thick; tubes cream, paler than subiculum, corky, up to 0.15 mm long. Hyphal system dimitic; generative hyphae bearing clamp connections; skeletal hyphae weakly dextrinoid, CB+; tissues unchanged in KOH (not dissolved). Subicular generative hyphae hyaline, thin-walled, occasionally branched, 1.5–1.8 µm in diam; skeletal hyphae dominant, thick-walled with a narrow to wide 1021 lumen, frequently branched, mostly flexuous, interwoven, 2.5–3 µm in diam. Tramal generative hyphae hyaline, thin-walled, occasionally branched, 1.5–1.8 µm in diam; skeletal hyphae dominant, thick-walled with a narrow to medium lumen, frequently branched, mostly flexuous, interwoven, 1.5–2 µm in diam. Dendrohyphidia present. Hyphal pegs absent. Cystidia absent; cystidioles present, subulate or ventricose, thin-walled, smooth, 14–41 × 4.8–14.8 µm. Basidia clavate to pearshaped, usually constricted in middle, with four sterigmata and a basal clamp connection, 20–35.2 × 10–14.8 µm; basidioles in shape similar to basidia, but distinctly smaller. Small tetrahedric or polyhedric crystals frequently present among hymenium. Basidiospores ellipsoid, hyaline, fairly thick-walled, smooth, IKI–, CB–, (10.5–)11.8–14(–14.8) × (5.5–)5.8–6.8(–7.5) µm, L = 12.67 µm, W = 6.53 µm, Q = 1.91–1.96 (n = 90/3).
Asexual morphs:
Cultures:
Habitat: on dead bamboo.
Distribution: China, Hainan Prov., Haikou, Jinniuling Park.
GenBank Accession: ITS: MW694884;SSU: MW694912;tef: MZ618631.
Notes: Megasporia bambusae is found from the tropical zone of China. It is readily distinguished from other species in Megasporoporia sensu lato by its fairly thick-walled basidiospores and growing on bamboo, all other members of Megasporoporia sensu lato have thinwalled basidiospores and growing on dicotyledon. Megasporia bambusae resembles Megasporia cystidiolophora, Megasporia guangdongensis and Megasporoporiella rhododendri by the overlapped distribution and almost the same size of pore (3–5 per mm), but the latter three species have thin-walled basidiospores and lacks dendrohyphidia. Phylogenetically, Megasporia bambusae is related to Megasporia ellipsoidea, M. yunnanensis, M. major, M. hexagonoides, M. fusiformis and M. rimosa (Figs 1–2), but the latter six species have thin-walled basidiospores and growing on another angiosperm rather than bamboo (Ryvarden et al. 1982, Yuan et al. 2017).
Reference: Wang YR, Wu YD, Vlasák J, Yuan Y, Dai YC 2021 – Phylogenetic analysis demonstrating four new species in Megasporoporia sensu lato (Polyporales, Basidiomycota). Mycosphere 12(1), 1012–1037, Doi 10.5943/mycosphere/12/1/11
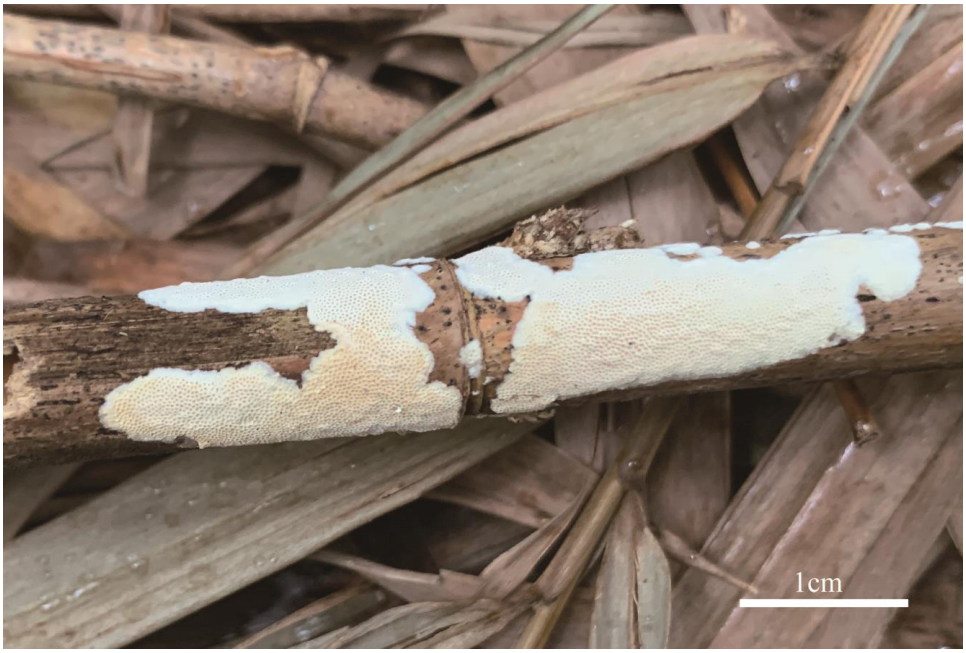

Basidiocarps of Megasporia bambusae (the holotype, Dai 22106).