Neofavolus squamatus J.H. Xing, J.L. Zhou & B.K. Cui 2020
MycoBank MB 834717
Holotype: CHINA, Xizang, Linzhi County, Lulang, Sejila Mountain, on fallen angiosperm branch, 18 September 2014, Cui 12175 (holotype, BJFC).
Morphological description
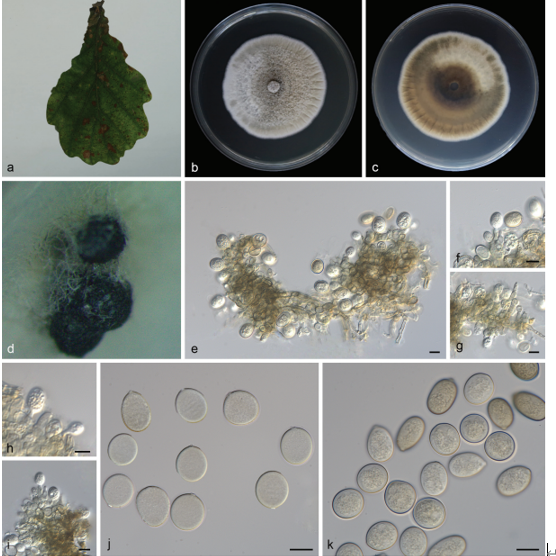
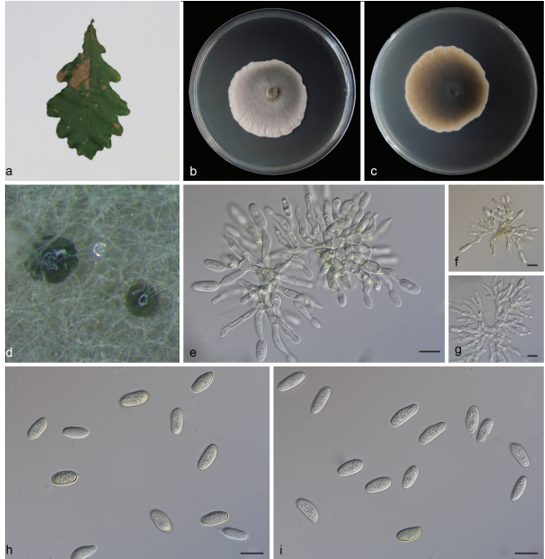
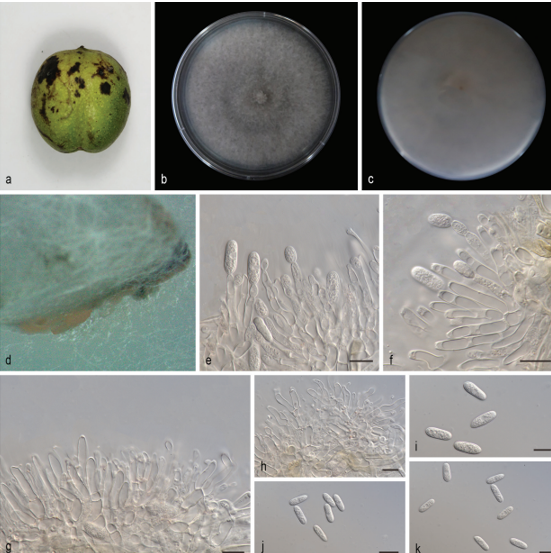
Fruiting body: Basidiomata annual, solitary, laterally stipitate, and soft-leathery when fresh and corky when dry. Pilei suborbicular, depressed toward the stipe, 1.1–2.7 cm long from base to margin, 3–3.8 cm wide, and up to 3 mm thick. Pileal surface white when fresh and buff to festucine when dry, covered by yellowish orange squamae when fresh, discoloring to apricot orange when dry, and more or less radially wrinkling on drying; margin incurved upon drying. Pore surface white to cream when fresh and buff when dry; pores angular, 0.7–3 mm long and 0.5–1.5 mm wide; dissepiments thin, entire. Context white, corky upon drying, up to 2.5 mm thick. Tubes white when fresh and light ivory to cream when dry, up to 1 mm thick, and decurrent on one side of the stipe. Stipe short, glabrous, white when fresh and buff yellow after drying, up to 6 mm long, and 5.5 mm in diameter.
Hyphal structure: Hyphal system dimitic; generative hyphae bearing clamp connections, hyaline, and thin-walled; skeleto-binding hyphae hyaline, thick-walled with a wide to narrow lumen, occasionally branched and with tapering ends, IKI–, and CB+; tissue unchanged in KOH.
Context: Generative hyphae frequent, hyaline, thin-walled, frequently branched, 2.8–9 μm in diameter, and occasionally inflated up to 27.7 μm in diameter at branched area; skeletobinding hyphae dominant, hyaline, thick-walled with a wide lumen, occasionally branched, interwoven, 2.6–9.5 μm in diameter, and occasionally inflated up to 13.5 μm in diameter. Hyphae in squamae with buff inclusion inside, thin-walled hyphae bearing clamp connections, thick-walled hyphae simpleseptate with a wide lumen, and 3.5–8.4 μm in diameter.
Tubes: Generative hyphae frequent, hyaline, thin-walled, frequently branched, and 2.2–4.2 μm in diam; skeleto-binding hyphae dominant, hyaline, thick-walled with a wide lumen, occasionally branched, interwoven, and 1.9– 6.4 μm in diameter. Cystidia and cystidioles absent. Basidia clavate, with a basal clamp and four sterigmata, 27.7–51.7 × 6.5–9.8 μm; basidioles in shape similar to basidia, but smaller.
Stipe: Generative hyphae infrequent, hyaline, thin-walled, frequently branched, 2.2–6.3 μm in diameter, and occasionally inflated up to 16 μm in diameter at clamping area; skeletobinding hyphae dominant, hyaline, thick-walled with a wide tonarrow lumen, occasionallybranched, interwoven, and 2.6– 8.6 μm in diameter.
Spores: Basidiospores cylindrical to navicular, hyaline, thin-walled, smooth, occasionally bearing one or two guttules, IKI–, CB–, (7.8–)8.9–12(−14.5) × 3.1–4.1(−4.3) μm, L = 10.34 ± 1.09 μm, W = 3.63 ± 0.29 μm, Q = 2.17–3.72, and Qm = 2.86 ± 0.31 (n = 70/1).
Rot type: A white rot.
Habitat: On fallen angiosperm branch.
Distribution: In China.
GenBank Accession: TS: KX900070 a; nLSU: KX900184 a; EF1-α: KX900370 a; mtSSU : KX900250 a;β-tubulin: KX899942 a; RPB2: KX900317 a; nSSU: KX900295 a
Notes:
Reference: Jia-Hui Xing1 & Jun-Liang Zhou1,2 & Bao-Kai Cui1
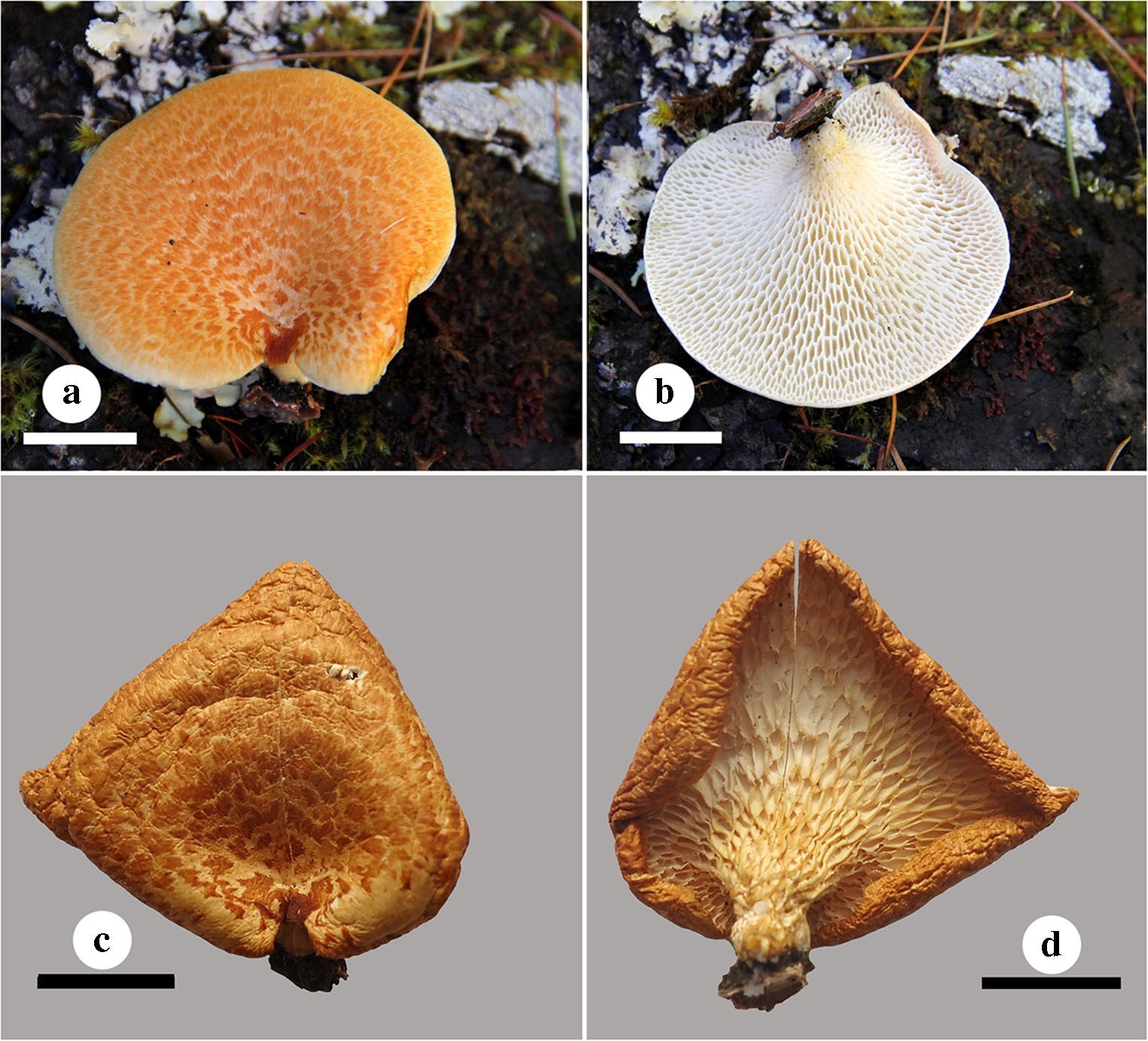

Basidiomata of Neofavolus squamatus (Cui 12175). Scale bar = 1 cm