Stagonospora poaceicola Tennakoon, Phookamsak R & K.D. Hyde 2020
Index Fungorum number: IF557371; Facesoffungi number: FoF07748
Holotype: CHINA, Yunnan Province, Xishuangbanna, Nabanhe, on dead stems of grass sp. (Poaceae), 25 November 2015, D.S. Tennakoon, KIB 029 (MFLU 17-0769, holotype; KUN-HKAS 96342, isotype).
Morphological description
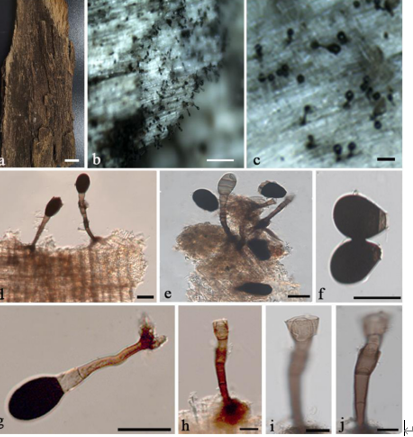
Sexual morph: Ascomata 170–220 × 160–190 μm diam. (x̅ = 197 × 177 μm, n = 8), solitary or aggregated, semi-immersed to erumpent, elongate, uniloculate, subglobose or obpyriform, coriaceous, black, ostiolate. Peridium 20–25 μm wide composed of 3–4 layers of thin-walled, lightly pigmented to dark brown, somewhat flattened cells of textura angularis. Hamathecium composed of dense, 1.8–2.5 µm wide, filamentous, distinctly septate, broad, cellular pseudoparaphyses, slightly constricted at the septum, anastomosing at the apex, embedded in a hyaline gelatinous matrix. Asci (65–)70–110(–115) × (12–)14–21(–23) µm (x̅ = 89 × 17 µm, n = 35), 8-spored, bitunicate, fissitunicate, clavate, short pedicellate (7–17.5 μm long), apically rounded with a shallow ocular chamber. Ascospores 21–28(–30) × 4.5–6.5 µm (x̅ = 24.4 × 5.5 µm, n = 35), overlapping, uniseriate to biseriate or triseriate, hyaline, narrowly fusiform, 2–3-septate, slightly constricted at the middle septum, straight to curved, with or without guttules, smooth-walled, without a sheath. Asexual morph: Undetermined.
Habitat: On dead stems of grasses.
Distribution: In China.
GenBank Accession: ITS: MT199603; LSU: MT199604; SSU: MT199602; TEF1: MT199325.
Notes: Stagonospora poaceicola shares similar morphological characteristics to S. perfecta Quaedvl., Verkley & Crous and S. pseudoperfecta Kaz. Tanaka & K. Hiray. in having short pedicellate asci and hyaline, fusiform, straight to curved ascospores. However, S. perfecta and S. pseudoperfecta differs from S. poaceicola by having ascospores with clear sub-median septum surrounded by a mucilaginous sheath (Tanaka et al. 2015). Furthermore, S. poaceicola has semiimmersed to erumpent ascomata, whereas S. perfecta and S. pseudoperfecta have immersed ascomata. According to the combined multi-gene phylogeny (LSU, SSU, ITS and TEF1), S. poaceicola grouped with other Stagonospora species and shows a closer affinity to S. bicolor (Fig. 12). However, S. bicolor (D. Hawksw., W.J. Kaiser & Ndimande) Kaz. Tanaka & K. Hiray. can be distinguished from S. poaceicola by having melanized ascospores. These ascospores appeared to be released in a hyaline or very pale brown stage with 1–3 septa, but later the upper central cell in the 3-septate spores slightly inflated and can become dark brown to almost black at maturity (Eriksson & Hawksworth 2003).
Reference: Brahmanage RS1,2,3, Dayarathne MC6, Wanasinghe DN4,5 et al.
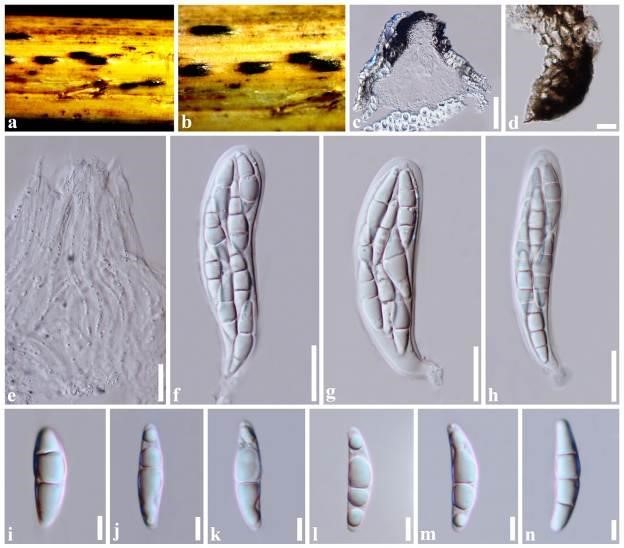
Stagonospora poaceicola (MFLU 17-0769, holotype). a Appearance of ascomata on host. b Close-up of ascomata. c Section of an ascoma. d Section of peridium. e Pseudoparaphyses. f–h Asci. i–n Ascospores. Scale bars: c = 50 µm, d = 10 µm, e–h = 20 µm, i–n = 5 µm.