Tomentella globospora H.S. Yuan & Y.C. Dai 2020
Index Fungorum number: IF555699; Facesoffungi number: FoF 05624
Holotype: CHINA, Liaoning Province, Huanren County, Laotudingzi Nature Reserve, on rotten angiosperm wood debris, 21 October 2015, Yuan 10668 (IFP 019287, holotype), 22 October 2015, Yuan 10748 (IFP 019288).
Morphological description
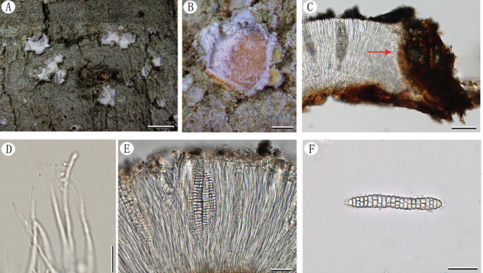
Basidiocarps annual, resupinate, adherent to the substrate, crustose, without odour or taste when fresh, 0.4–0.6 mm thick, continuous. Hymenophoral surface smooth, brown to darkbrown (6E5–6F7) and concolorous with subiculum when dry. Sterile margin often indeterminate, farinaceous, concolorous with hymenophore. Rhizomorphs absent. Subicular hyphae monomitic; generative hyphae clamped, thick-walled, occasionally branched, 5–6 μm diam, encrustated, greyish yellow in KOH, cyanophilous, inamyloid. Subhymenial hyphae clamped, slightly thick- to thick-walled, frequently branched, 4–6 μm diam; hyphal cells more or less uniform, greyish yellow in KOH, cyanophilous, inamyloid. Cystidia absent. Basidia 20–50 μm long and 4–9 μm diam at apex, 6–8 μm at base, with a clamp connection at the base, clavate, stalked, sinuous, rarely with transverse septa, greyish yellow in KOH, yellowish brown in distilled water, 4-sterigmate; sterigmata 3–5 μm long and 0.5–1.5 μm diam at base. Basidiospores thin- to slightly thick-walled, (8.5– )9.1–10.2(–10.5) × (8.5–)8.7–9.7(–10) μm, L = 9.66 μm, W = 9.33 μm, Q = 1.03–1.08 (n = 60/2), globose to subglobose in frontal and lateral views, aculeate, golden yellow in KOH, brownish yellow in distilled water, cyanophilous, inamyloid; echinuli usually isolated, sometimes grouped in 2, up to 2 μm long.
Habitat: On rotten angiosperm wood debris.
Distribution: In China.
GenBank Accession: ITS: KY686242, KY686243; LSU: MK446374, MK446375.
Notes: Tomentella terrestris (Berk. & Broome) M.J. Larsen is similar to T. globospora by having crustose basidiocarps adherent to the substrate, a smooth hymenophore, indeterminate sterile margins, the absence of rhizomorphs and cystidia, and clamped hyphae. However, the former species is differentiated by thin-walled subhymenial hyphae and smaller, triangular to ellipsoid basidiospores (7.5–9.5 μm, Kõljalg 1996). T. alpina resembles T. globospora by having continuous basidiocarps adherent to the substrates, the absence of rhizomorphs and cystidia, clamped and thickwalled subicular hyphae, and globose to subglobose basidiospores. However, it differs from T. globospora by having thick basidiocarps (up to 1 mm thick) and smaller basidiospores (6.5–8.5 μm, Peintner and Dämmrich 2012).
Reference: Hai‑Sheng Yuan1,2· Xu Lu1,2 · Yu‑Cheng Dai3 ·
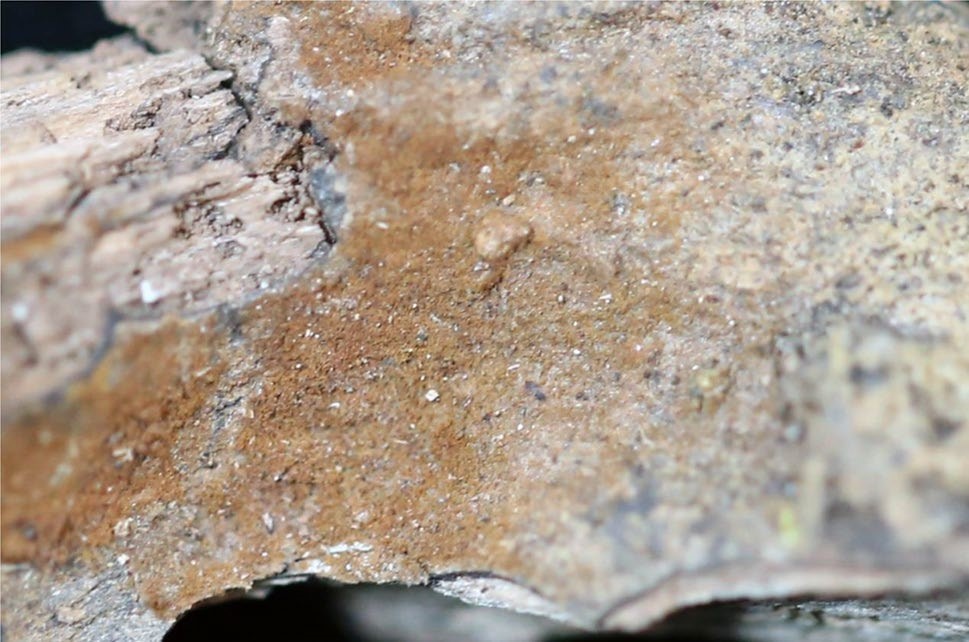

A basidiocarp of Tomentella globospora (IFP 019287, holotype)