Coniochaeta vineae S.K. Huang, T.C. Wen & K.D. Hyde 2020
Index Fungorum: IF556804; Facesoffungi number: FoF 06526
Holotype: CHINA, Xinjiang, Zhaosu, a lake near by the snow mountains, on dead vine, 14 September 2017, J.W. Liu, XJ03 (KUN-HKAS 99606, holotype), extype living culture KUMCC 17-0322.
Morphological description
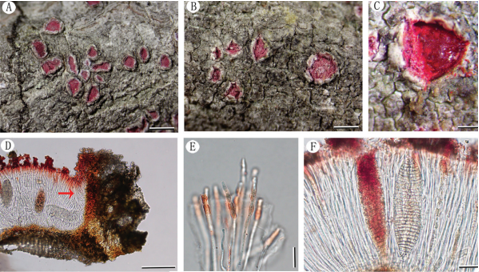
Sexual morph Ascomata 170–185 × 145–185 μm ( x̄ = 180 × 170 μm, n = 5), perithecial, gregarious and scattered, semi-immersed to superficial, unilocular, obpyriform to subglobose, dark brown to black, roughened surface, the ostiole periphysate, covered by dark brown, inconspicuous, straight setae with rounded apex. Peridium 15–35 μm diam. near to ostiole, 10–20 μm diam. at base, membranaceous, outer layer composed of brown cells of textura angularis; inner layer composed of hyaline cells of textura prismatica. Paraphyes 1–3.5 μm wide, numerous, filiform, septate, branched. Asci 85–115 × 5–10 μm ( x̄ = 98 × 7.5 μm, n = 20), 8-spored, unitunicate, cylindrical, with short pedicel, rounded at the apex, with a distinct, J-, apical ring. Ascospores 6.5–9.5 × 4–6 μm ( x̄ = 8 × 5 μm, n = 50), 1-seriate, hyaline becoming dark brown, ovoid to broadly ellipsoid, aseptate, multi-guttulate, with a conspicuous, straight germ slit across the entire length, smooth, without sheath or appendages. Asexual morph Undetermined.Culture characteristics: Ascospores germinating on PDA within one week at 23 °C. Colony on PDA reaching 2 cm diam., after 30 days at 23 °C. Mycelium superficial to semiimmersed, filamentous, branched, septate, hyaline. Colonies on PDA, initially white, becoming grayish-olivaceous, rough surface and raised elevation, with concentric zonations, smooth margins; reverse white to pale brown at the extremities.
Habitat: dead vine.
Distribution:China.
GenBank Accession: I TS:M N 4 7 3 4 6 9;LSU:MN473512;SSU:MN473471;TUB2:MN485898;RPB2:MN480811.
Notes: Based on LSU-ITS phylogenetic analyses, Coniochaeta vineae clusters with C. ligniaria (Grev.) Cooke and C. mutabilis (J.F.H. Beyma) Z.U. Khan, Gené & Guarro, with a significant support in the ML analysis (72% ML; Fig. 137). Coniochaeta vineae is compared across the ITS regions reveals 2% differences between C. ligniaria and 4% differences between C. mutabilis, and the LSU region reveals 2% differences between C. ligniaria and 7% differences between C. mutabilis. Coniochaeta mutabilis was reported as a human and plant pathogen which is only known in asexual morph (Mitteilung 1939; Drees et al. 2007; Ňancucheo and Johnson2012). Coniochaeta vineae is characterised by inconspicuous ostioles, surrounded by setae and ovoid to broadly ellipsoid ascospores, while C. ligniaria has irregular black setae covering the ascomata and ellipsoid ascospores (Checa et al. 1988).
Reference: Kevin D. Hyde1,5,8,22 · Yang Dong2,3 · Rungtiwa Phookamsak1,5,6,7 et al.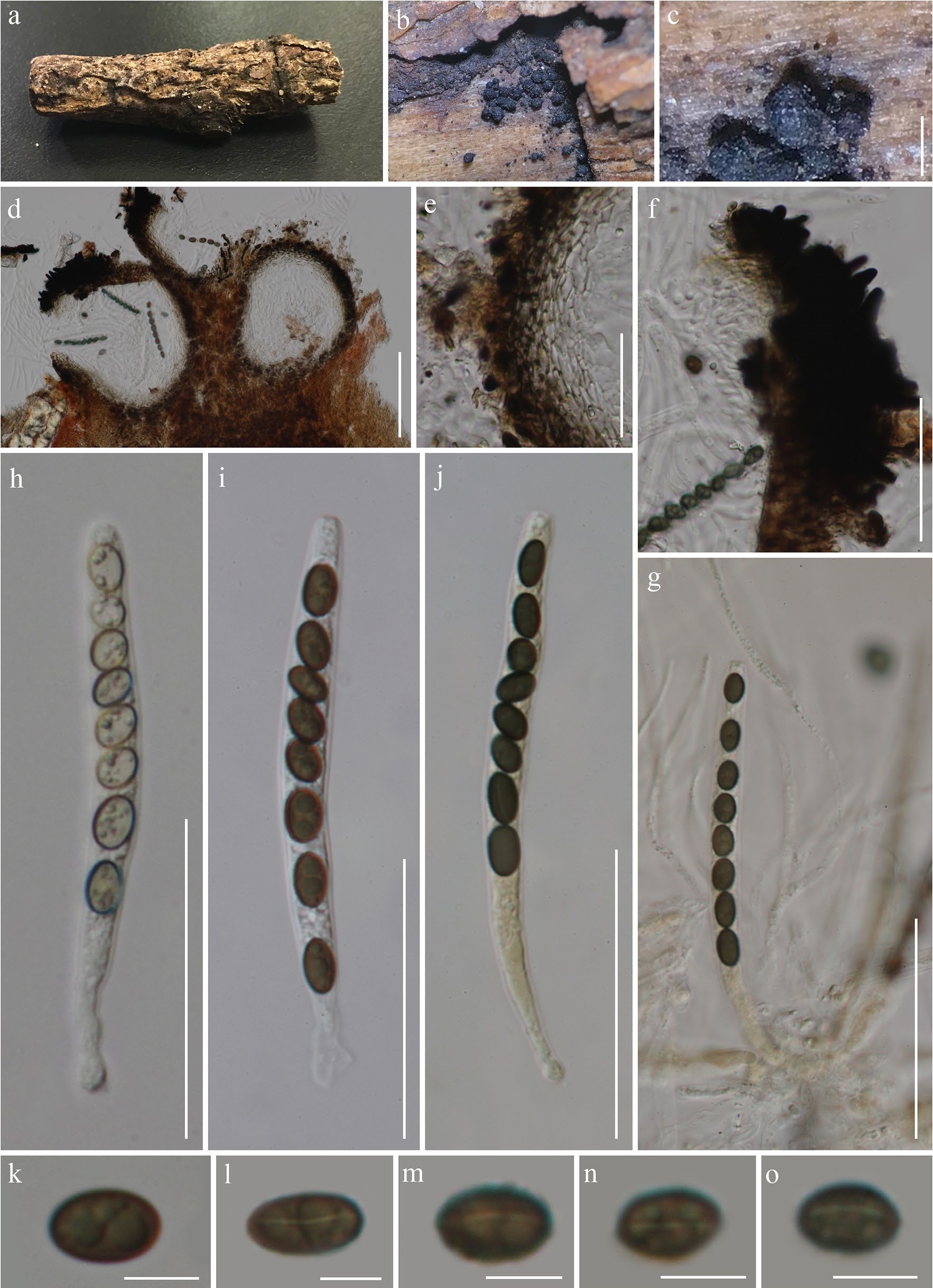
Coniochaeta vineae (KUN-HKAS 99606, holotype). a with paraphyses (in Melzer’s reagent). h–j Asci (j stained in MelzMaterial. b Appearance of ascomata on the host. c Obpyriform er’s reagent). k–o Ascospores (l–o show germ slits). Scale bars: ascoma. d Ascomata cross section. e Peridium. f Periphyses. g Asci c = 200 μm, d = 100 μm, e–j = 50 μm, k–o = 5 μm